1,2-二氯丙烷 | 78-87-5
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:−100 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:95-96 °C(lit.)
-
密度:1.156 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
蒸气密度:3.89 (vs air)
-
闪点:40 °F
-
溶解度:可与有机溶剂混溶(美国环保署,1985 年)。
-
介电常数:9.0(Ambient)
-
暴露限值:Potential occupational carcinogen. NIOSH REL: IDLH 400 ppm; OSHA PEL: TWA 75 ppm (350 mg/m3); ACGIH TLV: TWA 75 ppm, STEL 110 ppm (adopted).
-
LogP:2-2.25 at 20-25℃
-
物理描述:1,2-dichloropropane is a colorless watery liquid with a sweet odor. Sinks in water. Produces an irritating vapor. (USCG, 1999)
-
颜色/状态:Colorless liquid
-
气味:Sweet
-
蒸汽密度:3.9 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:53.3 mm Hg @ 25 °C
-
亨利常数:0.00 atm-m3/mole
-
稳定性/保质期:
其蒸气与空气可形成爆炸性混合物,遇明火、高温容易引发燃烧和爆炸,爆炸极限为3.4%~14.5%(体积)。受高温影响时还会分解产生有毒且具有腐蚀性的气体。
-
自燃温度:557 °C
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of /hydrogen chloride/.
-
腐蚀性:... It will attack some forms of plastics, rubber, & coatings.
-
燃烧热:-7300 Btu/lb= -4100 cal/g= -170x10+5 J/kg (est)
-
汽化热:8,428.5 g cal/g mole (multiply by 4.184 for J/g mole)
-
表面张力:29 dynes/cm = 0.029 N/m at 20 °C
-
电离电位:10.87 eV
-
气味阈值:... Human subjects described the odor as "strong" at 130 to 190 ppm & "not noticeable" at 15 to 23 ppm.
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.4388 at 20 °C/D
-
相对蒸发率:Greater than 1 (butyl acetate= 1)
-
保留指数:672;688;677.6;688;668.9;688;684;675.7;678.6;691;684;691;691;670;674;684;678.9;667;679
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.8
-
重原子数:5
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
ADMET
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:400 ppm
-
危险品标志:F
-
安全说明:S16,S24,S36/37,S45,S7
-
危险类别码:R20/22,R11
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2903199000
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1279 3/PG 2
-
危险类别:3
-
RTECS号:TX9625000
-
包装等级:II
-
储存条件:密封保存。应置于库房中通风、低温和干燥处,并与其他氧化剂和酸类分开存放。可使用铁、软钢或铝制容器进行储存。
SDS
| 国标编号: | 32036 |
| CAS: | 78-87-5 |
| 中文名称: | 1,2-二氯丙烷 |
| 英文名称: | 1,2-Dichloropropane |
| 别 名: | 氯化丙烯 |
| 分子式: | C 3 H 6 Cl 2 ;ClCH 2 CHClCH 3 |
| 分子量: | 112.99 |
| 熔 点: | -80℃ 沸点:96.8℃ |
| 密 度: | 相对密度(水=1)1.16; |
| 蒸汽压: | 15℃ |
| 溶解性: | 不溶于水,溶于多数有机溶剂 |
| 稳定性: | 稳定 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色液体,有类似氯仿的气味 |
| 危险标记: | 7(中闪点易燃液体) |
| 用 途: | 用作脂肪、油、蜡、树脂和树胶的溶剂及杀虫剂等 |
2.对环境的影响:
