苯硼酸酐 | 3262-89-3
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:217.0 to 221.0 °C
-
沸点:368.3±25.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.13±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted)
-
溶解度:溶于甲醇
-
稳定性/保质期:
在常温常压下,该物质保持稳定。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):8.95
-
重原子数:24
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:4.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:27.7
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:3
安全信息
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P301+P312,P302+P352,P304+P340,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H302,H315,H319,H335
-
储存条件:常温、避光、存放在通风干燥处。
SDS
: Triphenyl-Boroxin
产品名称
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
无数据资料
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅供科研用途,不作为药物、家庭备用药或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS分类
慢性水生毒性 (类别4)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
象形图 无
警示词 无
危险申明
H413 可能对水生生物造成长期持续有害影响。
警告申明
预防
P273 避免释放到环境中。
处理
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: C18H15B3O3
分子式
: 311.75 g/mol
分子量
组分 浓度或浓度范围
Triphenyl-Boroxin
-
CAS 号 3262-89-3
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 出示此安全技术说明书给到现场的医生看。
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如果停止了呼吸,给于人工呼吸。 请教医生。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
眼睛接触
用水冲洗眼睛作为预防措施。
食入
切勿给失去知觉者从嘴里喂食任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,耐醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物, 硼烷/氧化硼
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 人员的预防,防护设备和紧急处理程序
防止粉尘的生成。 防止吸入蒸汽、气雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。
6.2 环境保护措施
在确保安全的前提下,采取措施防止进一步的泄漏或溢出。 不要让产物进入下水道。
防止排放到周围环境中。
6.3 抑制和清除溢出物的方法和材料
收集、处理泄漏物,不要产生灰尘。 扫掉和铲掉。 存放进适当的闭口容器中待处理。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
在有粉尘生成的地方,提供合适的排风设备。一般性的防火保护措施。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 容器保持紧闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
按照良好工业和安全规范操作。 休息前和工作结束时洗手。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟) 检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
根据危险物质的类型,浓度和量,以及特定的工作场所来选择人体保护措施。,
防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和含量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
不需要保护呼吸。如需防护粉尘损害,请使用N95型(US)或P1型(EN 143)防尘面具。
呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 固体
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
无数据资料
f) 起始沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸汽压
无数据资料
l) 蒸汽密度
无数据资料
m) 相对密度
无数据资料
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
辛醇--水的分配系数的对数值: 5.066
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应的可能性
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不兼容的材料
强氧化剂
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
无数据资料
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞突变性
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 如服入是有害的。
皮肤 如果通过皮肤吸收可能是有害的。 可能引起皮肤刺激。
眼睛 可能引起眼睛刺激。
接触后的征兆和症状
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: 无数据资料
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久存留性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物蓄积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不利的影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和未回收的溶液交给处理公司。 联系专业的拥有废弃物处理执照的机构来处理此物质。
与易燃溶剂相溶或者相混合,在备有燃烧后处理和洗刷作用的化学焚化炉中燃烧
受污染的容器和包装
作为未用过的产品弃置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国(UN)规定的名称
