Octamethyltrigermane | 1066-63-3
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
Octamethyltrigermane
英文别名
Octamethyl-trigermanium;Octamethyltrigerman
CAS
1066-63-3
化学式
C8H24Ge3
mdl
——
分子量
338.049
InChiKey
GUYRXJZRUPMNEF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:43-45 °C(Press: 0.05 Torr)
-
密度:1.2311 g/cm3
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.53
-
重原子数:11.0
-
可旋转键数:2.0
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:0.0
-
氢给体数:0.0
-
氢受体数:0.0
安全信息
-
海关编码:2931900090
SDS
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— dimethylgermanium,trimethylgermanium 14938-41-1 C10H30Ge4 440.708
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:光诱导的电子转移引发的过甲基低聚锗烷中锗-锗键的氯化裂解摘要:在9,10-二氰基蒽(DCA)存在下,在CCl 4 -CH 3 CN中辐照过甲基低聚锗烷Me(Me 2 Ge)n Me(n = 2-5)。得到相应的氯锗烷和六氯乙烷。DCA的荧光被寡聚体以扩散控制的速率淬灭。提出了一种涉及寡锗烷阳离子自由基和DCA阴离子自由基的自由基氯化方法,用于锗-锗的裂解。DOI:10.1016/s0022-328x(98)00709-8
-
作为产物:描述:Hexamethyldigermane 、 7,7-dimethyl-1,4,5,6-tetraphenyl-2,3-benzo-7-germanorbornadiene 以 neat (no solvent) 为溶剂, 以7%的产率得到Octamethyltrigermane参考文献:名称:苯基五甲基二锗烷的光化学摘要:苯基五甲基二锗烷的光解得到氢锗烷和二锗烷,作为主要产物。它们来源于锗-锗键的光诱导均裂产生的两个锗基自由基。显示出二甲基锗烯也在光解中析出。DOI:10.1246/cl.1988.1089
文献信息
-
Photochemical Reactions of Vinyl-, Styryl-, and Benzyl- Substituted Digermanes作者:Kunio Mochida、Haruhiko Kikkawa、Yasuhiro NakadairaDOI:10.1246/bcsj.64.2772日期:1991.9reactions of vinyl-, styryl-, and benzyl-substituted digermanes were investigated by chemical trapping experiments. Photolysis of vinylpentamethyldigermane afforded 1-trimethyl-2-(pentamethyldigermyl)ethane as a major product, and styrylpentamethyldigermanes gave mainly styryltrimethylgermane. On the other hand, photolysis of benzyl-substituted digermanes (benzylpentamethyldigermane and 1,2-dibenzyltetramethyldigermane)
-
Photochemical reactions of aryl-substituted catenates of group 4B elements, PhMe2EE'Me3 (E, E' Si and Ge). Formation of a radical pair作者:Kunio Mochida、Haruhiko Kikkawa、Yasuhiro NakadairaDOI:10.1016/0022-328x(91)86036-p日期:1991.7reactions of phenyl substituted catenates of group 4B elements, PhMe2EE'Me2 (E,E' Si and Ge) have been investigated by chemical trapping experiments and lase flash-photolysis. On irradiation, the phenylated group 4B catenate undergoes E bond homolysis to give a pair of radicals (PhMe2E. and Me3'.). In CCl4, these radicals are converted to the corresponding chlorides by abstraction of a chlorine atom.4B族元素的苯基取代的catenates光化学反应,的PhMe 2 EE'Me 2(E,E”Si和Ge)已经通过化学捕集实验和LASE闪光光解的影响。