二氧化硅 | 14639-89-5
分子结构分类
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:1610 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:>100 °C(lit.)
-
密度:2.6 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
溶解度:不溶于水、酸溶液;溶于HF
-
物理描述:Transparent to gray, odorless powder. Irritating to the skin and eyes on contact. Inhalation will cause irritation in the respiratory tract. [Note: Amorphous silica is the non-crystalline form of SiO2.]
-
颜色/状态:Amorphous powder
-
气味:Odorless
-
味道:Tasteless
-
蒸汽压力:10 mm Hg @ 1732 °C
-
腐蚀性:Non-corrosive
-
燃烧热:/Non-combustible/
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.66
-
重原子数:3
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:-2147483.648
-
拓扑面积:34.1
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:D
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 0.05 mg/m3
制备方法与用途
方石英是一种低密度的SiO₂同质多象变体,其热力学稳定区为1470℃~1728℃(常压下)。β方石英为其高温相,但在较低温度下仍可以亚稳态形式保存,直到大约250℃时发生移位型相变形成α方石英。尽管方石英可通过SiO₂熔体在其热力学稳定区结晶形成,但自然界中大多数方石英则是在亚稳态条件下形成的。
例如,硅藻土在成岩过程中可转变成方石英质燧石或微晶蛋白石(蛋白石-CT、蛋白石-C),其主要矿物相为α方石英,转变温度处于石英的热力学稳定区;在麻粒岩相变质条件下,方石英从富Na-Al-Si熔体中析出,并以包裹体形式存在于石榴石中与钠长石共存。形成的温压条件为800℃, 1GPa,同样也处于石英的热力学稳定区。此外,在许多非金属矿物材料如陶瓷烧结、莫来石制备等过程中的亚稳态方石英形成,其形成温度均位于鳞石英的热力学稳定区。
形成机制硅藻土在900℃~1300℃时转变成方石英;蛋白石在1200℃转变成方石英;高岭石在1260℃也有方石英生成;人工合成的MCM-41中孔SiO₂分子筛在1000℃即转变成方石英。其他如陶瓷烧结、莫来石制备等过程中也有亚稳态方石英形成。
对于方石英这种亚稳态形成的机制,一致认为是一种非平衡热力学过程,主要受反应动力学机制控制。根据上述方石英的亚稳态形成方式,几乎一致地认为:方石英都是从非晶态SiO₂转变而成,即使在高岭石热处理、莫来石制备、陶瓷烧结过程中也是如此。
用途白炭黑自20世纪40年代工业化生产以来,在橡胶制品中作补强剂的用量已占总用量的70%。随着其应用领域的不断开发,非橡胶领域也获得了广泛的应用,国外市场中非橡胶领域的用量已经上升至总量的四分之一。
应用-
在橡胶中的应用 白炭黑的主要用途是在橡胶中起交联作用和作补强剂。
-
在油墨、油漆和涂料中的应用 在油墨、油漆和涂料中,白炭黑可作为增稠剂、触变剂、分散剂和防沉剂。它能使制剂色泽鲜艳,增加透明感,并且打印清晰、漆膜坚固;气相法白炭黑还在复印机和激光打印机的墨盒调色中用作分散剂和流量控制剂,浓度较大时可作消光剂。
-
其他方面的应用 除了上述领域外,白炭黑还可用于医药、农药、化妆品以及牙膏、造纸等领域。活性白炭黑具有很大的内、外表面积,是理想的医药和农药载体;在农药中能大量吸收杀虫剂;在牙膏中可洁齿除斑;在造纸工业中能提高纸张的白度,使纸张轻薄化,适合高速印刷。
总之,作为一种功能性添加剂,白炭黑的应用范围将更加广泛,并且其添加性能也将得到更大的提升。
生产方法方石英即白炭黑,化学分子式为SiO₂nH₂O。因其用途与炭黑相似且为白色而得名白炭黑。根据生产方法的不同,可分为沉淀白炭黑(沉淀水合二氧化硅)和气相法白炭黑(气相二氧化硅)。这两种产品的性质及用途存在很大差异。
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:FUNABASI, TOSIXIKO;KAMINODZONO, AKI;UTIMURA, IOSIXARU摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:1,5-dimethyl-3,3'-spirobi(6-oxa-3-silabicyclo<3.1.0>hexane) 以 solid matrix 为溶剂, 生成 白碳黑参考文献:名称:Generation, low-temperature stabilization, structure, and reactivity of intermediates with low-coordinated carbon, silicon, and germanium atoms摘要:The mechanisms of thermal and photochemical transformations of organic and organometallic compounds which pass through formation of different reactive intermediates were investigated by low-temperature matrix IR spectroscopy. Low-temperature matrix stabilization of the intermediates, the primary products of these reactions, was conducted at 10-15 K. The spectral and structural parameters of the free radicals (CCl3, CCl2Br, CClBr2, CH2CH=CH2, CF2CF=CF2, CH2-C=CH, CH2C=N, CH2Ph, CF2C6F5), halocarbenes and their silicon and germanium analogs, and unstable molecules with double-bond silicon and germanium atoms were obtained as a result.DOI:10.1007/bf00961022
