2,2'-dithiobispropanoic acid | 4775-93-3
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
2,2'-dithiobispropanoic acid
英文别名
dithiodilactic acid;2,2'-Dithio-dipropionsaeure;2-(1-Carboxylatoethyldisulfanyl)propanoate;hydron
CAS
4775-93-3
化学式
C6H10O4S2
mdl
MFCD00059649
分子量
210.275
InChiKey
UTDRPUGFHHVEDG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:117.5 °C
-
沸点:319.8°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.319 (estimate)
-
稳定性/保质期:
在常温常压下保持稳定
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.9
-
重原子数:12
-
可旋转键数:5
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.666
-
拓扑面积:125
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:6
安全信息
-
海关编码:2930909090
-
储存条件:请将产品存放在常温、避光、通风干燥处,并密封保存。
SDS
2,2'-二硫代二丙酸
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: 2,2'-Dithiodipropionic Acid
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 第2级
严重损伤/刺激眼睛 2A类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志
信号词 警告
危险描述 造成皮肤刺激
造成严重眼刺激
防范说明
[预防] 处理后要彻底清洗双手。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[急救措施] 眼睛接触:用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续冲洗。
眼睛接触:求医/就诊
皮肤接触:用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
脱掉被污染的衣物,清洗后方可重新使用。
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 2,2'-二硫代二丙酸
百分比: >98.0%(GC)(T)
CAS编码: 4775-93-3
分子式: C6H10O4S2
2,2'-二硫代二丙酸
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色-极淡的黄色
气味: 无资料
2,2'-二硫代二丙酸
模块 9. 理化特性
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 无资料
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 硫氧化物
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
2,2'-二硫代二丙酸
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: 2,2'-Dithiodipropionic Acid
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 第2级
严重损伤/刺激眼睛 2A类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志
信号词 警告
危险描述 造成皮肤刺激
造成严重眼刺激
防范说明
[预防] 处理后要彻底清洗双手。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[急救措施] 眼睛接触:用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续冲洗。
眼睛接触:求医/就诊
皮肤接触:用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
脱掉被污染的衣物,清洗后方可重新使用。
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 2,2'-二硫代二丙酸
百分比: >98.0%(GC)(T)
CAS编码: 4775-93-3
分子式: C6H10O4S2
2,2'-二硫代二丙酸
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色-极淡的黄色
气味: 无资料
2,2'-二硫代二丙酸
模块 9. 理化特性
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 无资料
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 硫氧化物
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
2,2'-二硫代二丙酸
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Loven, Journal fur praktische Chemie (Leipzig 1954), 1884, vol. <2>29, p. 368,376摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:多重耐药细胞对孤儿药硫普罗宁的附带敏感性。摘要:癌症治疗的一个主要挑战是化疗过程中产生的多药耐药性(MDR)。在这里,我们证明硫普罗宁 (1) 是一种硫醇取代的 N-丙酰甘氨酸衍生物,对一系列表达药物外排泵 P-糖蛋白 (P-gp、ABCB1) 和 MRP1 (ABCC1) 的细胞系具有选择性毒性。尽管功能测定表明硫普罗宁不与 P-gp 相互作用,但用 1 处理 MDR 细胞会导致 ABCB1 mRNA 不稳定,从而导致 P-gp 蛋白减少。表达 P-gp 的细胞长期暴露于 1 会使它们对阿霉素和紫杉醇(这两种 P-gp 底物)敏感。用硫普罗宁处理 MRP1 过表达细胞导致 MRP1 蛋白显着减少。硫普罗宁类似物的合成和筛选表明,硫醇官能团对于附带敏感性至关重要,而氨基酸主链的取代会改变但不会破坏特异性,这为未来开发靶向类似物指明了方向。DOI:10.1021/jm2001663
文献信息
-
[EN] METAL-CATALYZED OXIDATIVE COUPLING OF THIOLS<br/>[FR] COUPLAGE OXYDATIF CATALYSÉ PAR UN MÉTAL DE THIOLS申请人:ECOLAB USA INC公开号:WO2017024092A1公开(公告)日:2017-02-09Disclosed are methods for preparing disulfide compounds through oxidative coupling of thiol compounds. Thiols are oxidized to the corresponding disulfide compound in high yield in presence of a base and a metal salt. The method uses low catalyst loadings and provides organic disulfide compounds with little to no byproducts.
