7S,8S-nitidanin
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
7S,8S-nitidanin
英文别名
4-[(2S,3S)-3-(hydroxymethyl)-7-[(E)-3-hydroxyprop-1-enyl]-5-methoxy-2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-2-yl]-2,6-dimethoxyphenol
CAS
——
化学式
C21H24O8
mdl
——
分子量
404.417
InChiKey
AZTAGXIJLPKJOR-BJUCQYRTSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.9
-
重原子数:29
-
可旋转键数:7
-
环数:3.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.33
-
拓扑面积:107
-
氢给体数:3
-
氢受体数:8
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:7S,8S-nitidanin 在 platinum(IV) oxide 氢气 作用下, 以 乙醇 为溶剂, 反应 2.0h, 以1.8 mg的产率得到4-[(2S,3S)-3-Hydroxymethyl-7-(3-hydroxy-propyl)-5-methoxy-2,3-dihydro-benzo[1,4]dioxin-2-yl]-2,6-dimethoxy-phenol参考文献:名称:来自Santalum专辑L的心材的芳香成分。摘要:对印度桑塔卢姆专辑L.心心中的极性成分进行植物化学研究后,分离出三种新的新木脂素(1-3)和一种新的芳香酯(4),以及14种已知成分。使用光谱方法建立了新化合物(1-4)的结构。DOI:10.1248/cpb.53.641
-
作为产物:描述:bilagrewin 在 sodium tetrahydroborate 、 cerium(III) chloride heptahydrate 作用下, 以 甲醇 为溶剂, 反应 6.0h, 以0.6 mg的产率得到7S,8S-nitidanin参考文献:名称:Lignans from Santalum album and Their Cytotoxic Activities摘要:从山檀树(山檀科)的心材中分离出了一种新的新木质素--(7R,8R)-5-O-去甲基比拉格鲁因(1),以及四种已知的木质素(2-5)。通过分析大量光谱数据,确定了 1 的结构。评估了分离出的化合物及其衍生物对 HL-60 人类早幼粒细胞白血病细胞和 A549 人类肺腺癌细胞的细胞毒活性。化合物 1 和 2 对 HL-60 细胞的细胞毒性 IC50 值分别为 1.5±0.02 和 4.3±0.13 μM,对 A549 细胞的细胞毒性 IC50 值分别为 13.6±0.32 和 19.9±1.27 μM。研究发现,1 和 2 的醛基是这类木脂素产生细胞毒性的结构要求。研究表明,这些肿瘤细胞的死亡是通过诱导细胞凋亡介导的。DOI:10.1248/cpb.58.587
文献信息
-
Insights into lignin primary structure and deconstruction from Arabidopsis thaliana COMT (caffeic acid O-methyl transferase) mutant Atomt1作者:Syed G. A. Moinuddin、Michaël Jourdes、Dhrubojyoti D. Laskar、Chanyoung Ki、Claudia L. Cardenas、Kye-Won Kim、Dianzhong Zhang、Laurence B. Davin、Norman G. LewisDOI:10.1039/c004817h日期:——The Arabidopsis mutant Atomt1 lignin differs from native lignin in wild type plants, in terms of sinapyl (S) alcohol-derived substructures in fiber cell walls being substituted by 5-hydroxyconiferyl alcohol (5OHG)-derived moieties. During programmed lignin assembly, these engender formation of benzodioxane substructures due to intramolecular cyclization of their quinone methides that are transiently formed following 8-O-4′ radical-radical coupling. Thioacidolytic cleavage of the 8-O-4′ inter-unit linkages in the Atomt1 mutant, relative to the wild type, indicated that cleavable sinapyl (S) and coniferyl (G) alcohol-derived monomeric moieties were stoichiometrically reduced by a circa 2 : 1 ratio. Additionally, lignin degradative analysis resulted in release of a 5OHG–5OHG–G trimer from the Atomt1 mutant, which then underwent further cleavage. Significantly, the trimeric moiety released provides new insight into lignin primary structure: during polymer assembly, the first 5OHG moiety is linked via a C8–O–X