间二甲苯 | 108-38-3
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-48 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:138-139 °C (lit.)
-
密度:0.868 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
-
蒸气密度:3.7 (vs air)
-
闪点:77 °F
-
溶解度:与许多有机溶剂混溶,包括乙醇和乙醚
-
介电常数:2.3999999999999999
-
暴露限值:NIOSH REL: 100 ppm (435 mg/m3), STEL 150 ppm (655 mg/m3), IDLH 900 ppm; OSHA PEL: TWA 100 ppm; ACGIH TLV: TWA 100 ppm, STEL 150 ppm (adopted).
-
LogP:3.16 at 20℃
-
物理描述:M-xylene appears as a colorless watery liquid with a sweet odor. Less dense than water. Insoluble in water. Irritating vapor. (USCG, 1999)
-
颜色/状态:Clear, colorless liquid
-
气味:Sweet odor
-
味道:Taste threshold: 0.3 ppm
-
蒸汽密度:3.66 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:8.29 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:Henry's Law constant = 7.18X10-3 atm-cu m/mole at 25 °C
-
大气OH速率常数:2.36e-11 cm3/molecule*sec
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
自燃温度:982 °F (527 °C)
-
分解:Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions - Carbon oxides.
-
粘度:0.581 mPa.s at 25 °C
-
腐蚀性:No reaction with common materials
-
燃烧热:-17,554 Btu/lb = -9752.4 cal/g = -408.31X10+5 J/kg
-
汽化热:42.65 kJ/mol at 25 °C; 35.66 kJ/mol at 139.07 °C
-
表面张力:28.47 dynes/cm at 25 °C
-
电离电位:8.56 eV
-
气味阈值:Odor Threshold Low: 0.05 [mmHg]; Odor threshold from CHRIS
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.4973 at 20 °C/D
-
相对蒸发率:Evaporation rate: 9.2 (Ether = 1)
-
保留指数:853.2 ;853.2 ;859.4 ;838 ;863 ;848.2 ;849 ;847 ;847 ;855.5 ;879.49 ;844.6 ;850.2 ;853.8 ;855.4 ;854 ;852.91 ;853.44 ;854 ;853.38 ;853.85 ;853 ;861 ;871 ;853.96 ;850.24 ;852.98 ;854.72 ;852 ;848.4 ;850.5 ;852.1 ;852.3 ;855.2 ;856.7 ;859 ;863 ;856.77 ;865.05 ;876 ;876 ;876 ;863.3 ;871.2 ;855.9 ;856.1 ;856.4 ;856.4 ;856.6 ;858 ;857 ;857 ;867 ;867 ;856 ;865.3 ;865.8 ;866.2 ;865.2 ;866 ;866 ;866 ;865 ;865 ;866 ;866 ;862 ;868 ;880 ;862 ;866 ;866 ;867 ;867 ;856.1 ;856.6 ;859.6 ;864 ;876 ;867 ;871 ;877 ;852 ;866.6 ;871.1 ;876.6 ;859 ;861 ;863 ;864 ;859 ;864 ;864 ;863 ;882 ;886 ;857.8 ;861 ;859 ;860 ;877 ;864 ;856.2 ;851 ;853 ;860 ;866 ;859.9 ;862.6 ;855 ;849 ;848 ;864 ;856.6 ;847.12 ;855.7 ;856 ;866 ;864 ;864.9 ;846.4 ;860 ;857 ;853.2 ;863.2 ;864.2 ;863 ;854 ;856 ;865 ;869 ;871 ;860 ;866 ;866 ;866 ;866 ;867 ;855 ;866 ;863 ;855 ;856 ;866 ;867 ;870 ;871 ;860 ;848 ;851 ;851 ;869 ;871 ;856 ;857 ;852 ;852 ;866 ;849 ;845 ;852 ;863 ;852 ;853 ;849 ;852 ;854 ;858 ;864 ;853 ;858 ;863 ;854 ;871 ;860 ;874 ;874 ;853.2 ;857.6 ;870
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.2
-
重原子数:8
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.25
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
ADMET
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:A
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 100 ppm (435 mg/m3), STEL: 150 ppm (655 mg/m3)
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S16,S25,S36/37,S45,S7
-
危险类别码:R20/21,R10,R36/38
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:2902420000
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1307 3/PG 3
-
危险类别:3
-
RTECS号:ZE2275000
-
包装等级:II
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS07,GHS08
-
危险性描述:H226,H304,H312 + H332,H315,H319,H335,H412
-
危险性防范说明:P210,P261,P280,P301 + P310,P305 + P351 + P338,P370 + P378
-
储存条件:储存注意事项: - 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。 - 远离火种、热源,库温不宜超过37℃。 - 保持容器密封,并与氧化剂分开存放,切忌混储。 - 使用防爆型照明和通风设施,禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。 - 储区应备有泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。
SDS
| 国标编号: | 33535 |
| CAS: | 108-38-3 |
| 中文名称: | 1,3-二甲苯 |
| 英文名称: | 1,3-xylene;p-xylene |
| 别 名: | 间二甲苯 |
| 分子式: | C 8 H 10 ;C 6 H 4 (CH 3 ) 2 |
| 分子量: | 106.17 |