欧洲陆运危规: 非危险货物
国际海运危规: 非危险货物
国际空运危规: 非危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 海运污染物: 否 国际空运危规: 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
模块 16. 其他信息
进一步信息
版权所有:2012 Co. LLC. 公司。许可无限制纸张拷贝,仅限于内部使用。
上述信息视为正确,但不包含所有的信息,仅作为指引使用。本文件中的信息是基于我们目前所知,就正
确的安全提示来说适用于本品。该信息不代表对此产品性质的保证。
参见发票或包装条的反面。
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
合成制备方法
- 详细步骤和方法在此处描述。
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— Boroxin, 1-(4-oxo-2-penten-2-yl)-3,5-diphenyl- —— C17H17B3O5 333.8
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Abel, E. W.; Gerrard, W.; Lappert, M. F., Journal of the Chemical Society摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:丁氧基(二苯基)硼烷 生成 苯硼酸酐参考文献:名称:Gmelin Handbuch der Anorganischen Chemie, Gmelin Handbook: B: B-Verb.9, 6.2.4, page 286 - 292摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:描述:2-(2-甲氧基乙基)吡啶 在 苯硼酸酐 、 亚磷酸三苯酯 、 甲醇 、 [ruthenium(II)(η6-1-methyl-4-isopropyl-benzene)(chloride)(μ-chloride)]2 作用下, 生成 2-(2-苯基乙基)吡啶参考文献:名称:Ruthenium-Catalyzed Conversion of sp3 C–O Bonds in Ethers to C–C Bonds Using Triarylboroxines摘要:Catalytic conversion of unreactive sp(3) C-O bonds in alkyl ethers to C-C bonds is described. Alkyl ethers bearing 2- or 4-pyridyl groups were coupled with triarylboroxines in the presence of a ruthenium catalyst. Triarylboroxines bearing a variety of functional groups including electron-withdrawing and -donating groups can be used for the reaction. No additional base was required for the coupling with the organoboron reagents, and base-sensitive groups can be tolerated. The reaction is considered to proceed via dehydroalkoxylation followed by addition of triarylboroxines to form C-C bonds.DOI:10.1021/ol2012007
文献信息
-
Room Temperature Coupling of Aryldiazoacetates with Boronic Acids Enhanced by Blue Light Irradiation作者:Amanda F. Silva、Marco A. S. Afonso、Rodrigo A. Cormanich、Igor D. JurbergDOI:10.1002/chem.201905812日期:2020.5.4visible-light-promoted photochemical protocol is reported for the coupling of aryldiazoacetates with boronic acids. This photochemical reaction shows great enhancement compared to the same protocol performed in the absence of light. Except for a few cases, the room temperature coupling in the dark (thermal process) generally does not work. When it does, it is likely to also involve free carbenes as key intermediates
-
Asymmetric Conjugate Addition of Organoboron Reagents to Common Enones Using Copper Catalysts作者:Chunlin Wu、Guizhou Yue、Christian Duc-Trieu Nielsen、Kai Xu、Hajime Hirao、Jianrong (Steve) ZhouDOI:10.1021/jacs.5b11441日期:2016.1.27Copper complexes of phosphoramidites efficiently catalyzed asymmetric addition of arylboron reagents to acyclic enones. Importantly, rare 1,4-insertion of arylcopper(I) was identified which led directly to O-bound copper enolates. The new mechanism is fundamentally different from classical oxidative addition/reductive elimination of organocopper(I) on enones.
-
Intermolecular Reductive C–N Cross Coupling of Nitroarenes and Boronic Acids by P<sup>III</sup>/P<sup>V</sup>═O Catalysis作者:Trevor V. Nykaza、Julian C. Cooper、Gen Li、Nolwenn Mahieu、Antonio Ramirez、Michael R. Luzung、Alexander T. RadosevichDOI:10.1021/jacs.8b10769日期:2018.11.14intermolecular C-N coupling is reported. The method employs a small-ring organophosphorus-based catalyst (1,2,2,3,4,4-hexamethylphosphetane) and a terminal hydrosilane reductant (phenylsilane) to drive reductive intermolecular coupling of nitro(hetero)arenes with boronic acids. Applications to the construction of both Csp2-N (from arylboronic acids) and Csp3-N bonds (from alkylboronic acids) are demonstrated;
