二嗪磷 | 333-41-5
中文名称
二嗪磷
中文别名
O,O-二乙基-O-(2-异丙基-4-甲基嘧啶-6-基)硫代磷酸酯;二嗪农;大亚仙农;敌匹硫磷;0,0-二乙基-0-(2-异丙基-4-甲嘧啶-6-甲)硫逐磷酸酯;地亚农
英文名称
`Diazinon`
英文别名
DZN;Diazinon;diethoxy-(6-methyl-2-propan-2-ylpyrimidin-4-yl)oxy-sulfanylidene-λ5-phosphane
CAS
333-41-5
化学式
C12H21N2O3PS
mdl
MFCD00036204
分子量
304.35
InChiKey
FHIVAFMUCKRCQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:>120°C (dec.)
-
沸点:306°C
-
密度:1.117
-
闪点:104.4 °C
-
溶解度:氯仿:微溶
-
暴露限值:OSHA PEL: TWA 0.1 mg/m3; ACGIH TLV: TWA 0.1 mg/m3.
-
物理描述:Liquid; light to dark brown. Sinks in water. Commercial solutions can contain ethanol/xylene/acetone with a flash point in the range 82-105° F.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless oil
-
气味:Faint ester-like odor
-
蒸汽压力:9.01X10-5 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:1.13e-07 atm-m3/mole
-
稳定性/保质期:
对家兔的皮肤和眼睛有轻微刺激作用,在试验剂量下,未观察到动物出现致畸、致癌或致突变的作用。
-
自燃温度:> 400 °C. /Diazinon 50W/
-
分解:120 °C
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.4978-1.4981 at 20 °C/D
-
解离常数:pKa = 2.6
-
碰撞截面:173.38 Ų [M+H]+
-
保留指数:1766;1743;1743;1746;1756;1774;1745;1767;1772;1776;1776;1772;1769;1760;1779.1;1774.1;1768;1760.1;1778.2;1759.1;1762.3;1785.1;1761;1770.1;1789.2;1775;1780;1781.8;1758;1759.4;1773.5;1769.7;1772.9;1766
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.8
-
重原子数:19
-
可旋转键数:7
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.666
-
拓扑面积:85.6
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:6
ADMET
代谢
敌百虫的主要代谢途径包括:酯键断裂形成羟基嘧啶衍生物;P-S基团转化为P-O衍生物;异丙基取代基的氧化形成相应的叔醇和伯醇衍生物;甲基取代基的氧化形成相应的醇;以及谷胱甘肽介导的酯键断裂形成谷胱甘肽结合物。
The main metabolic pathways of degradation of diazinon are: cleavage of the ester bond leading to the hydroxypyrimidine derivatives; transformation of P-S moiety to the P-O derivative; oxidation of isopropyl substituent leading to the corresponding tertiary and primary alcohol derivatives; oxidation of the methyl substituent leading to the corresponding alcohol; glutathione-mediated cleavage of the ester bond leading to a glutathione conjugate.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
/对大鼠进行地亚农代谢研究,发现/其代谢物2-异丙基-4-甲基-6-羟基嘧啶.../和两种未识别的代谢物/这些代谢物通过尿液和粪便排出,占总剂量的70%。...在大鼠中亚农的代谢...用(14)C标记,...通过跟踪静脉注射后的代谢命运,定位了3种代谢物在一般代谢途径上。由于这3种化合物的急性口服毒性都比亚农低1/10,生物转化与解毒有关。
/STUDY OF METABOLISM IN RATS OF DIAZINON FOUND THAT/ THE METABOLITES 2-ISOPROPYL-4-METHYL-6-HYDROXYPYRIMIDINE ... /& TWO UNIDENTIFIED METABOLITES/ WHICH WERE EXCRETED IN THE URINE AND FECES, ACCOUNT FOR 70% OF THE DOSE. ... METB IN RATS OF DIAZINON ... LABELLED WITH (14)C, ... 3 METABOLITES WERE LOCATED ON GENERAL METABOLIC PATHWAY BY FOLLOWING THEIR METABOLIC FATE AFTER IV INJECTION. SINCE ACUTE ORAL TOXICITIES OF ALL 3 CMPD ARE LESS THAN 1/10 OF THAT OF DIAZINON, BIOTRANSFORMATION IS ASSOC WITH DETOXICATION.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
DIAZINON ... APPEARS TO BE METABOLIZED INTO CORRESPONDING PHOSPHATE IN LACTATING COWS, AND INTO THE HYDROLYTIC PRODUCTS DIETHYL PHOSPHOROTHIOATE AND DIETHYL PHOSPHATE WITH LIBERATION OF 2-HYDROXY-6-ISOPROPYL-4-METHYLPYRIMIDINE /PLUS METABOLITE DIAZOXON/.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
AFTER ADMIN OF DIAZINON BY STOMACH TUBE TO SHEEP, HYDROXYDIAZINON WAS FOUND IN TISSUES. DIAZINON, WHEN FED TO SHEEP, WAS METABOLIZED ALSO BY HYDROXYLATION OF C-4 METHYL GROUP. RESIDUES OF THIS & C-1' ISOPROPANOL ANALOG WERE FOUND ... .