| 熔 点: | -47.9℃ |
| 密 度: | 相对密度(水=1)0.86; |
| 蒸汽压: | 25℃ |
| 溶解性: | 不溶于水,可混溶于乙醇、乙醚、氯仿等多数有机溶剂 |
| 稳定性: | 稳定 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色透明液体,有类似甲苯的气味 |
| 危险标记: | 7(易燃液体) |
| 用 途: | 用作溶剂,医药、染料中间体、香料等 |
2.对环境的影响:
一、健康危害
侵入途径:吸入、食入、经皮吸收。 健康危害:二甲苯对眼及上呼吸道有刺激作用,高浓度时对中枢神经系统有麻醉作用。 急性中毒:短期内吸入较高浓度核武器中可出现眼及上呼吸道明显的刺激症状、眼结膜及咽充血、头晕、恶心、呕吐、胸闷、四肢无力、意识模糊、步态蹒跚。重者可有躁动、抽搐或昏迷,有的有癔病样发作。 慢性影响:长期接触有神经衰弱综合征,女工有月经异常,工人常发生皮肤干燥、皲裂、皮炎。
二、毒理学资料及环境行为
毒性:属低毒类。 急性毒性:LD505000mg/kg(大鼠经口);14100mg/kg(兔经皮) 刺激性:家兔经皮开放性刺激实验:10µg(24小时),重度刺激。 生殖毒性:大鼠吸入最低中毒浓度(TDL0):3000mg/m3,24小时(孕7~4天用药),对胚泡植入前的死亡率、胎鼠肌肉骨骼形态有影响,有胚胎毒性。
污染来源:二甲苯是重要的化工原料,有机合成、合成橡胶、油漆和染料、合成纤维、石油加工、制药、纤维素等生产工厂的废水废气,以及生产设备不密封和车间通风换气,是环境中二甲苯的主要来源。运输、贮存过程中的翻车、泄漏,火灾也会造成意外污染事故。 代谢和降解:在人和动物体内,吸入的二甲苯除3%~6%被直接呼出外,二甲苯的三种异构体都有代谢为相应的苯甲酸(60%的邻-二甲苯、80%~90%的间、对-二甲苯),然后这些酸与葡萄糖醛酸和甘氨酸起反应。在这个过程中,大量邻-苯甲酸与葡萄粮醛酸结合,而对-苯甲酸必乎完全与甘氨酸结合生成相应的甲基马尿酸而排出体外。与此同时,可能少量形成相应的二甲苯酚(酚类)与氢化2-甲基-3-羟基苯甲酸(2%以下)。 残留与蓄积:在职业性接触中,二甲苯主要经呼吸道进入身体。对全部二甲苯的异构体而言,由肺吸收其蒸气的情况相同,总量达60%~70%,在整个的接触时期中,这个吸收量比较恒定。二甲苯溶液可经完整皮肤以平均吸收率为2.25µg/(cm3·min)(范围0.7~4.3µg/(cm3·min))被吸收,二甲苯蒸气的经皮吸收与直接接触液体相比是微不足道的。二甲苯的鲍留和蓄积并不严重,上面我们已经说过进入人体的二甲苯,可以在人体的NADP(转酶II)和NAD(转酶I)存在下生成甲基苯甲酸,然后与甘氨酸结合形成甲基马尿酸在18小时内几乎全部排出体外。即使是吸入后残留在肺部的3%~6%的二甲苯,也在接触后的3小时内(半衰期为0.5~1小时)全部被呼出体外。评价接触二甲苯的残留试验,主要是测定尿内甲基马尿酸的含量,也有人建议测定咱出气体中或血液中二甲苯的含量,但后者的结果往往并不准确。由于甲基马尿酸并不天然存在于尿中,又由于它几乎是全部滞留的二甲苯代谢物,因而测定它的存在是最好的二甲苯接触试验的确证。二甲苯能相当持久地存在于饮水中。自来水中二甲苯的浓度为5mg/L时,其气味强度相当于5级,二甲苯的特有气味则要过7至8天才能消失;气味强度为3级时则需4至5天。河水中二甲苯的气味保持的时间较短,这与起始浓度的高低有关,一般可保留3至5天。 迁移转化:二甲苯主要由原油在石油化工过程中制造,它广泛用于颜料、油漆等的稀释剂,印刷、橡胶、皮革工业的溶剂。作为清洁剂和去油污剂,航空燃料的一种成分,化学工厂和合成纤维工业的原材料和中间物质,以及织物的纸张的涂料和浸渍料。二甲苯可通过机械排风和通风设备排入大气而造成污染。一座精炼油厂排放入大气的二甲苯高达13.18~1145g/h,二甲苯可随其生产和使用单位所排入的废水进入水体,生产1吨二甲苯,一般排出含二甲苯300~1000mg/L的废水2立方米。由于二甲苯在水溶液中挥发的趋势较强,因此可以认为其在地表水中不是持久性的污染物。二甲苯在环境中也可以生物降解,但这种过程的速度比挥发过程的速率低得多。挥发到空中的二甲苯也可能被光解,这是它的主要迁移转化过程。