2-氯庚烷 | 1001-89-4
中文名称
2-氯庚烷
中文别名
——
英文名称
2-chloroheptane
英文别名
2-Chlor-heptan
CAS
1001-89-4
化学式
C7H15Cl
mdl
——
分子量
134.649
InChiKey
PTSLUOSUHFGQHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-69.5°C (estimate)
-
沸点:146 °C
-
密度:0,87 g/cm3
-
闪点:39.2±16.5℃
-
LogP:3.970 (est)
-
保留指数:897;894.2;894
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.6
-
重原子数:8
-
可旋转键数:4
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
安全信息
-
危险等级:3
-
安全说明:S16,S26,S36/37/39
-
危险类别码:R10,R36/37/38
-
海关编码:2903199000
-
WGK Germany:3
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1993
-
储存条件:应存放在室温、密封且干燥的环境中。
SDS
2-氯庚烷
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: 2-Chloroheptane
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害
易燃液体 第3级
健康危害
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 第2级
严重损伤/刺激眼睛 2A类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志
信号词 警告
危险描述 易燃液体和蒸气
造成皮肤刺激
造成严重眼刺激
防范说明
[预防] 远离热源/火花/明火/热表面。禁烟。
保持容器密闭。
使用防爆的电气/通风/照明设备。采取预防措施以防静电和火花引起的着火。
处理后要彻底清洗双手。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[急救措施] 眼睛接触:用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续冲洗。
眼睛接触:求医/就诊
皮肤接触:立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
脱掉被污染的衣物,清洗后方可重新使用。
[储存] 存放于通风良好处。保持凉爽。
[废弃处置] 根据当地政府规定把物品/容器交与工业废弃处理机构。
2-氯庚烷
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 2-氯庚烷
百分比: >97.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 1001-89-4
俗名: 2-Heptyl Chloride
分子式: C7H15Cl
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,二氧化碳
不适用的灭火剂: 水(有可能扩大灾情。)
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:喷水,保持容器冷却。如果安全,消除一切火源。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。确保足够通风。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 回收到密闭容器前用干砂或惰性吸收剂吸收泄漏物。一旦大量泄漏,筑堤控制。附着
物或收集物应该根据相关法律法规废弃处置。
副危险性的防护措施 移除所有火源。一旦发生火灾应该准备灭火器。使用防火花工具和防爆设备。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止烟雾产生。远离热源/火花/明火
/热表面。禁烟。采取措施防止静电积累。使用防爆设备。处理后彻底清洗双手和脸。
注意事项: 如果可能,使用封闭系统。如果蒸气或浮质产生,使用通风、局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗、通风良好处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统。同时安装淋浴器和洗眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防毒面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
2-氯庚烷
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
液体
外形(20°C):
外观: 透明
颜色: 无色-几乎无色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 无资料
沸点/沸程 146 °C
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 0.87
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
避免接触的条件: 火花, 明火, 静电
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 氯化氢
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
2-氯庚烷
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守
