1,3-双(三甲基硅氧基)丙烷 | 17887-80-8
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:77°C/15mmHg(lit.)
-
密度:0.843 g/cm3
-
保留指数:1073
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.08
-
重原子数:13
-
可旋转键数:6
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:18.5
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:2
安全信息
-
危险性防范说明:P210,P264,P280,P302+P352+P332+P313+P362+P364,P305+P351+P338+P337+P313,P370+P378,P403+P235,P501
-
危险性描述:H227,H315,H319
-
储存条件:室温
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: 1,3-Bis(trimethylsilyloxy)propane
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害
易燃液体 第4级
健康危害
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 第2级
严重损伤/刺激眼睛 2A类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志
信号词 警告
危险描述 可燃液体
造成皮肤刺激
造成严重眼刺激
防范说明
[预防] 远离明火/热表面。
处理后要彻底清洗双手。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[急救措施] 眼睛接触:用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续冲洗。
眼睛接触:求医/就诊
皮肤接触:用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
脱掉被污染的衣物,清洗后方可重新使用。
[储存] 存放于通风良好处。保持凉爽。
[废弃处置] 根据当地政府规定把物品/容器交与工业废弃处理机构。
1,3-双(三甲基硅氧基)丙烷
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 1,3-双(三甲基硅氧基)丙烷
百分比: >98.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 17887-80-8
分子式: C9H24O2Si2
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,二氧化碳
不适用的灭火剂: 水(有可能扩大灾情。)
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。确保足够通风。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 用合适的吸收剂(如:旧布,干砂,土,锯屑)吸收泄漏物。一旦大量泄漏,筑堤控
制。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的法律法规废弃处置。
副危险性的防护措施 移除所有火源。一旦发生火灾应该准备灭火器。使用防火花工具和防爆设备。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止烟雾产生。远离明火和热表面。
采取措施防止静电积累。使用防爆设备。处理后彻底清洗双手和脸。
注意事项: 使用封闭系统,通风。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗、通风良好处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防毒面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
1,3-双(三甲基硅氧基)丙烷
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
液体
外形(20°C):
外观: 透明
颜色: 无色-几乎无色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 无资料
沸点/沸程 77 °C/2kPa
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 0.84
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
避免接触的条件: 明火
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 氧化硅
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
1,3-双(三甲基硅氧基)丙烷
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守
国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Ein neues Verfahren zur Überführung von Alkyl-silylethern in Alkylbromide unter schonenden Bedingungen摘要:DOI:10.1055/s-1982-29802
-
作为产物:描述:六甲基二硅氮烷 、 1,3-丙二醇 在 lithium perchlorate 、 silica gel 作用下, 以 二氯甲烷 为溶剂, 反应 0.67h, 以96%的产率得到1,3-双(三甲基硅氧基)丙烷参考文献:名称:在中性条件下使用可重复使用的高氯酸锂分散在硅胶中的高效且实用的羟基甲硅烷基化方案摘要:在室温下几分钟内,用六甲基二硅氮烷在六氯二硅氮烷上分散含有LiClO 4的硅胶表面上的多种醇,包括伯,烯丙基,苄基,仲,受阻仲,叔和苯酚的三甲基甲硅烷基化反应,非常高效,温和据报道在中性条件下产量极高。该方法还允许在存在胺和酚羟基的情况下在LP-SiO 2系统下对醇进行甲硅烷基化具有优异的选择性。DOI:10.1016/j.jorganchem.2005.11.005
-
作为试剂:描述:(2-Acetylamino-2,2-dimethyl)ethyl cis-4-furylcyclopentanone-3-carboxylate 在 1,3-双(三甲基硅氧基)丙烷 、 三氟甲磺酸三甲基硅酯 、 lithium aluminium tetrahydride 、 水 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 为溶剂, 反应 2.0h, 以55%的产率得到cis-3-(2-Furyl)-4-(hydroxymethyl)cyclopentanone参考文献:名称:铬烯基卡宾配合物与烯基恶唑啉的反应:环戊酮的非对映选择性 [3 + 2] 环化途径摘要:五羰基(烯基甲氧基)碳铬络合物 1 与缺电子烯类(如烯基噁唑啉衍生物 2)发生区域和非对映选择性的正规 [3 + 2] 环加成反应,生成环戊烷 3 和 4,顺式异构体 3 是主要的立体异构体。在适当的反应条件下,分离出环丙烷中间体 5/6,并进一步转化为 3 和 4。环加合物 3b 被有效地转化为 3,4-二取代的环戊酮 10 和 11。DOI:10.1055/s-2000-6306
文献信息
-
Functionalised bicyclic alcohols by enantioselective α-deprotonation–rearrangement of meso-epoxides†作者:David M. Hodgson、Iain D. Cameron、Martin Christlieb、Rebecca Green、Gary P. Lee、Lesley A. RobinsonDOI:10.1039/b105369h日期:——Enantioselective α-deprotonationârearrangement of achiral substituted cyclooctene oxides 7, 27 and 28 and N-Boc hexahydroazonine oxide 45 using organolithiums in the presence of (â)-sparteine 3 or (â)-α-isosparteine 4 gives the functionalised bicyclo[3.3.0]octan-2-ols 9, 29, and 32 and indolizinol 47 in 50â72% yields and 83â89% ees.