二甲苯由呼气和代谢物从人体排出的速度很快,在接触停止18小时内几乎全部排出体外,二甲苯能相当持久的存在于饮水中。由于二甲苯在水溶液中挥发性较强,因此,可以认为其在地表水中不是持久性污染物。二甲苯在环境中也可以生物降解和化学降解,但其速度比挥发低得多,挥发到空气中的二甲苯可被光解。可与氧化剂反应,高浓度气体与空气混合发生爆炸。二甲苯有中等程度的燃烧危险。由于其蒸气比空气重,燃烧时火焰沿地面扩散。二甲苯易挥发,发生事故现场会弥漫着二甲苯的特殊芳香味,倾泄入水中的二甲苯可漂浮在水面上,或呈油状物分布在水面,可造成鱼类和水生生物的死亡。 危险特性:易燃,其蒸气与空气可形成爆炸性混合物。遇明火、高热能引起燃烧爆炸。与氧化剂能发生强烈反应。流速过快,容易产生和积聚静电。其蒸气比空气重,能在较低处扩散至相当远的地方,遇明火会引着回燃。 燃烧(分解)产物:一氧化碳、二氧化碳。
3.现场应急监测方法:
气体检测管法;便携式气相色谱法;水质检测管法快速检测管法《突发性环境污染事故应急监测与处理处置技术》万本太主编气体速测管(北京劳保所产品、德国德尔格公司产品)
4.实验室监测方法:
| 监测方法 | 来源 | 类别 |
| 气相色谱法 | GB11890-89 | 水质 |
| 气相色谱法 | GB/T14677-93 | 空气 |
| 无泵型采样气相色谱法 | WS/T153-1999 | 作业场所空气 |
| 气相色谱法 | 《固体废弃物试验与分析评价手册》中国环境监测总站等译 | 固体废弃物 |
| 色谱/质谱法 | 美国EPA524.2方法 | 水质 |
5.环境标准:
| 中国(TJ36-79) | 车间空气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 | 100mg/m 3 (二甲苯) |
| 中国(TJ36-79) | 居住区大气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 | 0.30mg/m 3 (一次值、二甲苯) |
| 中国(GB16297-1996) | 大气污染物综合排放标准(二甲苯) | ①最高允许排放浓度(mg/m 3 ): 70(表2);90(表1) ②最高允许排放速率(kg/h): 二级1.0~10(表2);1.2~12(表1) 三级1.5~15(表2);1.8~18(表1) ③无组织排放监控浓度限值: 1.2mg/m 3 (表2);1.5mg/m 3 (表1) |
| 中国(待颁布) | 饮用水源中有害物质的最高容许浓度 | 0.5mg/L(二甲苯) |
| 中国(GHZB1-1999) | 地表水环境质量标准(I、II、III类水域特定值) | 0.5mg/L(二甲苯) |
| 中国(GB8978-1996) | 污水综合排放标准 | 一级:0.4mg/L 二级:0.6mg/L 三级:1.0mg/L |
6.应急处理处置方法:
一、泄漏应急处理
迅速撤离泄漏污染区人员至安全区,并进行隔离,严格限制出入。切断火源。建议应急处理人员戴自给正压式呼吸器,穿消防防护服。尽可能切断泄漏源,防止进入下水道、排洪沟等限制性空间。小量泄漏:用活性炭或其它惰性材料吸收。也可以用不燃性分散剂制成的乳液刷洗,洗液稀释后放入废水系统。大量泄漏:构筑围堤或挖坑收容;用泡沫覆盖,抑制蒸发。用防爆泵转移至槽车或专用收集器内,回收或运至废物处理场所处置。迅速将被二甲苯污染的土壤收集起来,转移到安全地带。对污染地带沿地面加强通风,蒸发残液,排除蒸气。迅速筑坝,切断受污染水体的流动,并用围栏等限制水面二甲苯的扩散。
二、防护措施
呼吸系统防护:空气中浓度较高时,佩戴过滤式防毒面具(半面罩)。紧急事态抢救或撤离时,建议佩戴空气呼吸器。 眼睛防护:戴化学安全防护眼镜。 身体防护:穿防毒物渗透工作服。 手防护:戴橡胶手套。 其它:工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作毕,淋浴更衣。注意个人清洁卫生。
三、急救措施
皮肤接触:脱去被污染的衣着,用肥皂水和清水彻底冲洗皮肤。 眼睛接触:提起眼睑,用流动清水或生理盐水冲洗。就医。 吸入:迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。如呼吸困难,给输氧。如呼吸停止,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。 食入:饮足量水,催吐。就医。
