N-cyclohexyl-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazol-2-amine | 56242-66-1
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
N-cyclohexyl-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazol-2-amine
英文别名
2-cyclohexylimino-2-thiazolidine;2-Cyclohexylamino-2-thiazoline;cyclohexyl-(4,5-dihydro-thiazol-2-yl)-amine;Cyclohexyl-(4,5-dihydro-thiazol-2-yl)-amin
CAS
56242-66-1
化学式
C9H16N2S
mdl
MFCD00726597
分子量
184.305
InChiKey
SGMNKDCGMQDDCB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2
-
重原子数:12
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.888
-
拓扑面积:49.7
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:2
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:N-cyclohexyl-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazol-2-amine 在 亚硝酸丁酯 、 sodium methylate 作用下, 以 乙醚 为溶剂, 以73%的产率得到2-(cyclohexylimino)-3-nitrosothiazolidine参考文献:名称:Rao, K. V.; Nizar, P. N. H.; Chauhan, S. M. S., Indian Journal of Chemistry - Section B Organic and Medicinal Chemistry, 1985, vol. 24, p. 974 - 976摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Hirashima, Akinori; Yoshii, Yutuka; Eto, Morifusa, Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 1991, vol. 55, # 10, p. 2537 - 2546摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
Beitrag zur Synthese und Umlagerung 1-substituierter Thiocarbamyläthylenimine in N-substituierte Derivate des 2-Amino-2-thiazolins. 5. Mitteilung: Zur Chemie der substituierten Thiosemicarbazide und Thioharnstoffe作者:M. TišlerDOI:10.1002/ardp.19582910906日期:——
-
Stereoelectronic control in the aqueous decomposition of novel nitrosothioureas作者:J. William Lown、Shive M. S. ChauhanDOI:10.1021/jo00170a006日期:1983.11
-
New 2-Aminothiazoline derivatives lower blood pressure of spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) via I1-imidazoline and alpha-2 adrenergic receptors activation作者:Renan B. Ferreira、Mariana G. de Oliveira、Edson Antunes、Wanda P. Almeida、Badr M. Ibrahim、Abdel A. Abdel-RahmanDOI:10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.10.009日期:2016.112-Aminothiazolines share an isosteric relationship with imidazolines and oxazolines with antihypertensive activity mainly mediated by the imidazoline I-1-receptor. In the present work, we have prepared five aminothiazolines, following a previously described synthetic pathway. Aminothiazolines derived from dicyclo-propylmethylamine (ATZ1) and cyclohexylamine (3) are unprecedented in the literature. Competitive radioligand assay was carried out with all synthetic compounds, and the I-1 receptor affinity in comparison to rilmenidine in PC12 cells was determined. Surprisingly, the rilmenidine isoster (ATZ1) showed no I-1-receptor interaction. Diethyl (ATZ4) and 2-ethyl-hexylamine (ATZ5) derivatives bind to the receptor with 11.98 and 10.94 nmol/l, respectively. These compounds were selected for in vivo experiments. Both compounds reduced the blood pressure of spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). The hypotensive effect of these compounds was abrogated in the presence of a(2) adrenergic (yohimbine) and I-1 (efaroxan) receptor antagonists suggesting that both aminothiazolines bind to the adrenergic and imidazoline receptors. Lipinski's descriptors of the synthesized aminothiazolines were calculated and are similar to the known imidazoline I-1 receptor ligands. 3D-Similarity between ATZ5 and agmatine, the natural imidazoline receptor ligand, was also observed.