国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 第3类 易燃液体 。
UN编号: 1993
正式运输名称: 易燃液体, 不另作详细说明
包装等级: III
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: 2-Chloroheptane
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害
易燃液体 第3级
健康危害
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 第2级
严重损伤/刺激眼睛 2A类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志
信号词 警告
危险描述 易燃液体和蒸气
造成皮肤刺激
造成严重眼刺激
防范说明
[预防] 远离热源/火花/明火/热表面。禁烟。
保持容器密闭。
使用防爆的电气/通风/照明设备。采取预防措施以防静电和火花引起的着火。
处理后要彻底清洗双手。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[急救措施] 眼睛接触:用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续冲洗。
眼睛接触:求医/就诊
皮肤接触:立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
脱掉被污染的衣物,清洗后方可重新使用。
[储存] 存放于通风良好处。保持凉爽。
[废弃处置] 根据当地政府规定把物品/容器交与工业废弃处理机构。
2-氯庚烷
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 2-氯庚烷
百分比: >97.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 1001-89-4
俗名: 2-Heptyl Chloride
分子式: C7H15Cl
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,二氧化碳
不适用的灭火剂: 水(有可能扩大灾情。)
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:喷水,保持容器冷却。如果安全,消除一切火源。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。确保足够通风。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 回收到密闭容器前用干砂或惰性吸收剂吸收泄漏物。一旦大量泄漏,筑堤控制。附着
物或收集物应该根据相关法律法规废弃处置。
副危险性的防护措施 移除所有火源。一旦发生火灾应该准备灭火器。使用防火花工具和防爆设备。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止烟雾产生。远离热源/火花/明火
/热表面。禁烟。采取措施防止静电积累。使用防爆设备。处理后彻底清洗双手和脸。
注意事项: 如果可能,使用封闭系统。如果蒸气或浮质产生,使用通风、局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗、通风良好处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统。同时安装淋浴器和洗眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防毒面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
2-氯庚烷
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
液体
外形(20°C):
外观: 透明
颜色: 无色-几乎无色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 无资料
沸点/沸程 146 °C
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 0.87
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
避免接触的条件: 火花, 明火, 静电
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 氯化氢
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
2-氯庚烷
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守
国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 第3类 易燃液体 。
UN编号: 1993
正式运输名称: 易燃液体, 不另作详细说明
包装等级: III
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Reactions of Atoms and Free Radicals in Solution. XXIV. The Reactions of Acetyl Peroxide with Chloro- and Dichloroalkanes1摘要:DOI:10.1021/ja01146a041
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:三氯化铁催化羰基化合物的脱氧氯化:氯二甲基硅烷和二氯甲基硅烷体系的比较摘要:已经系统地研究了使用 HMe2SiCl/FeCl3/EtOAc 和 HMeSiCl2/FeCl3/EtOAc 系统对羰基化合物进行脱氧氯化。HMe2SiCl-FeCl3体系具有底物适用性好、反应条件温和、操作简单、成本低、原料易得等优点。为羰基脱氧氯化的一锅法提供了一条简单有效的合成路线。使用HMeSiCl2/FeCl3/EtOAc体系,除了获得氯化化合物外,还可以以良好的收率获得β-甲基查尔酮衍生物。最后,提出了两种可能的反应路线来描述氯化化合物和 β-甲基查尔酮衍生物的形成。DOI:10.1177/1747519820910959