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:CIRCULAR RNA COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS摘要:Circular RNA, along with related compositions and methods are described herein. In some embodiments, the inventive circular RNA comprises post splicing group I in iron fragments, spacers, an IRES, optional duplex forming regions, and more than one expression sequence. In some embodiments, the expression sequences are separated by one or more polynucleotide sequences encoding a cleavage site. In some embodiments, circular RNA of the invention has improved expression, functional stability, immunogenicity, ease of manufacturing, and/or half-life when compared to linear RNA. In some embodiments, inventive methods and constructs result in improved circularization efficiency, splicing efficiency, and/or purity when compared to existing RNA circularization approaches.公开号:US20240245805A1
文献信息
-
Azole derivatives, process for their preparation and their use申请人:Hoechst Aktiengesellschaft公开号:US05482957A1公开(公告)日:1996-01-09Azole derivatives, process for their preparation, and their use Azole derivatives of the formula (I) ##STR1## in which A, L, O, R.sup.1, X, Y, Z and q have the meanings given, process for their preparation, pharmaceutical preparations and the use of the compounds are described. Azole derivatives of the formula I where the symbols have for example the following meanings: R.sup.1 is (C.sub.2 -C.sub.10)-alkyl, Z is nitrogen, X and Y are independently of one another CR.sup.2, L is --CH.sub.2 --, q is zero or 1, A is a biphenyl radical which is substituted for example by R.sup.15, R.sup.2 is halogen or hydrogen, R.sup.15 is SO.sub.2 --NH--CO--OR.sup.6 and R.sup.6 is phenyl, are highly active antagonists of angiotensin II receptors.
-
INHIBITORS OF HEMOPOIETIC CELL KINASE (P59-HCK) AND THEIR USE IN THE TREATMENT OF INFLUENZA INFECTION申请人:Charron Catherine Elisabeth公开号:US20120244120A1公开(公告)日:2012-09-27The present invention relates inter alia to the treatment or prevention of influenza virus infection (including subtypes influenza A virus, influenza B virus, avian strain H5N1, A/H1N1, H3N2 and/or pandemic influenza) using compounds which inhibit the activity of p59-HCK and to a method of screening for a candidate drug substance intended to prevent or treat influenza virus infection in a subject, said method comprising identifying a test substance capable of inhibiting p59-HCK activity.本发明涉及治疗或预防流感病毒感染(包括亚型流感A病毒、流感B病毒、禽流感H5N1、A/H1N1、H3N2和/或大流行性流感)的化合物,这些化合物抑制p59-HCK的活性,并涉及一种筛选候选药物物质的方法,该方法旨在预防或治疗受试者的流感病毒感染,所述方法包括识别能够抑制p59-HCK活性的试验物质。
-
ANTI-BACTERIAL CALCIUM-DEPENDENT ANTIBIOTIC (CDA) ANALOGS AND METHODS OF TREATING BACTERIAL INFECTIONS申请人:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG公开号:US20210324009A1公开(公告)日:2021-10-21Provided herein are calcium-dependent antibiotics (CDAs), as a novel therapeutic target for treating bacterial infections. The present invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds, and to methods of use thereof for combating bacteria and treating bacterial infections.