一、健康危害
侵入途径:吸入、食入、经皮吸收。
健康危害:吸入、摄入或经皮肤吸收后对身体有害。1,2-二氯丙烷对中枢神经系统有抑制作用;可使皮肤干燥,脱屑和皲裂;对粘膜有刺激作用;可引起肝、肾和心肌脂肪性变。
二、毒理学资料及环境行为
急性毒性:LD502196mg/kg(大鼠经口);8750mg/kg(兔经皮);小鼠吸入4.6g/m3×3~4小时,致死;小鼠经口860mg/kg,致死。
亚急性和慢性毒性:小鼠吸入1.85g/m3×4~7小时/2~12次,肝细胞轻度脂肪变性;大鼠吸入4.4g/m3×7小时×6~32次,半数动物死亡。
致突变性:Ames试验沙门氏菌株TA1535、TA1978、TA100,10~50mg/皿阳性。
危险特性:其蒸气与空气形成爆炸性混合物,遇明火、高热能引起燃烧爆炸。与氧化剂能发生强烈反应。受高热分解产生有毒的腐蚀性气体。其蒸气比空气重,能在较低处扩散到相当远的地方,遇火源引着回燃。若遇高热,容器内压增大,有开裂和爆炸的危险。
燃烧(分解)产物:一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氯化氢、光气。
3.现场应急监测方法:
便携式气相色谱法
4.实验室监测方法:
吹扫捕集-气相色谱法(中国环境监测总站,水质)
气相色谱法《固体废弃物试验与分析评价手册》中国环境监测总站等译
色谱/质谱法 美国EPA524.2方法
5.环境标准:
前苏联 车间空气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 10mg/m3
嗅觉阈浓度 50ppm
6.应急处理处置方法:
一、泄漏应急处理
疏散泄漏污染区人员至安全区,禁止无关人员进入污染区,切断火源。建议应急处理人员戴自给式呼吸器,穿一般消防防护服。在确保安全情况下堵漏。喷水雾能减少蒸发,但不不能降低泄漏物在受限制家间内的易燃性。用沙土或其它不燃性吸附剂混合吸收,然后收集运至废物处理场所处置。也可以用不燃性分散剂制成的乳液刷洗,经稀释的洗水放入废水系统。如大量泄漏,利用围堤收容,然后收集、转移、回收或无害处理后废弃。
废弃物处置方法:用焚烧法。废料同其它燃料混合后焚烧。燃烧要充分,防止生成光气。焚烧炉排气中的卤化氢通过酸洗涤器除去。
二、防护措施
呼吸系统防护:空气中浓度超标时,应该佩带防毒面具。紧急事态抢救或逃生时,佩带自给式呼吸器。
眼睛防护:戴化学安全防护眼镜。
身体防护:穿相应的工作服。
手防护:必要时戴防化学品手套。
其它:工作现场严禁吸烟、进食和饮水。工作后,淋浴更衣。注意个人清洁卫生。
三、急救措施
皮肤接触:脱去污染的衣着,用肥皂水及清水彻底冲洗。
眼睛接触:立即提起眼睑,用流动清水冲洗。
吸入:迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。呼吸困难时给输氧。呼吸停止时,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。
食入:误服者给饮大量温水,催吐,洗胃,就医。
灭火方法:雾状水、泡沫、二氧化碳、干粉、砂土。
制备方法与用途
1,2-二氯丙烷不溶于水,易溶于乙醚,并且能与大多数有机溶剂混溶。
用途1,2-二氯丙烷主要用于油漆、油墨的配制以及作为稀释剂和PVC胶粘剂的一部分。它是一种优良的有机溶剂,可替代二甲苯等苯类化合物用于制作无苯香蕉水和聚胺脂稀释剂。此外,该物质与苯、酮、酯等有机溶剂相容,并可用于氯醇法生产环氧氯丙烷的副产物稀料以及作为油漆稀释剂。
1,2-二氯丙烷具有低毒环保特性,可替代甲苯和二甲苯,在无苯天那水中有广泛应用。它还可用作有机合成原料、油类和脂肪溶剂及洗涤剂,也可用于树脂、农药的制备。经过氨化后可以得到丙二胺。
1,2-二氯丙烷亦可用于作为溶剂和有机合成过程中的中间体。该物质常被用作脱漆剂或去除木材涂装的溶剂,但在某些应用中已不再使用。
化学性质1,2-二氯丙烷是一种浅黄色至无色透明液体,凝固点为-100℃,沸点为95-96℃,相对密度为1.156(20/4℃),折射率为1.4388,闪点为4℃。它能与大多数有机溶剂混溶,并微溶于水。该物质易燃且具有氯仿气味,在高浓度下具麻醉性,可能刺激眼粘膜并损害肝、肾。大鼠口服致死量为1.19 mL/kg,大白鼠吸入致死浓度为9260 mg/m³。空气中能嗅到的浓度约为231 mg/m³。
二氯丙烷的闪点大约在30℃左右,属于中闪点易燃液体。其蒸汽与空气形成爆炸性混合物,在遇明火或高热时可能发生燃烧和爆炸。它与氧化剂会发生强烈反应,并在受高热分解后产生有毒腐蚀性气体。蒸汽比空气重,能在较低处扩散并遇火源引燃回燃。高温下容器内压力增大可能导致开裂和爆炸。
1,2-二氯丙烷是生产环氧氯丙烷时的副产物,也是合成四氯乙烯及其他含氯有机化合物时的重要中间体。它曾被用作烟熏消毒剂、化学反应中的中间体以及工业溶剂等用途,但在某些应用中已不再使用。
用途1,2-二氯丙烷还可用于有机合成原料和油类、脂肪的溶解,同时也是树脂、农药的生产原料。经过氨化后可制得丙二胺,并且可以作为滴滴混剂(D-D)、Vidden D等农药品种中的一种成分。D-D是一种播种前杀线虫剂,能够有效防治包括根瘤线虫、草地线虫、刺线虫、剑线虫和甜菜线虫在内的多种土壤线虫。当药剂施入15-20厘米深度的土壤时效果最佳。该产品具有一定的药害风险,在施药后至少需等待15天再进行种植。对蜜蜂毒性较小。
生产方法1,2-二氯丙烷由丙烯与氯气在二氯丙烷中液相低温氯化制得,也可通过高温氯化制取氯丙烷时作为副产物获得。