-
[EN] REDUCTION SENSITIVE BIODEGRADABLE POLYESTERAMIDES<br/>[FR] RÉDUCTION DE POLYESTERAMIDES BIODÉGRADABLES SENSIBLES申请人:DSM IP ASSETS BV公开号:WO2016020545A1公开(公告)日:2016-02-11The present invention relates to biodegradable polyesteramides (PEAs) comprising hydrophobic alpha -amino acids, diols, aliphatic dicarboxylic acids and optionally diamines whereby at least one of the dicarboxylic acids, diols or diamines comprises disulphide linkages. The present invention also relates to the use of the polyesteramides in medical applications such as cancer treatment, ophthalmic applications, therapeutic cardiovascular applications, veterinary applications, pain management applications, MSK applications and vaccine delivery compositions. The present invention also relates to a drug delivery composition comprising the PEA's and to a drug delivery system such as micro-or nanoparticles, micelles, liposomes, polymerosomes, micro- and nanogels, polymerosomes or nanotubes.
-
Dynamic Kinetic Resolution of Amines Involving Biocatalysis and in Situ Free Radical Mediated Racemization作者:Stéphane Gastaldi、Stéphanie Escoubet、Nicolas Vanthuyne、Gérard Gil、Michèle P. BertrandDOI:10.1021/ol063062o日期:2007.3.1[reaction: see text] The association of lipase-catalyzed enzymatic resolution with in situ racemization mediated with the thiyl radical enables the dynamic kinetic resolution of non-benzylic amines. It leads to (R)-amides with high enantioselectivities. It can be applied either to the conversion of racemic mixtures or to the inversion of (S)-enantiomers.
-
METHOD FOR PRODUCING 3-MERCAPTOPROPIONIC ACID, AND METHODS USING SAME FOR PRODUCING CARBOXYLIC ACID ESTER COMPOUND HAVING MERCAPTO GROUP AND THIOURETHANE-BASED OPTICAL MATERIAL申请人:KOC SOLUTION CO., LTD.公开号:US20180179154A1公开(公告)日:2018-06-28A method for producing 3-mercaptopropionic acid and methods using same for producing a carbonic acid ester compound having a mercapto group and a thiourethane-based optical material. The present invention improves a process during the production of 3-mercaptopropionic acid, significantly increases yield, and reduces the temperature and time during vacuum distillation, thereby preventing the destruction of a product and significantly increasing productivity. The present invention allows high-purity 3-mercaptopropionic acid having an excellent color to be finally yielded; accordingly, by using same, a high-purity carbonic acid ester compound having an excellent color and a