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
Diazinon has known human metabolites that include Diazoxon, Diethyl thiophosphate, and Pyrimidinol.
来源:NORMAN Suspect List Exchange
毒理性
识别:敌敌畏是一种无色透明的液体,具有淡淡的酯类气味。敌敌畏可溶于大多数有机溶剂。在中性介质中稳定,但在碱性介质中缓慢水解,在酸性介质中更快水解。敌敌畏是一种具有广泛杀虫活性的接触型有机磷杀虫剂。它也可以与其他杀虫剂混合配方使用。另一个主要用途是作为兽药。人类暴露:敌敌畏的环境水平通常较低。一般人群的暴露途径是吸入和饮食。通过水的暴露可以忽略不计。职业暴露主要是通过皮肤。已有多起因敌敌畏意外或自杀中毒的报道,其中一些是致命的。在一些情况下,由于存在高度有毒的杂质,如TEPP,胆碱能综合症可能比预期的更严重。在某些情况下,急性可逆性胰腺炎与严重的胆碱能综合症有关。据报道,职业暴露后的中毒案例总是与杂质的 presence 有关。动物研究:急性口服、皮肤和吸入毒性较低。小鼠、大鼠、家兔、狗和猴子的短期和长期研究表明,唯一值得关注的效果是与剂量相关的乙酰胆碱酯酶活性的抑制。敌敌畏对家兔皮肤有轻微刺激性,但对眼睛无刺激性。敌敌畏不是皮肤致敏剂。生殖和发育研究没有发现胚胎毒性或致畸潜力的证据。在不对亲代动物产生毒性的剂量水平下,对生殖性能没有影响。在体内和体外进行的各种终点的致突变性研究没有显示出致突变潜力。没有大鼠或小鼠致癌性的证据。据报道,敌敌畏在狗和豚鼠中会引起急性胰腺炎;这被认为是一种特定物种的效果。敌敌畏可能通过胃肠道吸收,通过完整的皮肤和吸入。敌敌畏被微粒体酶氧化为抑制胆碱酯酶的代谢物,如氧化敌敌畏、羟基氧化敌敌畏和羟基敌敌畏。
IDENTIFICATION: Diazinon is a clear colorless liquid with a faint ester-like odor. Diazinon is soluble in most organic solvents. It is stable in neutral media, but is slowly hydrolyzed in alkaline media and more rapidly in acid media. Diazinon is a contact organophosphorus insecticide with a wide range of insecticidal activity. It is also available in mixed formulations with other insecticides. Another major use is as a drug in veterinary medicine. HUMAN EXPOSURE: Environmental levels of diazinon are generally low. The routes of exposure for the general population are inhalational and dietary. Exposure through water is negligible. Occupational exposure is primarily dermal. Several cases of accidental or suicidal poisoning by diazinon hae been reported, some of which were fatal. In some of these the cholinergic syndrome may have been more severe than expected because of the presence of highly toxic impurities such as TEPP. In certain cases, acute reversible pancreatitis was associated with a severe cholinergic syndrome. Reported cases of poisoning after occupational exposure have always been associated with the presence of impurities. ANIMAL STUDIES: The acute oral, dermal and inhalational toxicity is low. Short-term and long-term studies in mice, rats, rabbits, dogs and monkeys have shown that the only effect of concern is dose-related inhibition of acetyl cholinesterase activity. Diazinon is slightly irritant to rabbit skin but not to the eye. Diazinon is not a dermal sensitizer. Reproductive and developmental studies have revealed no evidence of