inter-unit linkage, whereas subsequent addition of monomers apparently involves sequential addition of 5OHG and G moieties to the growing chain in a 2 : 1 overall stoichiometry. This quantification data thus provides further insight into how inter-unit linkage frequencies in native lignins are apparently conserved (or near conserved) during assembly in both instances, as well as providing additional impetus to resolve how the overall question of lignin macromolecular assembly is controlled in terms of both type of monomer addition and primary sequence.拟南芥突变体 Atomt1 木质素与野生型植物中的原生木质素不同,纤维细胞壁中由 sinapyl (S) 醇衍生的亚结构被 5-hydroxyconiferyl 醇 (5OHG) 衍生的分子取代。在木质素的程序化组装过程中,由于 8-O-4′ 自由基-自由基偶联后瞬时形成的醌基甲烷的分子内环化作用,这些醌基甲烷会形成苯并二恶烷亚结构。与野生型相比,Atomt1 突变体中 8-O-4′ 单元间连接的硫代酸裂解表明,可裂解的桧醇(S)和松柏醇(G)衍生的单体分子以约 2 :1 的比例减少。此外,木质素降解分析还导致 Atomt1 突变体释放出 5OHG-5OHG-G 三聚体,然后进一步裂解。值得注意的是,释放出的三聚体提供了对木质素一级结构的新认识:在聚合物组装过程中,第一个 5OHG 分子通过 C8-O-X 单元间连接,而随后单体的添加显然涉及 5OHG 和 G 分子以 2 :1 的总比例。因此,这些定量数据让我们进一步了解了在这两种情况下,原生木质素中的单元间连接频率是如何在组装过程中保持不变(或接近不变)的,同时也为解决木质素大分子组装的整体问题提供了更多动力,即单体添加类型和主序是如何受控的。
-
Total synthesis of (±)-nitidanin and novel procedures for determination of the location of the side chains on 1,4-benzodioxane作者:Atsuhito Kuboki、Toru Yamamoto、Mamie Taira、Tetsuya Arishige、Susumu OhiraDOI:10.1016/j.tetlet.2006.11.170日期:2007.1Regioselective cycloaddition of o-quinone 4 and protected sinapyl alcohol 2 gave 1,4-benzodioxane 5, which was converted to (+/-)-nitidanin (6), an antimalarial compound. Two novel procedures were developed to determine the location of the side chains of the adduct (5) based on partial ring cleavage. (c) 2006 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
表征谱图
-
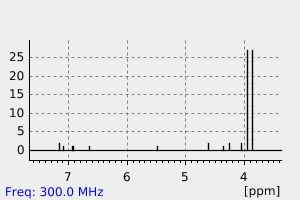
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
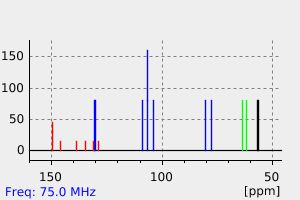
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
顺式-6-氯-4-甲基-4-苯基-4H-1,3-苯并二氧杂环己-2-羧酸
阿莫齐特
苯并二氧六环-6-甲酸甲酯
苯并二氧六环-6-甲酰胺
苯并二氧六环-5-甲酸甲酯
苯并二氧六环-5-甲酰胺
苯并二氧六环-2-磺酰氯
苯并-1,4-二氧六环-6-硼酸
艾泽罗西
脲,N-(4-甲基-1-哌嗪基)-
胍苯克生
胍美柳
胍生
羧基-6-苯并(4H)二恶英-1,3
美商陆酚A
维兰特罗杂质4
硫酸(2:1)(1,4-苯并二噁烷-6-基甲基)胍正离子
盐酸艾美洛沙
盐酸哌罗克生
盐酸[(7-溴-2,3-二氢-1,4-苯并二恶英-6-基)甲基]肼
甲基氨基甲酸1,4-苯并二恶烷-5-基酯
甲基8-甲基-2,3-二氢-1,4-苯并二氧杂环己烷-6-羧酸酯
甲基7-甲基-2,3-二氢-1,4-苯并二氧杂环己烷-5-羧酸酯
甲基4-[(1E)-3-乙基-3-(羟甲基)三氮杂-1-烯-1-基]苯酸酯
甲基-[2-[(7-丙-2-烯基-2,3-二氢-1,4-苯并二氧杂环己-8-基)氧基]乙基]氯化铵
甲基(2S,4R)-6-氯-4-甲基-4-(2-噻吩基)-4H-1,3-苯并二氧杂环己烷-2-羧酸酯
溴(2,3-二氢-1,4-苯并二氧杂环己-6-基)镁
沙丁胺醇缩丙酮
异美商陆素 A
异戊苯恶烷
度莫辛
布他莫生
安必罗山
地奥地洛
噻唑并[5,4-b]吡啶-2-胺,N-[[1-[(2,3-二氢-1,4-苯并二噁英-2-基)甲基]-4-哌啶基]甲基]-
哌扑罗生
咪洛克生
咪唑克生盐酸盐
吡啶-3-磺酰氯盐酸盐
叔丁基 (2,3-二氢苯并[b][1,4]二噁英-6-基)氨基甲酸酯
反式-2,3-二氢-N-((4-(2-苯氧基乙基)-1-哌嗪基)甲基)-1,4-苯并二氧六环-2-甲酰胺
双恶哌嗪
冰达卡醇
依利格鲁司特酒石酸盐
依利格鲁司特杂质
依利格鲁司特中间体5
依利格鲁司特
亚达唑散
二氨基亚甲基-(2,3-二氢-1,4-苯并二氧杂环己-2-基甲基)铵硫酸盐
二-(叔丁基)2-(2,2-二甲基-4H-1,3-苯并二恶英-6-基)-2-氧代乙基亚氨基二碳酸