mercapto group can be inexpensively obtained. A thiourethane-based polymeric composition and a thiourethane-based optical material obtained by polymerizing same can likewise be inexpensively obtained by using said carbonic acid ester compound. Such carbonic acid ester compound can be used for the production of inexpensive thiourethane optical lenses; consequently, inexpensive optical lenses having an excellent color can be obtained.
-
The mechanism of nitric oxide formation from S-nitrosothiols (thionitrites)作者:D. Lyn H. WilliamsDOI:10.1039/cc9960001085日期:——S-Nitrosothiols (RSNO) are easily made by electrophilic nitrosation of thiols and are a convenient source of nitric oxide. Reaction occurs readily (in many cases) in aqueous buffer at pH 7.4 to give in addition the corresponding disulfide RSSR. If oxygen is not rigorously excluded from the solution, then the nitric oxide is converted quantitatively to nitrite ion, whereas in the absence of oxygen nitric oxide can be detected using a commercial NO-probe. Reaction, however, only occurs (apart from the photochemical pathway) if Cu2+ is present. There is often enough Cu2+ in the distilled water–buffer components to bring about reaction, but decomposition is halted if Cu2+ is complexed with EDTA. Experiments with the specific Cu+ chelator neocuproine however show that the true effective reagent is Cu+, formed by reduction of Cu2+ with thiolate ion. Kinetic experiments show that the most reactive nitrosothiols are those which can coordinate bidentately with Cu+, and there is a wide range of reactivity amongst the structures studied. Reactivity is crucially dependent on the concentrations of Cu2+ and RS–.Reaction also occurs, although somewhat more slowly, if the source of copper is the CuII complex with the tripeptide diglycyl-L-histidine (GGH) or as the CuII complex with human serum albumin (HSA). This allows the possibility that nitrosothiols could in principle generate nitric oxide in vivo using the naturally occurring sources of CuII.Rapid exchange of the NO-group in RSNO with thiols occurs, again in aqueous buffer at pH 7.4. This reaction has been established as a nucleophilic substitution reaction by the thiolate ion at the nitroso nitrogen atom.The implications of these results with regard to possible involvement of nitrosothiols in vivo are discussed.S-亚硝基硫醇 (RSNO) 通过硫醇的电亲核亚硝化反应容易制备,并且是氮氧化物的便捷来源。在 pH 7.4 的水缓冲液中(在许多情况下),反应会迅速发生,从而生成相应的二硫化物 RSSR。如果溶液中没有严格排除氧气,则一氧化氮会定量转化为亚硝酸盐离子,而在缺氧的情况下,可以通过商业一氧化氮探针检测到一氧化氮。