-
A new approach to silicon rhodamines by Suzuki–Miyaura coupling – scope and limitations作者:Thines Kanagasundaram、Antje Timmermann、Carsten S Kramer、Klaus KopkaDOI:10.3762/bjoc.15.250日期:——
Background: Silicon rhodamines are of particular interest because of their advantageous dye properties (fluorescence- and biostability, quantum efficiency, tolerance to photobleaching). Therefore, silicon rhodamines find frequent application in STED (stimulated emission depletion) microscopy, as sensor molecules for, e.g., ions and as fluorophores for the optical imaging of tumors. Different strategies were already employed for their synthesis. Because of just three known literature examples in which Suzuki–Miyaura cross couplings gave access to silicon rhodamines in poor to moderate yields, we wanted to improve these first valuable experimental results.Results: The preparation of the xanthene triflate was enhanced and several boron sources were screened to find the optimal coupling partner. After optimization of the palladium catalyst, different substituted boroxines were assessed to explore the scope of the Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction.Conclusions: A number of silicon rhodamines were synthesized under the optimized conditions in up to 91% yield without the necessity of HPLC purification. Moreover, silicon rhodamines functionalized with free acid moieties are directly accessible in contrast to previously described methods.背景:硅罗丹明因其有利的染料特性(荧光和生物稳定性、量子效率、对光漂白的耐受性)而特别受到关注。因此,硅罗丹明常用于STED(受激发射耗尽)显微镜,作为例如离子和肿瘤光学成像的荧光团的传感器分子。已经采用了不同的策略来合成它们。因为在仅有的三个已知文献实例中,铃木-宫浦交叉偶联以较差到中等产率得到了硅罗丹明,我们想要改进这些初步有价值的实验结果。 结果:提高了xanthene triflate的制备,并筛选了多种硼源以找到最佳的偶联伴侣。在优化了钯催化剂之后,评估了不同的取代硼氧烷来探索钯催化的交叉偶联反应的范围。 结论:在优化的条件下合成了多种硅罗丹明,产率高达91%,无需HPLC纯化。此外,与先前描述的方法相比,带有自由酸基团的功能化硅罗丹明可以直接获得。 -
Asymmetric Catalysis in Liquid Confinement: Probing the Performance of Novel Chiral Rhodium–Diene Complexes in Microemulsions and Conventional Solvents作者:Max Deimling、Manuel Kirchhof、Barbara Schwager、Yaseen Qawasmi、Alex Savin、Tina Mühlhäuser、Wolfgang Frey、Birgit Claasen、Angelika Baro、Thomas Sottmann、Sabine LaschatDOI:10.1002/chem.201900947日期:2019.7.17studied using the 1,2‐addition of phenylboroxine (2) to N‐tosylimine 1 in the presence of [RhCl(C2H4)2]2 and chiral diene ligands as benchmark reaction. To get access to Rh complexes of different polarity, enantiomerically pure C2‐symmetric p‐substituted 3,6‐diphenylbicyclo[3.3.0]octadienes 4 and diastereomerically enriched unsymmetric norbornadienes 5 and 6 carrying either the Evans or the SuperQuat在[RhCl(C 2 H 4)2 ] 2存在下,以手性二烯配体为基准,研究了液相限制在不对称Rh催化中的作用,方法是将1,2,2-苯基环硼氧烷(2)加到N- tosylimine 1中。反应。为了获得不同极性的Rh络合物,对映体纯C 2对称的对位取代3,6-二苯基双环[3.3.0]辛二烯4和非对映体富集的不对称降冰片二烯5和6合成了携带Evans或SuperQuat辅助工具的产品。使用亲水性糖表面活性剂正辛基β- d-吡喃葡萄糖苷(C 8 G 1)配制包含等量H 2 O / KOH和甲苯/反应物的微乳液,以调解非极性反应物与KOH之间的混溶性激活Rh-二烯配合物。这种有组织的反应介质的突出特点是对温度不敏感,并且存在水和富含甲苯的隔室,通过小角度X射线散射(SAXS)证实了其区域大小为55Å。尽管双环辛二烯配体4 a,b,e在均相和微乳液条件下同样表现良好,配体4 c,d给出了不同的化学选
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
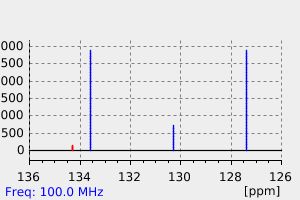
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息