embryotoxic or teratogenic potential. There was no effect on reproductive performance at dose levels that were not toxic to the parent animals. Mutagenicity studies with various end-points in vivo and in vitro gave no evidence of a mutagenic potential. There is no evidence of carinogenicity in rats or mice. In the dog and guinea-pig, diazinon has been reported to cause acute pancreatitis; this is considered to be a species-specific effect. Diazinon may be absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, through the intact skin and following inhalation. Diazinon is oxidized by microsomal enzymes to cholinesterase inhibiting metabolites such as diazoxon, hydroxydiazoxon and hydroxydiazinon.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
敌敌畏是一种胆碱酯酶或乙酰胆碱酯酶(AChE)抑制剂。胆碱酯酶抑制剂(或“抗胆碱酯酶”)抑制乙酰胆碱酯酶的作用。由于其基本功能,干扰乙酰胆碱酯酶作用的化学物质是强大的神经毒素,低剂量时会导致过度流涎和眼泪,随后是肌肉痉挛,最终导致死亡。神经气体和许多用于杀虫剂的物质已被证明通过结合乙酰胆碱酯酶活性位点的丝氨酸,完全抑制该酶。乙酰胆碱酯酶分解神经递质乙酰胆碱,该神经递质在神经和肌肉接合处释放,以便让肌肉或器官放松。乙酰胆碱酯酶抑制的结果是乙酰胆碱积累并继续发挥作用,使得任何神经冲动不断传递,肌肉收缩不会停止。最常见的乙酰胆碱酯酶抑制剂之一是基于磷的化合物,它们被设计成与酶的活性位点结合。结构要求是一个带有两个亲脂性基团的磷原子,一个离去基团(如卤素或硫氰酸盐),以及一个末端的氧。
Diazinon is a cholinesterase or acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor. A cholinesterase inhibitor (or 'anticholinesterase') suppresses the action of acetylcholinesterase. Because of its essential function, chemicals that interfere with the action of acetylcholinesterase are potent neurotoxins, causing excessive salivation and eye-watering in low doses, followed by muscle spasms and ultimately death. Nerve gases and many substances used in insecticides have been shown to act by binding a serine in the active site of acetylcholine esterase, inhibiting the enzyme completely. Acetylcholine esterase breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which is released at nerve and muscle junctions, in order to allow the muscle or organ to relax. The result of acetylcholine esterase inhibition is that acetylcholine builds up and continues to act so that any nerve impulses are continually transmitted and muscle contractions do not stop. Among the most common acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are phosphorus-based compounds, which are designed to bind to the active site of the enzyme. The structural requirements are a phosphorus atom bearing two lipophilic groups, a leaving group (such as a halide or thiocyanate), and a terminal oxygen.