制备方法与用途
这段文本提供了间二甲苯的详细信息,包括其物理化学性质、用途、生产方法以及安全储存和运输注意事项。以下是这些信息的总结:
物理化学性质 用途 生产方法 安全储存与运输- 应储存在通风、低温干燥的库房内,并与其他氧化剂分隔存放。
- 运输时需特别注意防火防爆。
- 口服:大鼠LD50为5000毫克/公斤。
- 皮肤接触:兔子实验显示中度刺激。
- 眼睛接触:兔子实验显示轻度刺激。
- 遇明火或高温容易燃烧,产生刺激烟雾。
- 可与空气形成爆混合物。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 均三甲苯 1,3,5-trimethyl-benzene 108-67-8 C9H12 120.194 甲苯 toluene 108-88-3 C7H8 92.1405 1,2,4-三甲基苯 1,2,4-Trimethylbenzene 95-63-6 C9H12 120.194 对二甲苯 para-xylene 106-42-3 C8H10 106.167 邻二甲苯 o-xylene 95-47-6 C8H10 106.167 五甲基苯 pentamethylbenzene, 700-12-9 C11H16 148.248 六甲基苯 Hexamethylbenzene 87-85-4 C12H18 162.275 间甲基苯腈 3-Methylbenzonitrile 620-22-4 C8H7N 117.15 3-甲基苄醇 3-methylbenzyl alcohol 587-03-1 C8H10O 122.167 3-甲基苯甲醛 m-Tolualdehyde 620-23-5 C8H8O 120.151 3-甲基苄基氯 1-chloromethyl-3-methyl-benzene 620-19-9 C8H9Cl 140.612 3-甲基苄溴 1-bromomethyl-3-methyl-benzene 620-13-3 C8H9Br 185.063 3,5-二甲基苯甲醛 3,5-dimethylbenzaldehyde 5779-95-3 C9H10O 134.178 间苯二甲醛 Isophthalaldehyde 626-19-7 C8H6O2 134.134 间二溴苄 1,3-Bis(bromomethyl)benzene 626-15-3 C8H8Br2 263.96 间二氯苄 3-(chloromethyl)benzyl chloride 626-16-4 C8H8Cl2 175.058 5-氯间二甲苯 1-chloro-3,5-dimethylbenzene 556-97-8 C8H9Cl 140.612 1,3-二甲基-5-碘苯 3,5-dimethylphenyl iodide 22445-41-6 C8H9I 232.064 - 1
- 2
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 均三甲苯 1,3,5-trimethyl-benzene 108-67-8 C9H12 120.194 三甲苯 1,2,3-trimethylbenzene 526-73-8 C9H12 120.194 甲苯 toluene 108-88-3 C7H8 92.1405 1,2,4,5-四甲苯 1,2,4,5-tetramethylbenzene 95-93-2 C10H14 134.221 1,2,4-三甲基苯 1,2,4-Trimethylbenzene 95-63-6 C9H12 120.194 对二甲苯 para-xylene 106-42-3 C8H10 106.167 邻二甲苯 o-xylene 95-47-6 C8H10 106.167 1,2,3,5-四甲基苯 1,2,3,5-Tetramethylbenzene 527-53-7 C10H14 134.221 四甲基萘 1,2,3,4-Tetramethylbenzene 488-23-3 C10H14 134.221 间甲基苯腈 3-Methylbenzonitrile 620-22-4 C8H7N 117.15 