扑灭津 | 139-40-2
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:212-214°C
-
沸点:368.7°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.162
-
闪点:11 °C
-
溶解度:氯仿(加热)、DMSO(少量溶解)、甲醇(少量溶解)
-
LogP:3.01 at 25℃ and pH7.1
-
物理描述:COLOURLESS CRYSTALLINE POWDER.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless powder
-
蒸汽压力:1.31X10-7 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
稳定性/保质期:
一般稳定,但在遇到强酸或强碱时会分解;温度越高,分解速度越快。
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of nitroxides and Cl-.
-
腐蚀性:NONCORROSIVE UNDER NORMAL USE CONDITIONS
-
解离常数:pKa = 1.7 at 21 °C
-
碰撞截面:155.5 Ų [M+H]+
-
保留指数:1753.88;1753.88;1767.32;1777.68;1735;1733;1733;1731.2;1728.3;1706;1739.4;1726.6;1727.4
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.9
-
重原子数:15
-
可旋转键数:4
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.666
-
拓扑面积:62.7
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:5
ADMET
安全信息
-
危险等级:9
-
危险品标志:Xn,N
-
安全说明:S16,S24,S36/37,S45,S60,S61,S7
-
危险类别码:R40,R50/53
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2933699011
-
危险品运输编号:UN 3077
-
RTECS号:XY5300000
-
储存条件:应密封保存。
SDS
| 第一部分:化学品名称 |
| 化学品中文名称: | 扑草津;2-氯-4,6-双(异丙氨基)-1,3,5-三嗪 |
| 化学品英文名称: | Propazine;2-Chloro-4,6-bis(isopropylamino)-1,3,5-triazine |
| 中文俗名或商品名: | |
| Synonyms: | |
| CAS No.: | 139-40-2 |
| 分子式: | C 9 H 16 ClN 5 |
| 分子量: | 229.75 |
| 第二部分:成分/组成信息 |
| 纯化学品 混合物 | |||
| 化学品名称:扑草津;2-氯-4,6-双(异丙氨基)-1,3,5-三嗪 | |||
|
| 第三部分:危险性概述 |
| 危险性类别: | 第6.1类毒害品 |
| 侵入途径: | 吸入 食入 |
| 健康危害: | 本品为低毒除草剂。对眼睛有刺激作用。资料报道为可疑致癌物。受热分解放出氯气和氮氧化物。 |
| 环境危害: | |
| 燃爆危险: |
| 第四部分:急救措施 |
| 皮肤接触: | 用肥皂水及清水彻底冲洗。就医。 |
| 眼睛接触: | 拉开眼睑,用流动清水冲洗15分钟。就医。 |
| 吸入: | 脱离现场至空气新鲜处。就医。 |
| 食入: | 误服者,饮适量温水,催吐。就医。 |
| 第五部分:消防措施 |
| 危险特性: | 不易燃烧。受高热分解,放出有毒的烟气。 |
| 有害燃烧产物: | |
| 灭火方法及灭火剂: | 泡沫、干粉、砂土。 |
| 消防员的个体防护: | |
| 禁止使用的灭火剂: | |
| 闪点(℃): | |
| 自燃温度(℃): | |
| 爆炸下限[%(V/V)]: | |
| 爆炸上限[%(V/V)]: | |
| 最小点火能(mJ): | |
| 爆燃点: | |
| 爆速: | |
| 最大燃爆压力(MPa): | |
| 建规火险分级: |
| 第六部分:泄漏应急处理 |
| 应急处理: | 隔离泄漏污染区,周围设警告标志,建议应急处理人员戴好防毒面具,穿化学防护服。用大量水冲洗,经稀释的污水放入废水系统。也可以用砂土吸收,铲入提桶,倒至空旷地方深埋。如大量泄漏,收集回收或无害处理后废弃。 |
| 第七部分:操作处置与储存 |
| 操作注意事项: | |
| 储存注意事项: |
| 第八部分:接触控制/个体防护 |
| 最高容许浓度: | 中 国 MAC:未制订标准前苏联MAC:5mg/m3 美国TLV—TWA:未制订标准美 |
| 监测方法: | |
| 工程控制: | 密闭操作,局部排风。 |
| 呼吸系统防护: | 可能接触其粉尘时,应该佩戴防尘口罩。紧急事态抢救或逃生时,佩戴防毒面具。 |
| 眼睛防护: | 戴化学安全防护眼镜。 |
| 身体防护: | 穿工作服。 |
| 手防护: | 必要时戴防护手套。 |
| 其他防护: | 工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作后,淋浴更衣。注意个人清洁卫生。实行就业前和定期的体检。 |
| 第九部分:理化特性 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色结晶固体。 |
| pH: | |
| 熔点(℃): | 213~214 |
| 沸点(℃): | |
| 相对密度(水=1): | |
| 相对蒸气密度(空气=1): | |
| 饱和蒸气压(kPa): | |
| 燃烧热(kJ/mol): | |
| 临界温度(℃): | |
| 临界压力(MPa): | |
| 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值: | |
| 闪点(℃): | |
| 引燃温度(℃): | |
| 爆炸上限%(V/V): | |
| 爆炸下限%(V/V): | |
| 分子式: | C 9 H 16 ClN 5 |