分类易燃液体
中毒(急性毒性)
- 大鼠口服LD50: 1947 毫克/公斤
- 小鼠口服LD50: 860 毫克/公斤
刺激数据
- 兔子眼睛:500毫克,轻度刺激
爆炸物危险特性
与空气混合可爆,在受热、明火情况下容易燃烧和爆炸。
可燃性危险特性
遇明火或高温时易燃;在高热条件下分解产生有毒的氯化物气体。
储运特性
库房应保持通风低温干燥,并且要与其他氧化剂及酸类分开存放。
灭火剂
干粉、干砂、二氧化碳、泡沫和雾状水均可用于扑灭该物质引起的火灾。
职业标准
TWA 350 毫克/立方米
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 1-氯丙烷 1-Chloropropane 540-54-5 C3H7Cl 78.5416 2-氯丙烷 2-chloropropane 75-29-6 C3H7Cl 78.5416 1,3-二氯丙烷 1,3-Dichloropropane 142-28-9 C3H6Cl2 112.987 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 1,2,3-三氯丙烷 1,2,3-trichloropropane 96-18-4 C3H5Cl3 147.432 2-氯丙烷 2-chloropropane 75-29-6 C3H7Cl 78.5416 —— 1,2,2-trichloropropane 3175-23-3 C3H5Cl3 147.432 1,1,2-三氯丙烷 1,1,2-trichloropropane 598-77-6 C3H5Cl3 147.432 1,3-二氯丙烷 1,3-Dichloropropane 142-28-9 C3H6Cl2 112.987
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Preparing tetrachloroethylene摘要:公开号:US01947491A1
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:将(±)-3-乙基-3-甲基邻苯二甲酸酯转化为3,3-二甲基-3,4-二氢异香豆素。3-甲基水胶素的合成摘要:与乙基甲基酮烷基化后,邻-硫代γ-甲基苯甲酰胺(1a-f)得到(±)-3-乙基-3-甲基邻苯二甲酸酯(2a-f),经浓H 2 SO 4或无水AlCl 3处理提供了相应的3,3-二甲基-3,4-二氢异香豆素(3a-f)和3-甲基蜜莱因(3g)。DOI:10.1002/jhet.5570390403
-
作为试剂:描述:1-(三甲基硅基)丙炔 、 N-(quinolin-8-yl)methacrylamide 在 1,2-二氯丙烷 、 ZnBr2*C6H16N2 、 (三甲基硅基)甲基氯化镁 、 顺-1,2-双(二苯基膦)乙烯 、 iron(III)-acetylacetonate 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 为溶剂, 反应 20.0h, 以98%的产率得到3,6-dimethyl-5-trimethylsilyl-1-(quinolin-8-yl)pyridin-2(1H)-one参考文献:名称:酰胺与炔烃的铁催化偶联氧化吡啶酮和异喹诺酮的CH-H活化方法摘要:铁催化剂与温和的有机氧化剂结合可促进CH键断裂和CN键形成,并分别从烯烃或芳基酰胺和内部炔烃形成2-吡啶酮和异喹诺酮。不对称炔烃使吡啶酮衍生物具有较高的区域选择性,这可能是由于铁的致密尺寸导致反应对空间效应的敏感性。DOI:10.1002/asia.201501095
文献信息
-
2,3,3,3-四氟丙烯的合成方法
-
Flash vacuum pyrolysis over magnesium. Part 1. Pyrolysis of benzylic, other aryl/alkyl and aliphatic halides作者:R. Alan Aitken、Philip K. G. Hodgson、John J. Morrison、Adebayo O. OyewaleDOI:10.1039/b108663d日期:2002.1.23Flash vacuum pyrolysis over a bed of freshly sublimed magnesium on glass wool results in efficient coupling of benzyl halides to give the corresponding bibenzyls. Where an ortho halogen substituent is present further dehalogenation gives some dihydroanthracene and anthracene. Efficient coupling is also observed for halomethylnaphthalenes and halodiphenylmethanes while chlorotriphenylmethane gives 4,4′-bis(diphenylmethyl)biphenyl. By using α,α′-dihalo-o-xylenes, benzocyclobutenes are obtained in good