3-乙基甲苯 1-Methyl-3-ethylbenzene 620-14-4 C9H12 120.194 3-甲基苄醇 3-methylbenzyl alcohol 587-03-1 C8H10O 122.167 3-甲基苄氟 1-(fluoromethyl)-3-methylbenzene 456-44-0 C8H9F 124.158 3-甲基苯甲醛 m-Tolualdehyde 620-23-5 C8H8O 120.151 3,5-二甲基苯腈 3,5-dimethylbenzonitrile 22445-42-7 C9H9N 131.177 3-甲基苯乙烯 3-methylstyrene 100-80-1 C9H10 118.178 5-乙基-3,5-二甲基苯 1-ethyl-3,5-dimethylbenzene 934-74-7 C10H14 134.221 3-甲基苄基氯 1-chloromethyl-3-methyl-benzene 620-19-9 C8H9Cl 140.612 3-甲基苄溴 1-bromomethyl-3-methyl-benzene 620-13-3 C8H9Br 185.063 3,5-二甲基苯甲醛 3,5-dimethylbenzaldehyde 5779-95-3 C9H10O 134.178 间苯二甲腈 benzene-1,3-dicarbonitrile 626-17-5 C8H4N2 128.133 间苯二甲胺 1,3-di(aminomethyl)benzene 1477-55-0 C8H12N2 136.197 间苯二甲醛 Isophthalaldehyde 626-19-7 C8H6O2 134.134 3,5-二甲基苄基氯 3,5-dimethylbenzyl chloride 2745-54-2 C9H11Cl 154.639 间二氯苄 3-(chloromethyl)benzyl chloride 626-16-4 C8H8Cl2 175.058 间二溴苄 1,3-Bis(bromomethyl)benzene 626-15-3 C8H8Br2 263.96 3,5-二乙基甲苯 3,5-diethyltoluene 2050-24-0 C11H16 148.248 3,5-二甲基氟苯 3,5-dimethylfluorobenzene 461-97-2 C8H9F 124.158 1,3-二甲基-5-碘苯 3,5-dimethylphenyl iodide 22445-41-6 C8H9I 232.064 - 1
- 2
- 3
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Freund; Fleischer, Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, 1916, vol. 411, p. 33摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Mailhe, Annales de Chimie (Cachan, France), 1922, vol. <9> 17, p. 308,317摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:描述:9-methyl-9H-fluorene-9-carbonyl chloride 在 三叔丁基膦 、 N,N-二异丙基乙胺 、 间二甲苯 、 bis(dibenzylideneacetone)-palladium(0) 作用下, 以 1,4-二氧六环 为溶剂, 反应 1.5h, 以93%的产率得到9-亚甲基芴参考文献:名称:化学计量和亚化学计量 12CO 和 13CO 的异位生成及其在钯催化氨基羰基化中的有效掺入摘要:使用简单的密封两室系统实现了异位生成一氧化碳 (CO) 及其在钯催化的羰基化反应中的有效结合的新技术。CO 的异位生成是通过钯催化的叔酰氯脱羰使用源自 Pd(dba)(2) 和 P(tBu)(3) 的催化剂产生的。使用新戊酰氯作为 CO 前体的初步研究为仅使用 1.5 当量的 CO 对 2-吡啶基甲苯磺酸酯衍生物进行氨基羰基化提供了另一种方法。 酰氯 CO 前体的进一步设计导致开发了一种新的固体、稳定、并且易于处理用于化学转化的 CO 源。这种 CO 前体的合成也为后期安装同位素碳标记的酰氯以随后释放气态 [(13)C]CO 提供了切入点。结合旨在应用 CO 作为限制剂的研究,该方法提供了高效的钯催化氨基羰基化,CO 结合率高达 96%。异位生成的 CO 和双室系统在几种药物化合物的合成中进行了测试,所有这些化合物都被标记为 [(13)C] 羰基对应物,基于限制 CO 的产率从良好到极好。DOI:10.1021/ja200818w