上照射下,苯基化组4B链状经历E键均裂,得到一对基团(的PhMe 2 ë 。和Me 3 ' 。)。在CCl 4中,这些自由基通过提取氯原子而转化为相应的氯化物。在一个nohalogenated溶剂,自由基一对夫妇在苯基的配对自由基(PhMe中的的本位位置2 ë 。)以产生相应的双基。这可以消除二价物种(Me 2 E :)并伴有三甲基苯基4B元素(PhMe 2 E')的形成,也可以通过分子内1,2-4B元素的迁移形成4B金属-碳双键物种。自由基从与自由基的金属原子偶联的溶剂笼中逸出,从而生成双金属产物。所观察到的反应路径高度依赖于包含苯基取代的catenate的4B族元素的性质。
-
Köcher, Jürgen; Lehnig, Manfred; Neumann, Wilhelm P., Organometallics, 1988, vol. 7, # 5, p. 1201 - 1207作者:Köcher, Jürgen、Lehnig, Manfred、Neumann, Wilhelm P.DOI:——日期:——
-
Nakadaira, Yasuhiro; Zhou, Da-Yang; Kako, Masahiro, Nippon Kagaku Kaishi/Journal of the Chemical Society of Japan作者:Nakadaira, Yasuhiro、Zhou, Da-Yang、Kako, Masahiro、Mochida, KunioDOI:——日期:——
-
Charge-transfer spectra of permethylated polygermanes-TCNE to afford 1:1 adducts作者:Kunio Mochida、Chikako Hodota、Rieko Hata、Shunichi FukuzumiDOI:10.1021/om00026a052日期:1993.2Charge-transfer spectra of permethylated polygermane-tetracyanoethylene (TCNE) complexes were observed. The frequency of charge-transfer spectra was linearly related to ionization potentials (or electrochemical oxidation potentials) of the polygermanes. Polygermanes inserted into TCNE to afford 1:1 adducts under mild conditions.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
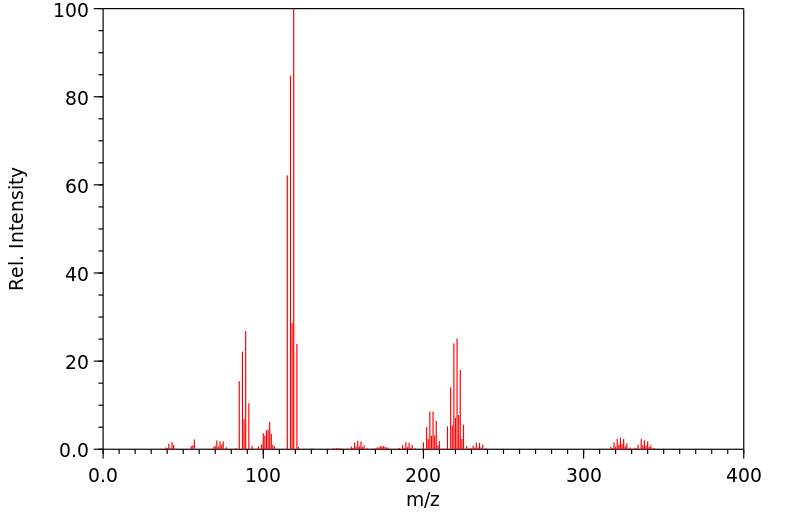
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
黄原酸环癸酯
高纯三甲基锑
顺式-二氯二(环丙胺)铂(II)
顺式-二氯二(乙二胺)氯化铑(1+)
顺式-二(环己基丁氨合)二氯铂(II)
顺式-二(异丙基氨合)二氯铂(II)
顺式-(2-氨基甲基-1-环戊基氨合)二氯铂(II)
顺二氯二羰基铂(II)
顺-二氯双(乙二胺)氯化铱
雷(酸)汞[含水或水加乙醇≥20]
间碳硼烷-9-硫醇
镍,加合(7:2)钪
镉二(二戊基二硫代氨基甲酸盐)
镁,溴-6-庚烯基-
manganese carbide
butyl manganese bromide
锡烷,氯二环己基-
锡四丁醇
锑,(1:1)混合物和钪
锌叔-丁氧化物
锌,溴-1-丙烯基-,(E)-
锇,加合(2:1)钪
锆酸四丁酯
锂丁酯
锂4-异丙氧基-2-甲基-丁烷-2-醇
锂1-丁醇
锂(三氟甲基)乙炔化物
锂(3-氨基丙基)酰胺
铼五羰基碘化物
铼五羰基
银(I)2-羟基乙烷-1-硫醇盐
铯三氯三羰基锇
铬三乙二胺
铬,五羰基(环己胺)-,(OC-6-22)-
铬,二(乙酰腈)二氯-
铝,加合(3:1)钪
铜-乙二胺络合物
铜(II)乙二胺
铜(I)乙炔化物
铍,环戊-1,3-二烯,溴化
铊N,N-二正丁胺
铊,甲氧基二甲基-
铂(2+)二氯化3-甲基丁烷-1,2-二胺(1:1)
铁(3+)三(1-丁醇)
铁(2+)1,1'-(硫烷二基二-1,1-乙二基)二-2,4-环戊二烯化
铀,三甲基-
钾,[三(三甲基甲硅烷基)甲基]-
钴四异硫氰酸酯
钴,乙烷-1,2-二胺
钠辛基二硫代氨基甲酸酯