| 分子量: | 229.75 |
| 蒸发速率: | |
| 粘性: | |
| 溶解性: | 微溶于水。 |
| 主要用途: | 用作除草剂。 |
| 第十部分:稳定性和反应活性 |
| 稳定性: | 在常温常压下 稳定 |
| 禁配物: | 强氧化剂、强碱、强酸。 |
| 避免接触的条件: | |
| 聚合危害: | 不能出现 |
| 分解产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氮氧化物、氯化氢。 |
| 第十一部分:毒理学资料 |
| 急性毒性: | LD50:3810mg/kg(小鼠经口) LC50: |
| 急性中毒: | |
| 慢性中毒: | |
| 亚急性和慢性毒性: | |
| 刺激性: | |
| 致敏性: | |
| 致突变性: | |
| 致畸性: | |
| 致癌性: |
| 第十二部分:生态学资料 |
| 生态毒理毒性: | |
| 生物降解性: | |
| 非生物降解性: | |
| 生物富集或生物积累性: |
| 第十三部分:废弃处置 |
| 废弃物性质: | |
| 废弃处置方法: | |
| 废弃注意事项: |
| 第十四部分:运输信息 |
| |
| 危险货物编号: | 61898 |
| UN编号: | 2763 |
| 包装标志: | |
| 包装类别: | |
| 包装方法: | |
| 运输注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风仓间内。远离火种、热源。专人保管。包装密封。防止受潮和雨淋。防止阳光曝晒。应与氧化剂、酸类、碱类分开存放。不能与粮食、食物、种子、饲料、各种日用品混装、混运。操作现场不得吸烟、饮水、进 |
| RETCS号: | |
| IMDG规则页码: |
| 第十五部分:法规信息 |
| 国内化学品安全管理法规: | |
| 国际化学品安全管理法规: |
| 第十六部分:其他信息 |
| 参考文献: | 1.周国泰,化学危险品安全技术全书,化学工业出版社,1997 2.国家环保局有毒化学品管理办公室、北京化工研究院合编,化学品毒性法规环境数据手册,中国环境科学出版社.1992 3.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety,CHEMINFO Database.1998 4.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety, RTECS Database, 1989 |
| 填表时间: | 年月日 |
| 填表部门: | |
| 数据审核单位: | |
| 修改说明: | |
| 其他信息: | 6 |
| MSDS修改日期: | 年月日 |
制备方法与用途
化学名称 2-氯-4,6-双异丙胺基-1,3,5-三氮苯。纯品无色结晶,熔点为212~214℃,在20℃时蒸气压为386.6×10⁻⁸ Pa。几乎不溶于水,难溶于有机溶剂,但能从2—乙氧基乙醇和二甲基甲酰胺中重结晶。工业品纯度大于95%,在中性、弱酸或弱碱溶液中稳定,遇强酸、强碱易分解。
作用方式与机理 扑灭津为选择性内吸传导型土壤处理除草剂,作用机理与西玛津相似,内吸作用比西玛津迅速,在土壤中的移动性也比西玛津大。有一定的触杀作用,通过根系吸收后传导到叶片,抑制光合作用的希尔反应,使叶片缺绿,植株饥饿死亡。可用于玉米、高粱、谷子、果园和苗圃,防除马唐、狗尾草、稗草、早熟禾、看麦娘、藜蓼、繁缕、荠菜等杂草。在土壤中残留期长,对后茬敏感作物易发生药害。对人、畜低毒,大鼠急性口服LD₅₀>5000 mg/kg,兔急性经皮LD₅₀>10200 mg/kg。
毒性 扑灭津对大鼠的急性口服LD₅₀>7 g/kg。急性经皮LD₅₀:大鼠>3.1 g/kg,兔>10.2 g/kg。对兔皮肤和眼睛有轻微刺激。兔急性吸入LC₅₀(4小时)>2.04 mg/L空气。在130天饲喂试验中,以250 mg/kg饲料对雌、雄大鼠无影响。90天饲养无作用剂量:大鼠200 mg ai/kg饲料[13 mg/(kg·d)],狗200 mg ai/kg饲料[7 mg/(kg·d)]。鹌鹑和野鸭LC₅₀(8天)>10 g/kg。鱼毒LC₅₀(96小时):虹鳟17.5 mg/L,蓝鳃>100 mg/L,金鱼>32.0 mg/L。对蜜蜂无毒。
制备方法 在缚酸剂存在下,由三聚氯氰与两个当量的异丙胺反应制得扑灭津(图2)。
分析方法
- 用吗啉处理后定放出的HCl量;
- 用高氯酸进行电位滴定。
残留量测定
- 将扑灭净转反应为羟基衍生物后进行紫外吸收;
- 薄层色谱法和气相色谱法。
开发单位 1957年由H.Gysin等报道除草活性,1958年瑞士Ciba—Geigy Ltd.开发,1960年由J.R.Geigy S.A.(现为Novartis Crop Protection AG)推广,获有专利Swiss P 329277;BP 814947;US 2891855;BE 540947。
化学性质 纯品为无色粉末;熔点:212~214℃,蒸气压0.0039 mmHg(20℃); 密度ρ1.162 g/cm³(20℃)。溶解度:水中5.0 mg/L(20℃),苯、甲苯中6.2 g/kg(22℃),四氯化碳中2.5 g/kg。在中性、弱酸或弱碱性介质中稳定,在较强酸碱中可水解成无除草性能的羟基衍生物,温度越高水解越快,无腐蚀性。
用途 扑灭津系选择性三嗪类除草剂,芽前用于防除高粱和伞形花科作物田中的阔叶和禾本科杂草,用量0.5-3.0 kg(a.i./hm²)。适用于谷子、玉米、高粱、甘蔗、芹菜、豌豆等作物。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 阿特拉津 6-chloro-N-ethyl-N'-isopropyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine 1912-24-9 C8H14ClN5 215.686 西玛津 Simazine 122-34-9 C7H12ClN5 201.659 2,4-二氯-6-异丙基氨基-1,3,5-三嗪 2,4-dichloro-6-isopropylamino-1,3,5-triazine 3703-10-4 C6H8Cl2N4 207.062 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 阿特拉津 6-chloro-N-ethyl-N'-isopropyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine 1912-24-9 C8H14ClN5 215.686 西玛津 Simazine 122-34-9 C7H12ClN5 201.659 —— 2-(4,6-Bis-isopropylamino-[1,3,5]triazin-2-ylamino)-ethanol 125101-22-6 C11H22N6O 254.335 —— 2,4-Bisisopropylamino-6-dimethylamino-1,3,5-triazin 74150-98-4 C11H22N6 238.336 —— 2,4-Bis(isopropylamino)-6-fluor-s-triazin 2711-02-6 C9H16FN5 213.258