文献信息
-
Metal-Free Intermolecular Oxidative C–N Bond Formation via Tandem C–H and N–H Bond Functionalization作者:Abhishek A. Kantak、Shathaverdhan Potavathri、Rose A. Barham、Kaitlyn M. Romano、Brenton DeBoefDOI:10.1021/ja2087085日期:2011.12.14development of a novel intermolecular oxidative amination reaction, a synthetic transformation that involves the simultaneous functionalization of both a N-H and C-H bond, is described. The process, which is mediated by an I(III) oxidant and contains no metal catalysts, provides a rapid and green method for synthesizing protected anilines from simple arenes and phthalimide. Mechanistic investigations
-
Regiospecific Cleavage of S–N Bonds in Sulfonyl Azides: Sulfonyl Donors作者:Zhiguo Zhang、Songnan Wang、Yong Zhang、Guisheng ZhangDOI:10.1021/acs.joc.8b03046日期:2019.4.5Sulfonyl azides have been widely used as sulfonamido, diazo, and azido donors, as well as all-nitrogen 1,3-dipoles donors in synthetic chemistry. Here, the sulfonyl azides were used as efficient sulfonyl donors, which is very unusual. Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid-induced formation of the sulfonyl cation reactive species from sulfonyl azides was developed and used for the first time to couple various
-
Synthesis of Phenanthridines through Palladium-Catalyzed Cascade Reaction of 2-Halo-<i>N</i>-Ms-arylamines with Benzyl Halides/Sulfonates作者:Si-Yi Yang、Wen-Yong Han、Ding-Lei Zhang、Xiao-Jian Zhou、Mei Bai、Bao-Dong Cui、Nan-Wei Wan、Wei-Cheng Yuan、Yong-Zheng ChenDOI:10.1002/ejoc.201601608日期:2017.2.3An efficient palladium-catalyzed nucleophilic substitution/C–H activation/aromatization