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
癌症分类:不太可能对人类致癌
Cancer Classification: Not Likely to be Carcinogenic to Humans
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
A4:不能归类为人类致癌物。
A4: Not classifiable as a human carcinogen.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
国际癌症研究机构致癌物:地亚农
IARC Carcinogenic Agent:Diazinon
来源:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
吸收、分配和排泄
四只产蛋的莱亨鸡通过胶囊形式连续七天每天按1.7毫克/千克体重的剂量接受2-14C-地亚农(比活度30.3 uCi/mg)的治疗,相当于饲料中25毫克/千克的摄入量。... 授予的大部分放射性物质通过排泄物排出,在研究期间有78.6%的剂量被排出。大约0.1%的放射性物质被发现存在于组织和血液中,不到0.01%出现在蛋黄中,0.07%在蛋白中被检测到。组织中残留的放射性物质在肾脏中达到0.148毫克/千克地亚农当量,血液中为0.137毫克/千克,肝脏中为0.11毫克/千克,其他检查的组织中为0.01-0.025毫克/千克。蛋黄中的残留物从0.006毫克/千克地亚农当量到0.065毫克/千克不等,而蛋白中的残留物从0.038毫克/千克到0.066毫克/千克不等。以整个鸡蛋为基础,治疗第4天达到了0.047毫克/千克的平稳浓度。
Four laying Leghorn hens were treated with 2-14C-diazinon (specific activity 30.3 uCi/mg) in gelatin capsules for seven consecutive days at daily doses of 1.7 mg/kg body weight, corresponding to a dietary exposure of 25 mg/kg in feed. ... Elimination of most of the administered radioactivity occurred via the excreta, with 78.6% of the total dose being excreted during the study period. Approximately 0.1% of the radioactivity was found in tissues and blood, less than 0.01% appeared in the egg yolks and 0.07% was detected in the egg whites. The residual radioactivity in the tissues amounted to 0.148 mg/kg diazinon equivalents in the kidney, 0.137 mg/kg in blood, 0.11 mg/kg in the liver and 0.01-0.025 mg/kg in the other tissues examined. The residues in the egg yolks ranged from 0.006 mg/kg diazinon equivalents to 0.065 mg/kg while those in the egg whites ranged from 0.038 mg/kg to 0.066 mg/kg. On a whole egg basis, a plateau concentration of 0.047 mg/kg was reached on day 4 of treatment.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
一头哺乳期的赫里福德牛(体重268公斤)口服了一颗含有20毫克/公斤32P-地亚农的明胶胶囊(比活性为518 cpm/微克)。...在36小时内,大约74%的放射性物质随尿液排出,6.5%出现在粪便中,0.08%在牛奶中找到。给药后18小时达到2.27毫克/公斤地亚农当量的峰值浓度。
A lactating Hereford cow (body weight 268 kg) was orally treated with a gelatin capsule containing 20 mg/kg 32P-diazinon (specific activity 518 cpm/ug). ... Within 36 hr, approximately 74% of the administered radioactivity was excreted with the urine, 6.5% appeared in the feces and 0.08% was found in the milk. A peak concentration of 2.27 mg/kg diazinon equivalents was reached 18 hr after the administration.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
两头泌乳的山羊口服了(嘧啶-14C)-地亚农(特定活性为9.7 uCi/mg),每天剂量为4.5 mg/kg,连续四天,相当于饲料中100 mg/kg的暴露量。在观察期间,平均64.1%的放射性物质通过尿液排出,10.4%通过粪便排出,0.31%通过乳汁排出。服药3天后乳汁中的放射性物质达到一个平台,平均水平为0.46 mg/kg的地亚农当量。在宰杀时,血液中的放射性物质占0.2%,检查的组织中积累了0.92%的给药剂量。在检查的组织中,肾脏(2.0 mg/kg)和肝脏(1.2 mg/kg)的残留放射性物质最高。其他检查的组织中含有0.23-0.3 mg/kg的地亚农当量。
Two lactating goats were orally treated with (pyrimidine-14C)-diazinon (specific activity 9.7 uCi/mg) in gelatin capsules for four consecutive days at a dose level of 4.5 mg/kg per day, corresponding to a dietary exposure of 100 mg/kg of feed. During the observation period, an average 64.1% of the administered radioactivity was excreted with urine, 10.4% with the feces and 0.31% with the milk. A plateau of radioactivity in the milk was reached after 3 days of dosing at a mean level of 0.46 mg/kg diazinon equivalent. At sacrifice, radioactivity in the blood accounted for 0.2% and the tissues examined accumulated 0.92% of the administered dose. The highest residual radioactivity was detected in the kidney (2.0 mg/kg) and the liver (1.2 mg/kg). The other tissues examined contained 0.23-0.3 mg/kg diazinon equivalents.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