-
LOWN, J. W.;CHAUHAN, S. M. S., J. ORG. CHEM., 1983, 48, N 22, 3901-3908作者:LOWN, J. W.、CHAUHAN, S. M. S.DOI:——日期:——
-
RAO K. V.; NIZAR P. N. H.; CHAUHAN S. M. S., INDIAN J. CHEM., 24,(1985) N 9, 974-976作者:RAO K. V.、 NIZAR P. N. H.、 CHAUHAN S. M. S.DOI:——日期:——
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
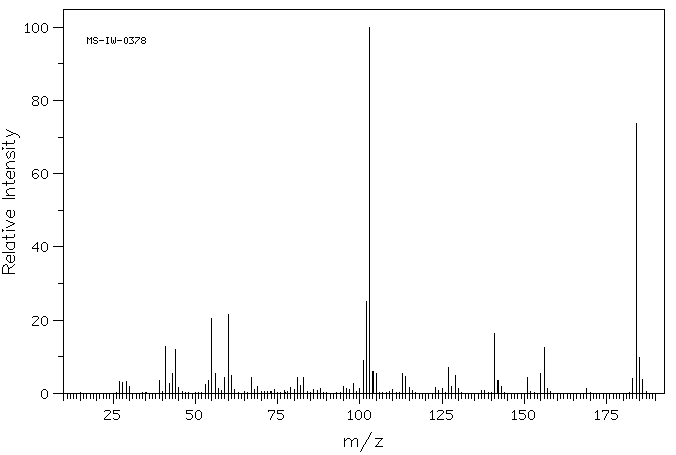
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
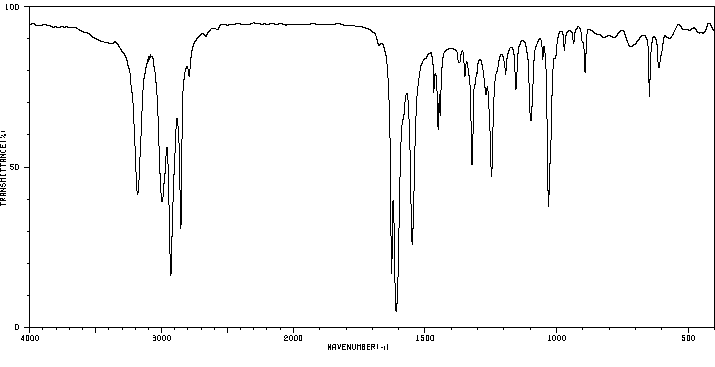
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(4S,4''S)-2,2''-环亚丙基双[4-叔丁基-4,5-二氢恶唑]
香豆素-6-羧酸
顺式-3a,5,6,6a-四氢-3-(1-甲基乙基)-4H-环戊二烯并[d]异恶唑
锌离子载体IV
钐(III) 离子载体 II
苯,1-(2E)-2-丁烯-1-基-2-氟-
苯,(2,2-二氟乙烯基)-
聚二硫二噻唑烷
缩胆囊肽9
绕丹酸钠
盐(1:?)5'-尿苷酸,钠
甲酰乙内脲
甲巯咪唑
甲基羟甲基油基噁唑啉
甲基5-羟基-3,5-二甲基-4,5-二氢-1H-吡唑-1-羧酸酯
甲基5-甲基-4,5-二氢-1H-吡唑-3-羧酸酯
甲基5-甲基-4,5-二氢-1H-吡唑-1-羧酸酯
甲基5-氰基-4,5-二氢-1,2-恶唑-3-羧酸酯
甲基5-乙炔基-4,5-二氢-1H-吡唑-3-羧酸酯
甲基5-(羟基甲基)-4,5-二氢-1,2-恶唑-3-羧酸酯
甲基4-甲基-5-氧代-4,5-二氢-1H-吡唑-3-羧酸酯
甲基4-甲基-4,5-二氢-1H-吡唑-3-羧酸酯
甲基4-乙炔基-4,5-二氢-1H-吡唑-3-羧酸酯
甲基4,5-二氮杂螺[2.4]庚-5-烯-6-羧酸酯
甲基4,5-二氢-5-乙基-1H-吡唑-1-羧酸酯
甲基3-甲基-4,5-二氢-1,2-恶唑-4-羧酸酯
甲基(E)-3-[6-[1-羟基-1-(4-甲基苯基)-3-(1-吡咯烷基)丙基]-2-吡啶基]丙烯酰酸酯
甲基(5-氧代-4,5-二氢-1,2-恶唑-3-基)乙酸酯
环戊二烯并[d]咪唑-2,5(1H,3H)-二硫酮
环己羧酸,3-氨基-2-甲氧基-,甲基酯,(1S,2S,3S)-
溶剂黄93
溴化1-十六烷基-3-甲基咪唑
溴化1-十二烷基-2,3-二甲基咪唑
泰比培南酯中间体
泰比培南酯中间体
氨甲酸,[4,5-二氢-4-(碘甲基)-2-噻唑基]-,1,1-二甲基乙基酯(9CI)
氨基甲硫酸,[2-[[(2-羰基-1-咪唑烷基)硫代甲基]氨基]乙基]-,O-甲基酯
异噻唑,4,5-二氯-2,5-二氢-2-辛基-
希诺米啉
四氟硼酸二氢1,3-二(叔-丁基)-4,5--1H-咪唑正离子
四唑硝基紫
噻唑烷-2,4-二酮-2-缩氨基脲
噻唑丁炎酮
噻唑,4,5-二氢-4-(1-甲基乙基)-,(S)-
噁唑,4,5-二氢-4,4-二甲基-2-(5-甲基-2-呋喃基)-
噁唑,2-庚基-4,5-二氢-
咪唑烷基脲
吡嗪,2,3-二氢-5,6-二甲基-2-丙基-
叔-丁基3-羟基-1,4,6,7-四氢吡唑并[4,3-c]吡啶-5-羧酸酯
双吡唑啉酮