然而,反应仅在存在 Cu2+ 的情况下发生(除了光化学途径)。通常在蒸馏水-缓冲液成分中有足够的 Cu2+ 促使反应发生,但如果 Cu2+ 与 EDTA 形成络合物,则分解会被阻止。然而,使用特定的 Cu+ 螯合剂新铜碱(neocuproine)进行的实验表明,真正的有效试剂是 Cu+,它是通过硫醇阴离子还原 Cu2+ 形成的。动力学实验表明,反应性最强的亚硝基硫醇是那些能够与 Cu+ 形成二配位的分子,而且在所研究的结构中反应性存在广泛的变异。反应性在很大程度上依赖于 Cu2+ 和 RS– 的浓度。当铜的来源是与三肽二甘氨基-L-组氨酸 (GGH) 的 CuII 络合物或与人血清白蛋白 (HSA) 的 CuII 络合物时,反应也会发生,虽然速度较慢。这使得亚硝基硫醇在原则上能够利用天然存在的 CuII 产生体内的一氧化氮。RSNO 中 NO 基团与硫醇之间的快速交换同样发生,在 pH 7.4 的水缓冲液中进行。此反应已被确定为硫醇阴离子在亚硝基氮原子上的亲核取代反应。讨论了这些结果对于亚硝基硫醇在体内可能参与的影响。
表征谱图
-
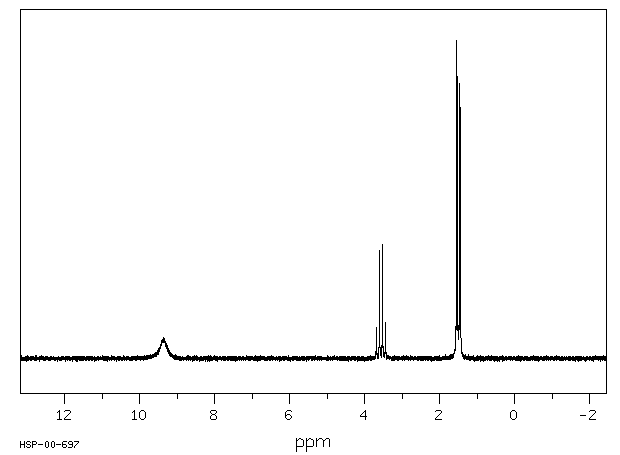
氢谱1HNMR
-
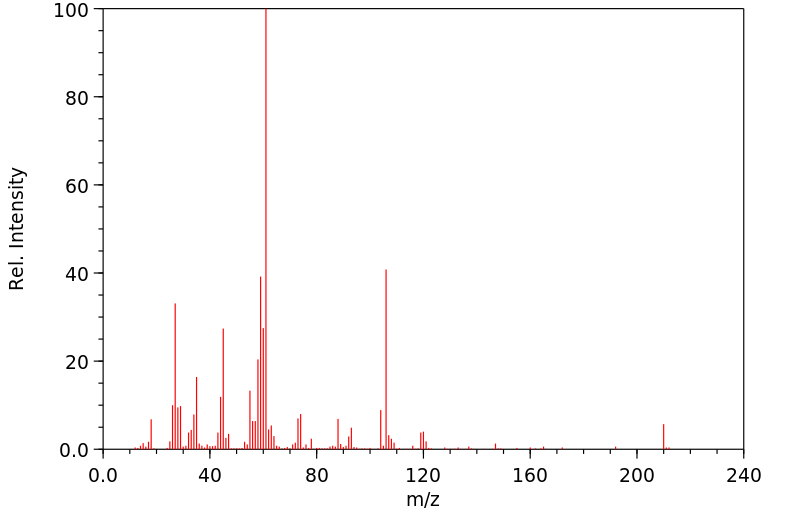
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
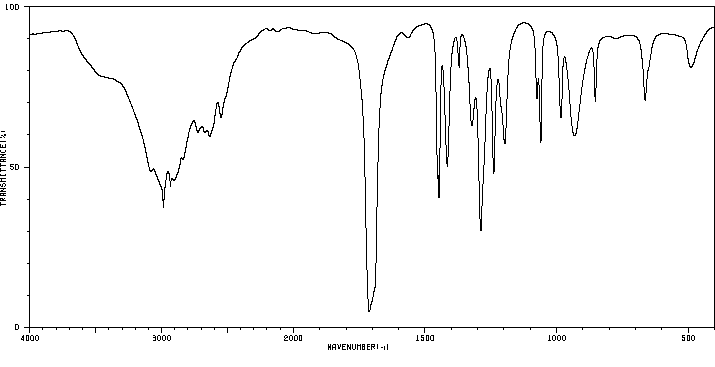
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(甲基3-(二甲基氨基)-2-苯基-2H-azirene-2-羧酸乙酯)
(±)-盐酸氯吡格雷
(±)-丙酰肉碱氯化物
(d(CH2)51,Tyr(Me)2,Arg8)-血管加压素
(S)-(+)-α-氨基-4-羧基-2-甲基苯乙酸
(S)-阿拉考特盐酸盐
(S)-赖诺普利-d5钠
(S)-2-氨基-5-氧代己酸,氢溴酸盐
(S)-2-[[[(1R,2R)-2-[[[3,5-双(叔丁基)-2-羟基苯基]亚甲基]氨基]环己基]硫脲基]-N-苄基-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(S)-2-[3-[(1R,2R)-2-(二丙基氨基)环己基]硫脲基]-N-异丙基-3,3-二甲基丁酰胺
(S)-1-(4-氨基氧基乙酰胺基苄基)乙二胺四乙酸
(S)-1-[N-[3-苯基-1-[(苯基甲氧基)羰基]丙基]-L-丙氨酰基]-L-脯氨酸
(R)-乙基N-甲酰基-N-(1-苯乙基)甘氨酸
(R)-丙酰肉碱-d3氯化物
(R)-4-N-Cbz-哌嗪-2-甲酸甲酯
(R)-3-氨基-2-苄基丙酸盐酸盐
(R)-1-(3-溴-2-甲基-1-氧丙基)-L-脯氨酸
(N-[(苄氧基)羰基]丙氨酰-N〜5〜-(diaminomethylidene)鸟氨酸)
(6-氯-2-吲哚基甲基)乙酰氨基丙二酸二乙酯
(4R)-N-亚硝基噻唑烷-4-羧酸
(3R)-1-噻-4-氮杂螺[4.4]壬烷-3-羧酸
(3-硝基-1H-1,2,4-三唑-1-基)乙酸乙酯
(2S,4R)-Boc-4-环己基-吡咯烷-2-羧酸
(2S,3S,5S)-2-氨基-3-羟基-1,6-二苯己烷-5-N-氨基甲酰基-L-缬氨酸
(2S,3S)-3-((S)-1-((1-(4-氟苯基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-4-基)-甲基氨基)-1-氧-3-(噻唑-4-基)丙-2-基氨基甲酰基)-环氧乙烷-2-羧酸
(2S)-2,6-二氨基-N-[4-(5-氟-1,3-苯并噻唑-2-基)-2-甲基苯基]己酰胺二盐酸盐
(2S)-2-氨基-N,3,3-三甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3-甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯基甲基)丁酰胺,
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S,4R)-1-((S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基丁酰基)-4-羟基-N-(4-(4-甲基噻唑-5-基)苄基)吡咯烷-2-甲酰胺盐酸盐
(2R,3'S)苯那普利叔丁基酯d5
(2R)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2-氯丙烯基)草酰氯
(1S,3S,5S)-2-Boc-2-氮杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-3-羧酸
(1R,5R,6R)-5-(1-乙基丙氧基)-7-氧杂双环[4.1.0]庚-3-烯-3-羧酸乙基酯
(1R,4R,5S,6R)-4-氨基-2-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-4,6-二羧酸
齐特巴坦
齐德巴坦钠盐
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,苯基甲基酯,(2a,3a)-
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,羧基甲基酯,(2a,3b)-(9CI)
黄酮-8-乙酸二甲氨基乙基酯
黄荧菌素
黄体生成激素释放激素(1-6)
黄体生成激素释放激素 (1-5) 酰肼
黄体瑞林
麦醇溶蛋白
麦角硫因
麦芽聚糖六乙酸酯
麦根酸