两只母比格犬通过静脉注射给予0.2毫克/公斤的(乙氧基-14C)-地亚农(比活度为3.4微居里/毫克),溶于0.7毫升乙醇中。... 从血液中消除的第二个阶段的半衰期计算为363分钟。在大约24小时内,约58%的给药放射性在尿液中回收。另外两只母比格犬通过胶囊口服给予4.0毫克/公斤的(乙氧基-14C)地亚农,溶于乙醇中。在大约24小时后,约85%的给药放射性被回收,其中53%发生在尿液中。
Two female Beagle dogs were intravenously dosed with 0.2 mg/kg (ethoxy-14C)-diazinon (specific activity 3.4 uCi/mg) in 0.7 mL ethanol. ... The half-life of elimination from blood for this second phase was calculated to be 363 min. Approximately 58% of the administered radioactivity was recovered in the urine within 24 hr after the administration. Another two female beagle dogs were orally dosed by capsule with 4.0 mg/kg (ethoxy-14C) diazinon in ethanol. Approximately 85% of the administered radioactivity was recovered within 24 hr after oral administration, with 53% of it occurring in urine.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:D
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 0.1 mg/m3 [skin]
-
危险等级:6.1(b)
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S16,S24/25,S26,S36,S60,S61
-
危险类别码:R22,R50/53
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2933599011
-
危险品运输编号:UN 2783/2810
-
危险类别:6.1(b)
-
RTECS号:TF3325000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS07,GHS09
-
危险性描述:H225,H302,H312,H319,H332,H411
-
危险性防范说明:P210,P273,P280,P305 + P351 + P338
-
储存条件:库房应保持通风、低温和干燥,并将库存与食品原料分开储运。
制备方法与用途
毒性
原药对大鼠急性经口LD50为285 mg/kg(范围:300~850 mg/kg),小鼠为163 mg/kg;雌性大鼠急性经皮LD50为455 mg/kg,大鼠经皮LD502150 mg/kg;小鼠急性吸入LD50为630 mg/m³。对家兔皮肤和眼睛有轻度刺激作用。大鼠慢性毒性饲喂试验无作用剂量为每天0.1 mg/kg,猴子为每天0.05 mg/kg。在试验剂量下,对动物无致畸、致癌、致突变作用。鲤鱼LD50为3.2 mg/L(48小时)。对蜜蜂高毒。
化学性质
纯品为无色油状液体,略带香味。沸点(b.p.) 83~84℃(1.33 Pa),125℃(133.32 Pa);蒸气压 1.867×10-2Pa (20℃);折射率 nD20 1.4981;相对密度 1.116~1.118(20℃)。可与丙酮、乙醇、二甲苯混溶,能溶于石油醚,在常温下水中溶解度为0.004%。50℃以上不稳定,对酸和碱均不稳定,但对光稳定。在水及稀酸中会慢慢水解,微量水分会促进其分解,生成高毒的四乙基硫代焦磷酸酯。工业品呈棕色透明液体。
急性毒性
口服-大鼠 LD50: 66 毫克/公斤;口服-小鼠 LD50: 17 毫克/公斤
刺激数据
皮肤-兔子 500 mg 中度刺激;眼睛-兔子 100 mg 强烈刺激
可燃性危险特性
储运特性
库房通风低温干燥,与食品原料分开储运
灭火剂
砂土、干粉、泡沫
职业标准
时间加权平均容许浓度(TWA)0.1 毫克/立方米;短时间接触容许浓度(STEL)0.3 毫克/立方米
类别
农药
毒性分级
剧毒
生产方法
-
二嗪磷的合成
-
合成过程
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Diethyl phosphite production from phosphorothioate degradation with molybdenum peroxides and hydrogen peroxide in ethanol摘要:A polystyrene-supported molybdate-peroxide polymer (Mo-Y(s)) destroys phosphorothioate pesticides of the form (ArO)P( = S)(OEt)(2) in EtOH under mild oxidative (H2O2) conditions and produces a commodity organophosphate. This is the first report of a metal-based system that successfully degrades the "live" pesticides parathion, diazinon and coumaphos. In addition to the operational advantages of heterogeneous reaction chemistry, the Mo-Y(s) support degrades multiple equivalents of the pesticide in H2O2(aq). Of particular importance is the predominant production of diethyl phosphite, a commodity chemical, from diazinon degradation over Mo-Y(s) in EtOH; no toxic oxon is found. Coumaphos and parathion produce the corresponding oxon which have Delta H-double dagger (kcal/mol) of 15.4 (0.5) and 21.7 (0.8), respectively; these activation parameters are consistent with key observations found in the relative amount of coumoxon and paraoxon produced. Finally, a discrete molybdate-peroxide complex is presented as a possible solution model for this heterogeneous reaction.DOI:10.1016/j.ica.2018.08.021