-
Silicon-29 NMR Spectra of tert-Butyldimethylsilyl and Trimethylsilyl Derivatives of Some Non-Rigid Diols作者:Magdalena Kvíčalová、Vratislav Blechta、Krzysztof Kobylczyk、Ryszard Piekos、Jan SchramlDOI:10.1135/cccc19970761日期:——
29Si NMR spectra of trimethylsilyl (TMS) and
tert -butyldimethylsilyl (TBDMS) derivatives of selected diols were measured under standardized conditions (i.e. , in diluted CDCl3 solutions). Application of the recently reported correlation between the chemical shifts in TMS and TBDMS derivatives revealed considerable and systematic deviations which exceeded experimental errors and error estimates from the correlation. Two possible explanations of the deviations are considered: interaction between the two bulky substituent groups and invalidity of the reported correlation for simple hydroxy derivatives. An independent study of analogous derivatives of monohydroxy compounds has shown that the linear correlation holds but the slope and intercept are significantly different from those reported previously on the basis of a study of amino acid derivatives. The data obtained for the diol derivatives fit the new correlation very well and no indication of an interaction between the bulky TBDMS groups was noticed. However, deviations do occur in branched diol derivatives in which branching reduces accessibility of the oxygen atoms surface to associate with proton donors. The largest deviation was found when intramolecular hydrogen bond was formed.29Si核磁共振谱测定了选定二醇的三甲基硅基(TMS)和叔丁基二甲基硅基(TBDMS)衍生物在标准化条件下(即在稀释的CDCl3溶液中)。应用最近报道的TMS和TBDMS衍生物化学位移之间的相关性显示出明显和系统性的偏差,超过了实验误差和相关性误差估计。对偏差的两种可能解释是:两个笨重取代基之间的相互作用以及对简单羟基衍生物的报道相关性的无效性。对单羟基化合物的类似衍生物的独立研究表明,线性相关性成立,但斜率和截距与以前基于氨基酸衍生物研究所报告的值显著不同。对二醇衍生物获得的数据非常符合新的相关性,没有发现叔丁基TBDMS基团之间的相互作用的迹象。然而,在支链二醇衍生物中确实存在偏差,其中支链减少了氧原子表面与质子供体结合的可及性。当形成分子内氢键时,发现最大的偏差。 -
Lewis Acid-Promoted Intermolecular Acetal-Initiated Cationic Polyene Cyclizations
-
<i>syn</i>-Selective Kobayashi Aldol Reaction Using Acetals作者:Hiroyuki Tsukada、Yuki Mukaeda、Seijiro HosokawaDOI:10.1021/ol303519y日期:2013.2.1The Kobayashi aldol reaction has been used to construct anti-aldol products by remote stereoinduction. Since the product of the Kobayashi aldol reaction has a typical polyketide structure, this reaction has been applied to the total synthesis of natural products. By varying this reaction, it was found that the reaction with acetals in the presence of Lewis acid proceeded to give syn adducts in high
-
Organoboranes. 32. Homologation of alkylboronic esters with methoxy(phenylthio)methyllithium: regio- and stereocontrolled aldehyde synthesis from olefins via hydroboration作者:Herbert C. Brown、Toshiro ImaiDOI:10.1021/ja00358a017日期:1983.9L'homologation d'alkyl-2 dioxaborinannes-1,3,2(I) en derives α-methoxyalkyl-2 (II) est realisee par reaction avec LiCH(OCH 3 )SC 6 H 5 suivie d'un traitement par HgCl 2 . Les intermediaires (II) sont oxydees par H 2 O 2 en tampon phosphate pour donner les aldehydes correspondants. Les groupes alkyles de (I) sont introduits par borhydratationL'homologation d'alkyl-2 dioxaborinannes-1,3,2(I) en衍生α-甲氧基烷基-2 (II) est realisee par反应avec LiCH(OCH 3 )SC 6 H 5 suvie d'un traitement par HgCl 2 . Les intermediaires (II) sont oxydees par H 2 O 2 en tampon phosphate pour donner les aldehydes 通讯员。Les groupesalkales de (I) sont 介绍了par borhydration
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
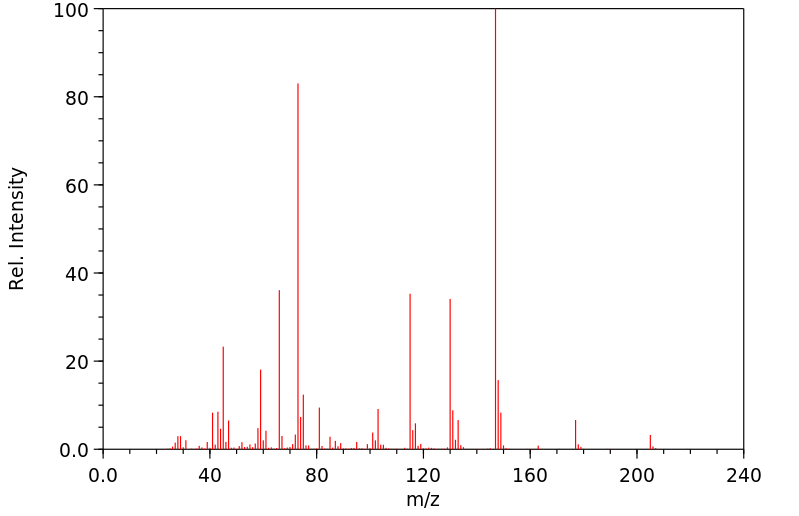
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息