-
Antibacterial agents, and 4-thio azetidinone intermediates申请人:Bristol-Myers Company公开号:US04272437A1公开(公告)日:1981-06-09This invention relates to 2-substituted and 2,6-disubstituted penem compounds of the formula ##STR1## wherein Y is hydrogen, halo or certain organic substituents and X represents certain organic substituents. Also included in the invention are pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the above compounds and derivatives of the above compounds in which the carboxyl group at the 3-position is protected as by an easily removable ester protecting group. The compounds of the present invention are potent antibacterial agents or are of use as intermediates in the preparation of such agents.本发明涉及2-取代和2,6-二取代的青霉烯化合物,其公式为##STR1##,其中Y是氢、卤素或某些有机取代基,X代表某些有机取代基。发明还包括上述化合物的药用可接受盐和上述化合物的衍生物,其中3位的羧基被易于移除的酯保护基团所保护。本发明的化合物是强效的抗菌剂,或可用于制备此类药物的中间体。
-
CROSSLINKED ARTIFICIAL NUCLEIC ACID ALNA申请人:MITSUBISHI TANABE PHARMA CORPORATION公开号:US20220002336A1公开(公告)日:2022-01-06The present invention provides a novel bridged artificial nucleic acid and an oligomer containing the same as a monomer. The present invention provides specifically a compound represented by general formula (I) (wherein each symbol is the same as defined in the specification) or salts thereof; as well as an oligonucleotide compound represented by general formula (I′) (wherein each symbol is the same as defined in the specification) or salts thereof.本发明提供了一种新型的桥接人工核酸和含有该人工核酸作为单体的寡聚物。本发明具体提供了一种由通式(I)表示的化合物(其中每个符号与规范中定义的相同)或其盐;以及由通式(I')表示的寡核苷酸化合物(其中每个符号与规范中定义的相同)或其盐。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
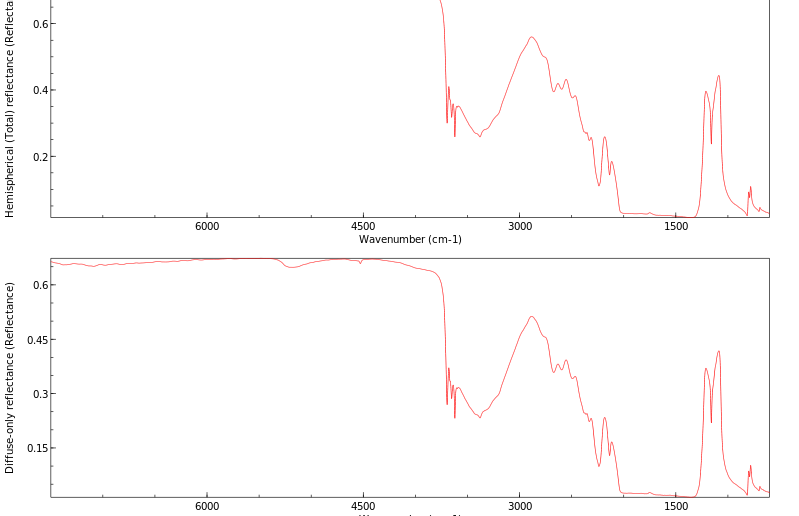
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息