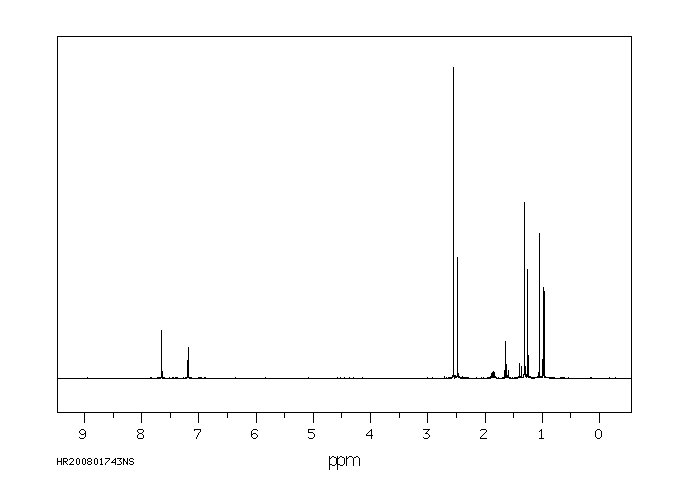
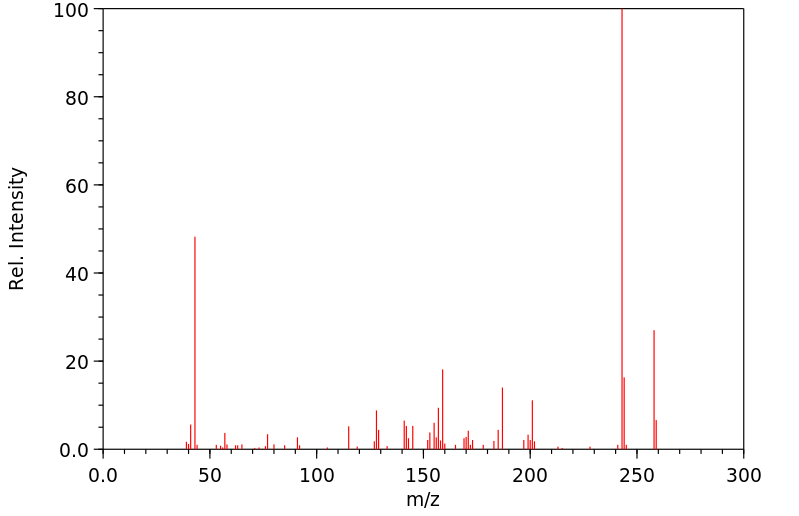
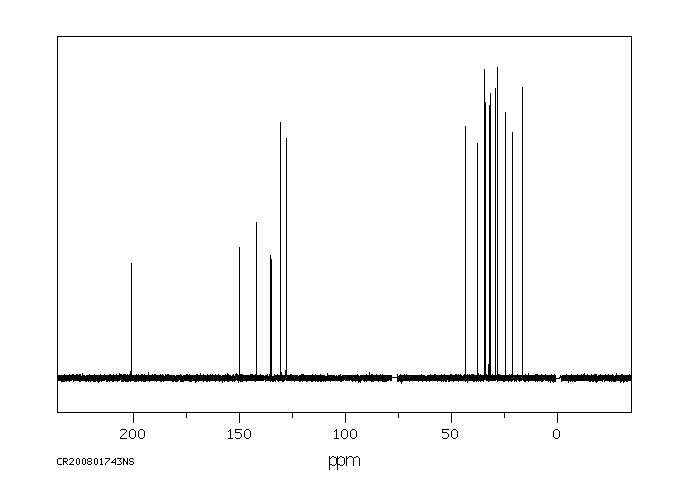
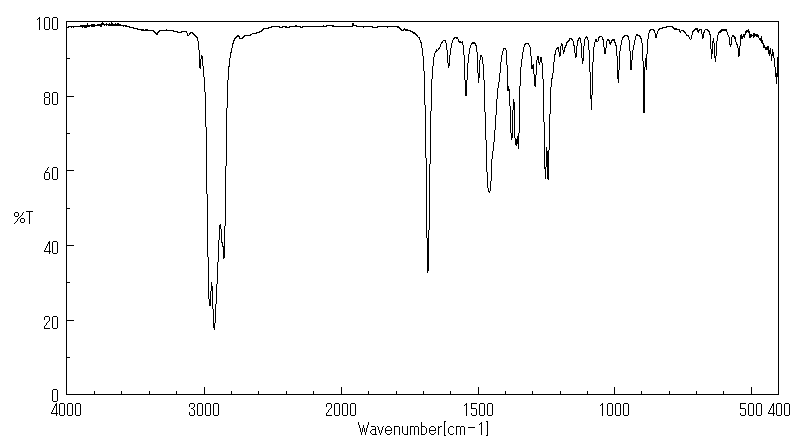
代谢
AHTN的三个色原性产物在光氧化后被检测到,并且显示与甘氨酸或白蛋白反应,首先产生蓝色,然后是粉色,最后是深绿色。与晚期绿色相关的吸收光谱显示,在光谱的长波长区域吸光度增加,类似于从AHTN处理动物的肝脏中提取的绿色。AHTN的色原性衍生物和邻二乙酰苯(一种模型色原性化合物)产生的颜色紧密地结合在蛋白质沉淀上,并且对酸性pH有抗性,与尼氏反应产生的颜色不同。通过给大鼠喂食AHTN在肝脏中产生的深绿色也紧密地结合在蛋白质上,并且在酸性pH下稳定。这些结果表明,AHTN的光氧化色原性衍生物和邻二乙酰苯通过与氨基酸和蛋白质反应产生有色衍生物的机制与尼氏反应无关。它们还表明,在长期使用高剂量AHTN治疗期间体内产生的AHTN的色原性衍生物可能是治疗动物肝脏和其他组织绿色的原因。数据表明,AHTN衍生的色原性物质与代谢物相关,而不是代表毒性过程...
Three chromogenic products of AHTN have been detected after photo-oxidation and shown to react with glycine or albumin, giving rise first to a blue color, followed by pink and, finally, a dark green color. The absorption spectrum associated with the late green color showed an increased absorbance in the long wavelength region of the spectrum, similar to the green color extracted from the liver of AHTN-treated animals. The color produced by the chromogenic derivatives of AHTN and by o-diacetylbenzene (a model chromogenic compound) were tightly bound to the protein pellet and resistant to acidic pH, unlike the color from the ninhydrin reaction. The dark green colour produced in the liver by feeding AHTN to rats was also tightly bound to proteins and stable to acidic pH. These results suggest that both the photo-oxidized chromogenic derivatives of AHTN and o-diacetylbenzene, produce colored derivatives with amino acids and proteins by a mechanism unrelated to ninhydrin. They also suggest that a chromogenic derivative of AHTN, produced in vivo during prolonged treatment with high doses of AHTN, may be responsible for the green color of the livers and other tissues from treated animals. The data suggest that the AHTN-derived chromogenic material is metabolite-related rather than representative of a toxic process ...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)