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:DEINHAMMER, W.;SCHILLING, B.摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
[EN] ACC INHIBITORS AND USES THEREOF<br/>[FR] INHIBITEURS DE L'ACC ET UTILISATIONS ASSOCIÉES
-
[EN] BICYCLYL-SUBSTITUTED ISOTHIAZOLINE COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS ISOTHIAZOLINE SUBSTITUÉS PAR UN BICYCLYLE申请人:BASF SE公开号:WO2014206910A1公开(公告)日:2014-12-31The present invention relates to bicyclyl-substituted isothiazoline compounds of formula (I) wherein the variables are as defined in the claims and description. The compounds are useful for combating or controlling invertebrate pests, in particular arthropod pests and nematodes. The invention also relates to a method for controlling invertebrate pests by using these compounds and to plant propagation material and to an agricultural and a veterinary composition comprising said compounds.本发明涉及公式(I)中变量如索权和说明中所定义的自行车基取代异噻唑啉化合物。这些化合物对抗或控制无脊椎动物害虫,特别是节肢动物害虫和线虫方面具有用途。该发明还涉及一种通过使用这些化合物来控制无脊椎动物害虫的方法,以及包含所述化合物的植物繁殖材料、农业和兽医组合物。
-
[EN] AZOLINE COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS AZOLINE申请人:BASF SE公开号:WO2015128358A1公开(公告)日:2015-09-03The present invention relates to azoline compounds of formula (I) wherein A, B1, B2, B3, G1, G2, X1, R1, R3a, R3b, Rg1 and Rg2 are as defined in the claims and the description. The compounds are useful for combating or controlling invertebrate pests, in particular arthropod pests and nematodes. The invention also relates to a method for controlling invertebrate pests by using these compounds and to plant propagation material and to an agricultural and a veterinary composition comprising said compounds.本发明涉及式(I)的噁唑啉化合物,其中A、B1、B2、B3、G1、G2、X1、R1、R3a、R3b、Rg1和Rg2如权利要求和描述中所定义。这些化合物对抗或控制无脊椎动物害虫,特别是节肢动物害虫和线虫方面具有用途。该发明还涉及一种利用这些化合物控制无脊椎动物害虫的方法,以及包括所述化合物的植物繁殖材料、农业和兽医组合物。
-
Dual Pharmacophores - PDE4-Muscarinic Antagonistics申请人:Callahan James Francis公开号:US20090203657A1公开(公告)日:2009-08-13The present invention is directed to novel compounds of Formula (I) and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, pharmaceutical compositions and their use as dual chromaphores having inhibitory activity against PDE4 and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs), and thus being useful for treating respiratory diseases.本发明涉及具有式(I)的新化合物及其药用盐,药物组合物及其用作对PDE4和肌胆碱受体(mAChRs)具有抑制活性的双色素,因此可用于治疗呼吸道疾病。
-
[EN] DUAL PHARMACOPHORES - PDE4-MUSCARINIC ANTAGONISTICS<br/>[FR] PHARMACOPHORES DUALS, ANTAGONISTES DES RÉCEPTEURS MUSCARINIQUES ET INHIBITEURS DE L'ACTIVITÉ PDE4申请人:GLAXO GROUP LTD公开号:WO2009100169A1公开(公告)日:2009-08-13The present invention is directed to novel compounds of Formula's (I) - (VI), and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, pharmaceutical compositions and their use in therapy, for example as inhibitors of phosphodiesterase type IV (PDE4) and as antagonists of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs), in the treatment of and/or prophylaxis of respiratory diseases, including inflammatory and/or allergic diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, rhinitis (e.g. allergic rhinitis), atopic dermatitis or psoriasis.