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:DOVLATYAN V. V.; XACHATRYAN L. A.; AMBARTSUMYAN EH. N., AJKAKAN KIMIAKAN AMSAGIR, ARM. XIM. ZH., 1979, 32, HO 7, 569-573摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:三聚氯氰 以2%的产率得到参考文献:名称:HAUSKRECHT, PETER;VAVRINEC, FERDINAND;MRAVEC, JAN;MARKUSEK, JULIUS;SVITEK+摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
[EN] 3-[(HYDRAZONO)METHYL]-N-(TETRAZOL-5-YL)-BENZAMIDE AND 3-[(HYDRAZONO)METHYL]-N-(1,3,4-OXADIAZOL-2-YL)-BENZAMIDE DERIVATIVES AS HERBICIDES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE 3-[(HYDRAZONO))MÉTHYL]-N-(TÉTRAZOL-5-YL)-BENZAMIDE ET DE 3-[(HYDRAZONO)MÉTHYL]-N-(1,3,4-OXADIAZOL-2-YL)-BENZAMIDE UTILISÉS EN TANT QU'HERBICIDES申请人:SYNGENTA CROP PROTECTION AG公开号:WO2021013969A1公开(公告)日:2021-01-28The present invention related to compounds of Formula (I): or an agronomically acceptable salt thereof, wherein Q, R2, R3, R4, R5 and R6 are as described herein. The invention further relates to compositions comprising said compounds, to methods of controlling weeds using said compositions, and to the use of compounds of Formula (I) as a herbicide.本发明涉及以下式(I)的化合物或其农业上可接受的盐,其中Q、R2、R3、R4、R5和R6如本文所述。该发明还涉及包含所述化合物的组合物,使用这些组合物控制杂草的方法,以及将式(I)的化合物用作除草剂的用途。
-
[EN] INSECTICIDAL TRIAZINONE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE TRIAZINONE INSECTICIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2013079350A1公开(公告)日:2013-06-06Compounds of the formula (I) or (I'), wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1, are useful as pesticides.式(I)或(I')的化合物,其中取代基如权利要求1所定义的那样,可用作杀虫剂。
-
[EN] HERBICIDALLY ACTIVE HETEROARYL-S?BSTIT?TED CYCLIC DIONES OR DERIVATIVES THEREOF<br/>[FR] DIONES CYCLIQUES SUBSTITUÉES PAR HÉTÉROARYLE À ACTIVITÉ HERBICIDE OU DÉRIVÉS DE CELLES-CI申请人:SYNGENTA LTD公开号:WO2011012862A1公开(公告)日:2011-02-03The invention relates to a compound of formula (I), which is suitable for use as a herbicide wherein G is hydrogen or an agriculturally acceptable metal, sulfonium, ammonium or latentiating group; Q is a unsubstituted or substituted C3-C8 saturated or mono-unsaturated heterocyclyl containing at least one heteroatom selected from O, N and S, or Q is heteroaryl or substituted heteroaryl; m is 1, 2 or 3; and Het is an optionally substituted monocyclic or bicyclic heteroaromatic ring; and wherein the compound is optionally an agronomically acceptable salt thereof.