cascade reaction between readily available 2-halo-N-Ms-arylamines (Ms = methanesulfonyl) and benzyl halides/sulfonates has been described. A wide variety of phenanthridines were synthesized in a one-pot fashion in moderate to high yields (37–86 %). Notably, this method provides a straightforward, facile approach
-
Synthesis of aromatic aldehydes via 2-aryl-n,n'-diacyl-4-imidazolines作者:Jan Bergman、Lars Renström、Birger SjöbergDOI:10.1016/0040-4020(80)80230-4日期:1980.1Diacylimidazolium ions yield adducts with aromatic compounds. Thus the N,N'-diacetylimidazolium ion and indole gives 1,3-diacetyl-2-(3-indolyl)-4-imidazoline. Less reactive substrates such as thiophene, anisole and 1,3-dimethylbenzene fail to react with this reagent but do form adducts (e.g. 1,3-bis-(trifluoroacetyl)-2-(2-thienyl)-4-imidazoline) with an imidazole/trifluoroacetic anhydride reagent.
-
Hydrogenation of arenes, nitroarenes, and alkenes catalyzed by rhodium nanoparticles supported on natural nanozeolite clinoptilolite作者:Seyed Meysam Baghbanian、Maryam Farhang、Seyed Mohammad Vahdat、Mahmood TajbakhshDOI:10.1016/j.molcata.2015.06.029日期:2015.10Nanozeolite clinoptilolite supported rhodium nanoparticles (Rh/NZ-CP) has been prepared and characterized by a variety of techniques, including XRD, BET, TEM, EDX, ICP-OES and XPS analysis. This nanomaterial contains 2 wt% Rh in the range of 5–20 nm metallic nanoparticles distributed on nanozeolite. The catalytic performance of Rh/NZ-CP was evaluated by the hydrogenation of arenes, nitroarenes, and alkenes under
表征谱图
-
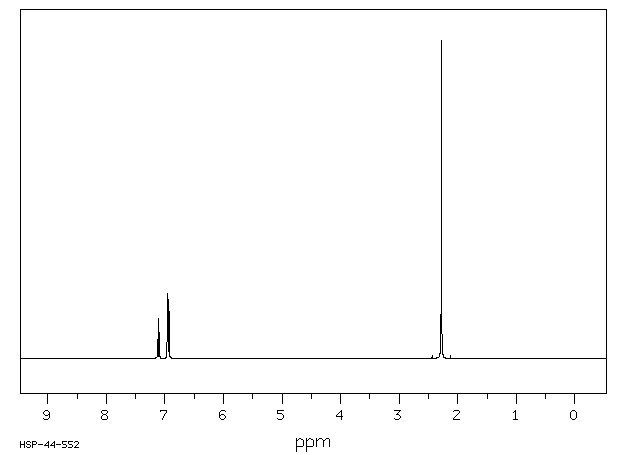
氢谱1HNMR
-
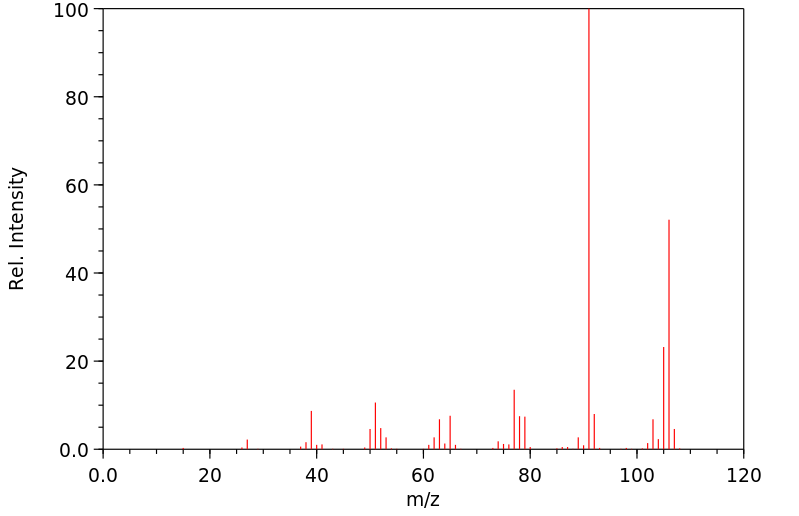
质谱MS
-
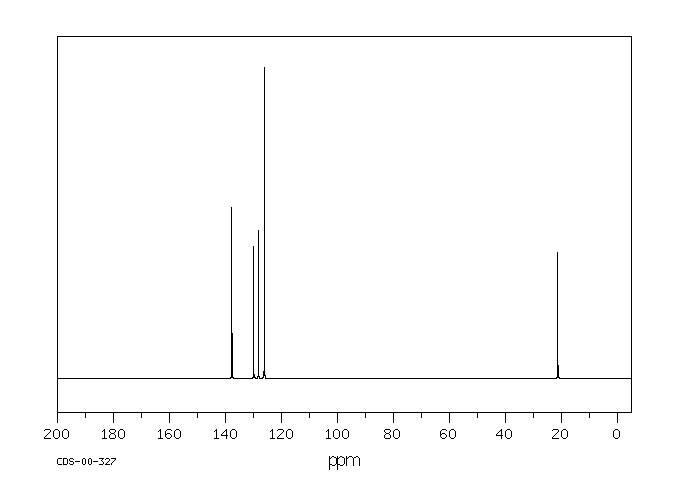
碳谱13CNMR
-
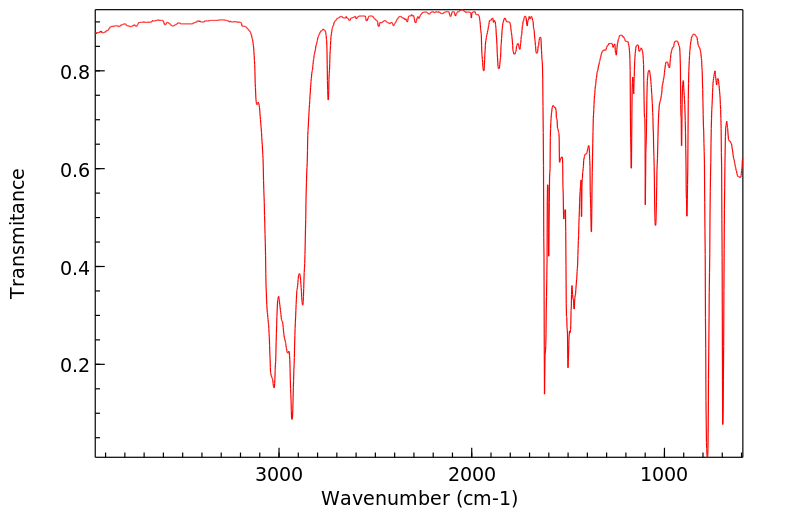
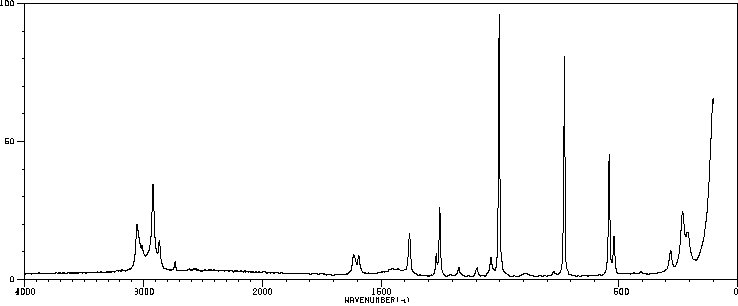
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息