文献信息
-
Cobalt(II)-porphyrin catalyzed selective functionalization of alkanes with sulfurylchloride: A remarkable substituent effect作者:Vibha Khanna、Pitchiah Tamilselvan、Swinder Jeet Singh Kalra、Javed IqbalDOI:10.1016/s0040-4039(00)78223-2日期:1994.8Cobalt(II)-porphyrin complex 1 and 2 catalyses the chlorination and sulfochlorination respectively of n-alkanes and cycloalkanes with sulfuryl chloride in benzene. The p-substituent of the benzene ring in the porphyrin complex 1 and 2 shows a remarkable chemoselectivity in these reactions.
-
Iron-Catalyzed Negishi Coupling Toward an Effective Olefin Synthesis作者:Takuji Hatakeyama、Naohisa Nakagawa、Masaharu NakamuraDOI:10.1021/ol901555r日期:2009.10.15cross-coupling of alkyl halides with alkenylzinc reagents is described. Primary and secondary alkyl chlorides, bromides, and iodides take part in the reaction to give the corresponding olefins in good to excellent yields in a stereospecific manner. High functional group compatibility is also demonstrated by using combinations of substrates possessing rather reactive substituents.
-
Method for producing organic compounds by substituting halogen atoms申请人:MITSUI CHEMICALS, INC.公开号:EP1486479A1公开(公告)日:2004-12-15The invention pertains to a method in which a halogen atom of an organic compound is replaced with a group derived from a nucleophilic agent, at high yield and high efficiency, by the following method which includes a step of reacting the nucleophilic agent with an organic material having a halogen atom bonded to a carbon atom having four σ bonds, more specifically: a method for producing an organic compound having Q, the method including a step of reacting a compound represented by general formula (2) with an organic starting material having at least one halogen atom bonded to a carbon atom having four σ bonds so as to replace the halogen atom in the organic starting material with Q: MQa (2) (wherein M represents an alkali metal atom, an alkali earth metal atom, or a rare earth metal atom; Q represents a moiety of an inorganic acid or an active hydrogen compound derived by eliminating a proton, wherein Q is a halogen atom different from the halogen atom in the organic starting material having the halogen atom bonded to the carbon atom having the four σ bonds; and a represents an integer of 1 to 3) in the presence of a compound represented by general formula (1) (wherein Z- represents an anion derived by eliminating a proton from an inorganic acid or an active hydrogen compound; R2 is the same or different; R2 each independently represent a C1-C10 hydrocarbon group or two R2 on the same nitrogen atom may be bonded with each other to form a ring with the nitrogen atom).