-
Molecules having pesticidal utility, and intermediates, compositions, and processes, related thereto申请人:Dow AgroSciences LLC公开号:US20180279612A1公开(公告)日:2018-10-04This disclosure relates to the field of molecules having pesticidal utility against pests in Phyla Arthropoda, Mollusca, and Nematoda, processes to produce such molecules, intermediates used in such processes, pesticidal compositions containing such molecules, and processes of using such pesticidal compositions against such pests. These pesticidal compositions may be used, for example, as acaricides, insecticides, miticides, molluscicides, and nematicides. This document discloses molecules having the following formula (“Formula One”).
-
[EN] NOVEL HERBICIDES<br/>[FR] NOUVEAUX HERBICIDES
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
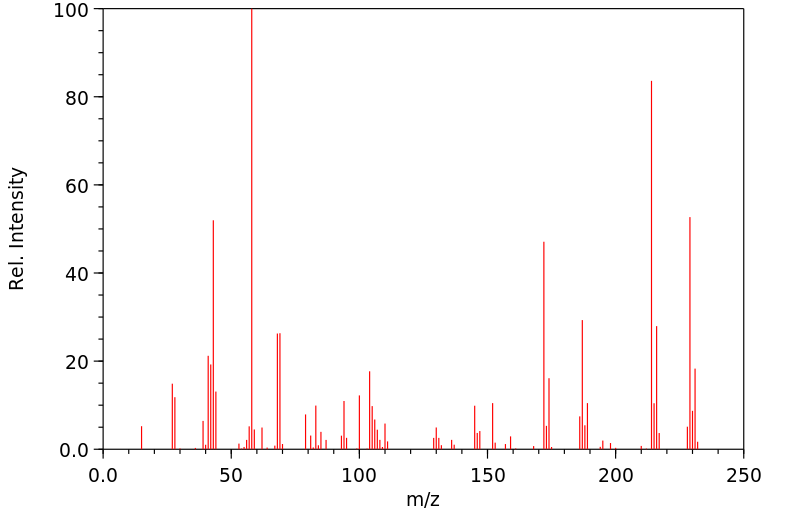
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
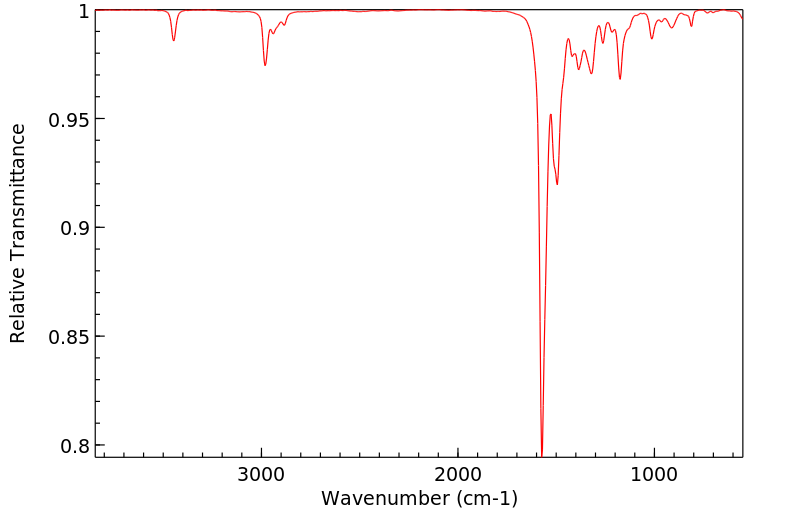
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息