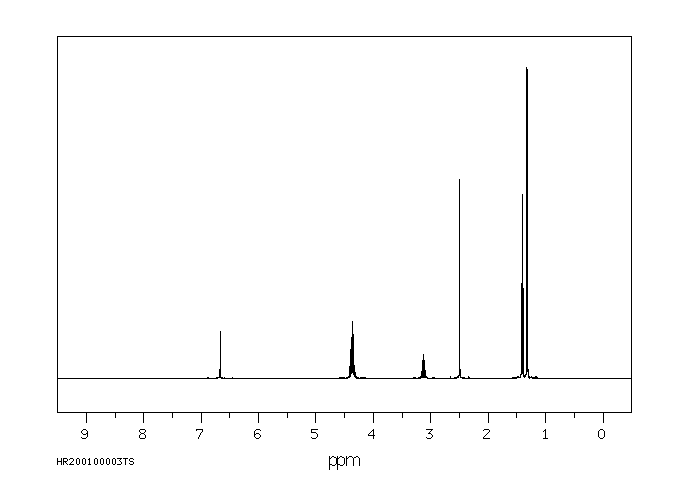
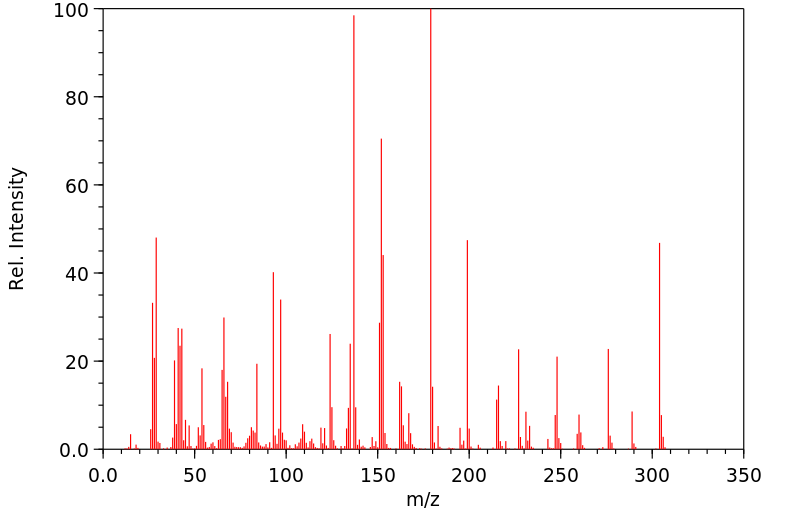
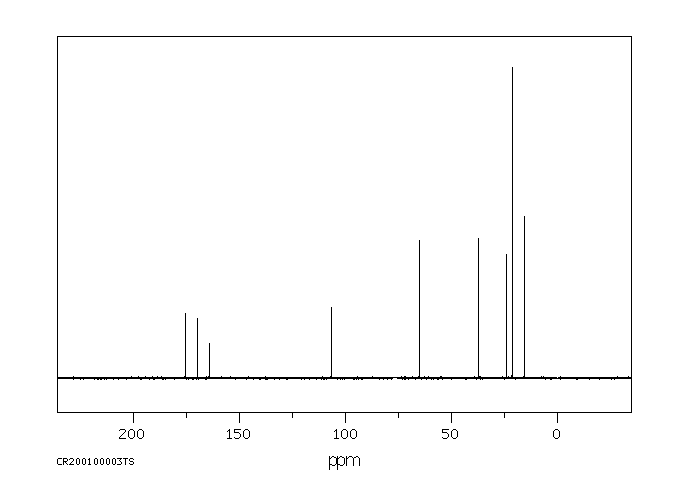
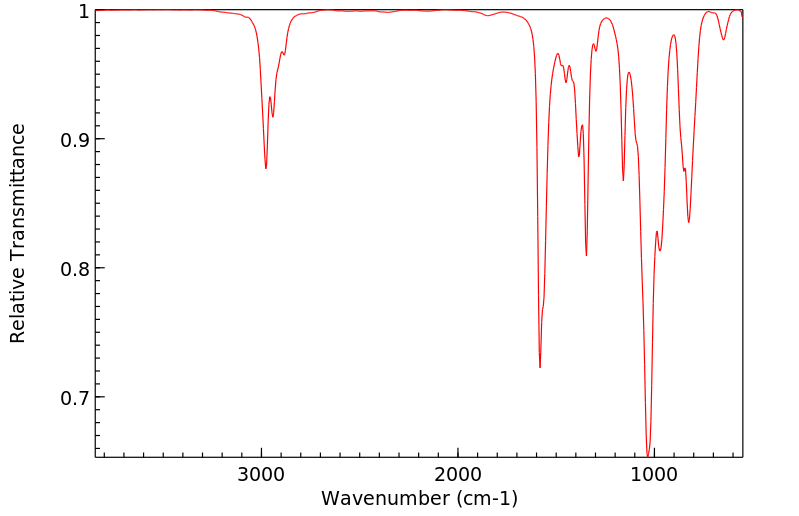
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
除线磷
锌,二[O,O-二[(9Z)-9-十八碳烯-1-基]磷二硫酸根-kS,kS']-,(T-4)-
赛灭磷
虫螨磷砜,10ΜG/ΜL于环己烷
虫螨磷亚砜,10ΜG/ΜL于环己烷
虫螨磷II
虫螨磷I
虫螨畏
虫线磷
蔬果磷
精胺
磷酸氢1,2-二[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-(4-氨基-2-羰基-嘧啶-1-基)-3,4-二羟基-四氢呋喃-2-基]乙酯磷羧酯
磷亚威
碘硫磷
硫代磷酸二氢O-甲酯
硫代磷酸三(4-苯基异氰酸酯)
硫代磷酸O-乙基O-甲基O-[3-甲基-4-(甲硫基)苯基]酯
硫代磷酸O-乙基O-异丙基O-(1,6-二氢-5-甲氧基-6-氧代-1-苯基哒嗪-4-基)酯
硫代磷酸O-(3,5-二甲基-4-硝基苯基)O,O-二甲基酯
硫代磷酸O,O-二甲基O-[4-[(乙基氨基)磺酰基]苯基]酯
硫代磷酸O,O-二甲基O-(3-异丙基-4-硝基苯基)酯