这项发明涉及一种方法,其中有机化合物中的卤素原子被来自亲核试剂的基团取代,且产率高效率高,通过以下方法实现,包括以下步骤:将亲核试剂与具有与碳原子形成四个σ键的卤素原子相结合的有机材料反应的步骤,更具体地说:一种用于生产具有Q的有机化合物的方法,包括以下步骤:将由通式(2)表示的化合物与至少一个卤素原子与碳原子形成四个σ键的有机起始材料反应,以将有机起始材料中的卤素原子替换为Q: MQa (2) (其中M代表碱金属原子、碱土金属原子或稀土金属原子;Q代表由消除质子衍生的无机酸或活性氢化合物的基团,其中Q是不同于有机起始材料中卤素原子的卤素原子,该卤素原子与具有四个σ键的碳原子相结合;a表示1到3的整数),在通式(1)表示的化合物的存在下 (其中Z-代表由无机酸或活性氢化合物中消除质子衍生的阴离子;R2相同或不同;R2各自独立地表示C1-C10烃基,或者两个R2在同一氮原子上可能与彼此结合形成与氮原子的环)。
-
Efficient cross-coupling of aryl Grignard reagents with alkyl halides by recyclable ionic iron(iii) complexes bearing a bis(phenol)-functionalized benzimidazolium cation作者:Chong-Liang Xia、Cun-Fei Xie、Yu-Feng Wu、Hong-Mei Sun、Qi Shen、Yong ZhangDOI:10.1039/c3ob41376d日期:——designed and used to prepare ionic iron(III) complexes of the type [H3L][FeX4] (X = Cl, 2; X = Br, 3). Both 2 and 3 were characterized by elemental analysis, Raman spectroscopy, electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and X-ray crystallography. The catalytic performances of 2 and 3 in cross-coupling reactions using aryl Grignard reagents with primary and secondary alkyl halides bearing β-hydrogens were
-
Cross-Electrophile Coupling of Unactivated Alkyl Chlorides作者:Holt A. Sakai、Wei Liu、Chi “Chip” Le、David W. C. MacMillanDOI:10.1021/jacs.0c04812日期:2020.7.8Alkyl chlorides are bench-stable chemical feedstocks that remain among the most underutilized electrophile classes in transition metal catalysis. Overcoming intrinsic limitations of C(sp3)-Cl bond activation, we report the development of a novel organosilane reagent that can participate in chlorine atom abstraction under mild photocatalytic conditions. In particular, we describe the application of
表征谱图
-
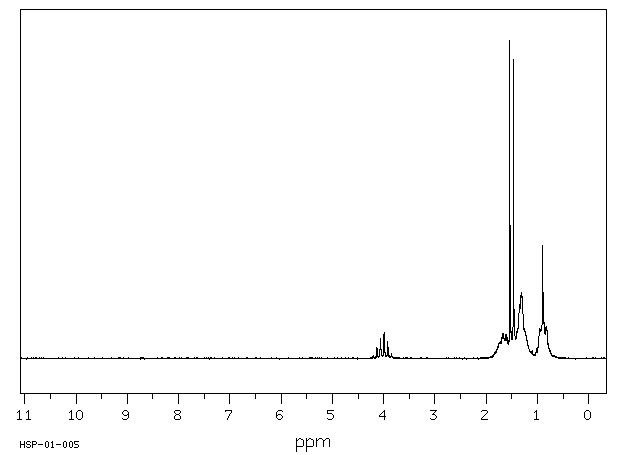
氢谱1HNMR
-
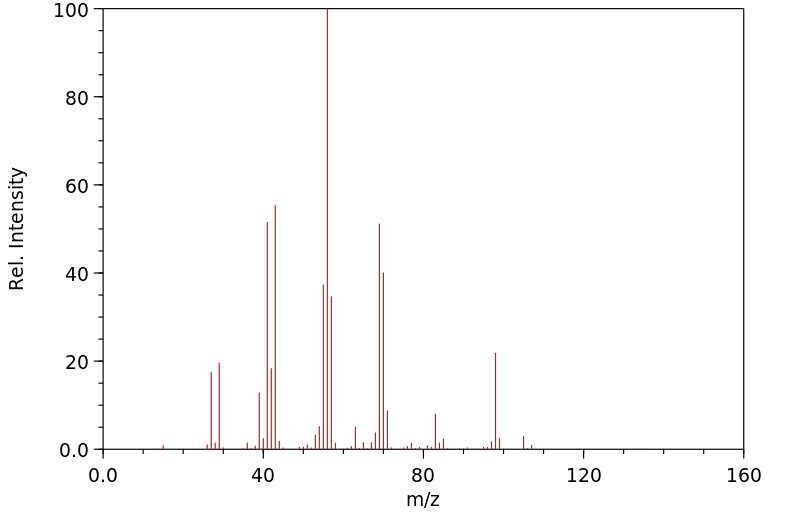
质谱MS
-
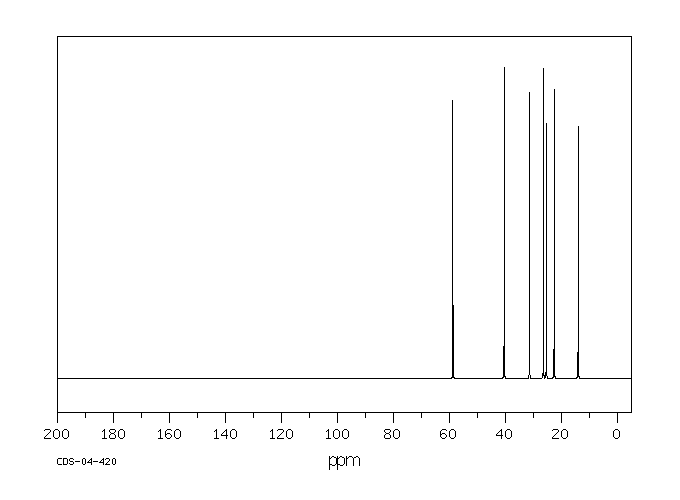
碳谱13CNMR
-
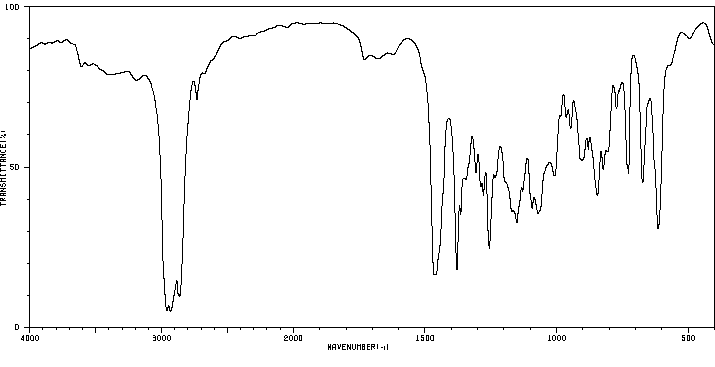
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
顺式1,4-二氯-2-甲基-2-丁烯
顺式1,1,1,5-四氯-4-甲基-3-戊烯
顺式-7-甲基环庚-2-烯基氯
顺式-4-甲基环庚-2-烯基氯
顺式-1-氨基-4-氯-2-丁烯
顺式-1,4-二氯-2-丁烯
顺-6-氯-2-己烯
顺-4-氯-2-丁烯胺盐酸盐
锡烷,二(4-氯丁基)羰基-
锡烷,三氯(2-乙烯基壬基)-
重氮乙酰氯
辛基癸基二甲基氯化铵
聚乙烯胺
羟肟基乙酰氯
磷亚胺三氯化,[1,2,2,2-四氯-1-(三氯甲基)乙基]-
硫代氯甲酸-O-辛酯
癸醛,2,2-二氯-
甲醛与氨和氯乙烷的聚合物
甲基(2E)-2-(3-氯-2-丁烷亚基)肼羧酸酯
环己烷,(氯甲基)-
环丙烷,2-丁基-1-氯-1-(1-戊炔基)-,顺-
环丙烷,1,2-二溴-3,3-二氯-1,2-二丙基-,反-
环丙烷,1,1-二溴-2,3-二氯-2,3-二乙基-,反-
环丙烷,1,1-二氯-3-(氯甲基)-2,2-二甲基-
环丙烷,1,1,2,3-四氯-2,3-二甲基-,反-
环丙基甲基氯
环丁基氯
特比萘芬杂质17
溴代二氯丁烷
油酰氯
油酰氯
水合2-氯乙醛
氯螺戊烷
氯磺酸-(2,3-二氯丙酯)
氯甲醇
氯甲氧基
氯甲基自由基
氯甲基环丁烷
氯甲基氯磺酸酯
氯甲基二氯甲基醚
氯甲基(甲基)次磷酰氯
氯环辛烷
氯环癸烷
氯环庚烷
氯环丙烷
氯十七烷
氯化链烷烃
氯化环十二烷
氯化新戊烷
氯代环戊烷