硫代磷酸O,O-二甲基O-(2-氯-4-氰基苯基)酯
硫代磷酸O,O-二乙基O-[2-[(仲-丁氧基甲基)硫代]乙基]酯
硫代磷酸O,O-二乙基O-(6-氟-2-吡啶基)酯
硫代磷酸O,O-二乙基O-(4-(1-((((二甲基氨基)羰基)氧基)亚氨基)乙基)苯基)酯
硫代磷酸O,O-二乙基O-(4-(((((二甲基氨基)羰基)氧基)亚氨基)甲基)苯基)酯
硫代磷酸O,O-二乙基O-(2-丙基-6-甲基嘧啶-4-基)酯
硫代磷酸O,O-二(4-硝基苯基)O-乙酯
硫代磷酸O,O,O-三(2-氯-1-甲基乙基)酯
硫代磷酸,O-丁基O,O-二(4-硝基苯基)酯
硫代磷酸,O-(6-甲氧基-4-嘧啶基)O,O-二甲基酯
硫代磷酸,O,O-二乙基O-(3,4,5,6-四氯-2-吡啶基)酯
硫代磷酸 O-[3-(羟基甲基)-4-硝基苯基] O,O-二甲基酯
硫代磷酸 O-[2-(乙基亚磺酰)乙基] O,O-二甲基酯
硫代磷酸 O,O-二甲基 O-(3-硝基苯基)酯
硫代磷酸 O,O-二乙基 O-[2-(乙基亚磺酰)乙基]酯
硫代磷酸 O,O-二乙基 O-(2-氯-4-硝基苯基)酯
硫代磷酸 O,O'-二异丙基酯
硫代磷酰基-苯氧基甲基(甲基肼)树枝状聚合物,1.5代
硫代磷基-pmmh-3树枝状聚合物,代1.0
皮蝇磷
甲硫涕巴
甲氧基-二(4-硝基苯氧基)-硫代膦烷
甲基立枯磷
甲基毒死蜱
甲基对硫磷
甲基增效磷
甲基嘧啶磷
甲基内吸磷
甲基1059粉剂