yield, while the isomeric α,α′-dihalo-p-xylenes give a range of high thermal stability polymers by polymerisation of the initially formed p-xylylenes. Other haloalkylbenzenes undergo largely dehydrohalogenation where this is possible, in some cases resulting in cyclisation. Deoxygenation is also observed with haloalkyl phenyl ketones to give phenylalkynes as well as other products. With simple alkyl halides there is efficient elimination of HCl or HBr to give alkenes. For aliphatic dihalides this also occurs to give dienes but there is also cyclisation to give cycloalkanes and dehalogenation with hydrogen atom transfer to give alkenes in some cases. For 5-bromopent-1-ene the products are those expected from a radical pathway but for 6-bromohex-1-ene they are clearly not. For 2,2-dichloropropane and 1,1-dichloropropane elimination of HCl occurs but for 1,1-dichlorobutane, -pentane and -hexane partial hydrolysis followed by elimination of HCl gives E,E-, E,Z- and Z,Z- isomers of the dialk-1-enyl ethers and fully assigned 13C NMR data are presented for these. With 6-chlorohex-1-yne and 7-chlorohept-1-yne there is cyclisation to give methylenecycloalkanes and -cycloalkynes. The behaviour of 1,2-dibromocyclohexane and 1,2-dichlorocyclooctane under these conditions is also examined. Various pieces of evidence are presented that suggest that these processes do not involve generation of free gas-phase radicals but rather surface-adsorbed organometallic species.在玻璃棉上覆盖一层新升华的镁,进行闪式真空热解,能有效促使苄基卤化物耦合生成相应的联苄。当有邻位卤素取代基存在时,进一步脱卤生成部分二氢蒽和蒽。卤甲基萘和二苯基甲烷也能高效耦合,而三苯基氯甲烷则生成4,4′-双(二苯甲基)联苯。用α,α′-二卤代邻二甲苯可以获得较高产率的苯并环丁烯,而异构的α,α′-二卤代对二甲苯,通过形成的对二甲苯的聚合,可以得到一系列高热稳定性的聚合物。其他卤代烃苯大体上会脱卤化氢,某些情况下能产生环化反应。同样可以观察到,苯基卤代烷烃脱去羰基生成苯乙炔以及其他产物。简单的烷基卤化物则高效地脱去HCl或HBr生成烯烃。脂肪族二卤化物也会发生这一反应生成二烯,但不发生环化反应生成环烷烃,或在某些情况下发生氢原子转移的脱卤反应生成烯烃。5-溴戊-1-烯的产物符合自由基途径的预期,但6-溴己-1-烯并不符合。2,2-二氯丙烷和1,1-二氯丙烷能脱去HCl,但1,1-二氯丁烷、戊烷和己烷则能部分水解,随后脱去HCl,生成E,E-, E,Z-和Z,Z-异构体二烷-1-烯基醚,并且得到了这些物质的13C NMR全归属数据。6-氯己-1-炔和7-氯庚-1-炔能发生环化反应生成亚甲基环烷烃和环炔烃。本文还考察了1,2-二溴环己烷和1,2-二氯环辛烷在上述条件下的行为。本文给出了众多种证据,表明这些反应过程不涉及气相自由基的形成,而是表面吸附的金属有机物种。
-
A systematic study on the activation of simple polyethers by MoCl5 and WCl6作者:Sara Dolci、Fabio Marchetti、Guido Pampaloni、Stefano ZacchiniDOI:10.1039/c001377c日期:——MoCl5, 1a, and WCl6, 1b, activate 1,3-dioxolane at room temperature in chlorinated solvents: the compound [MoOCl3OC(H)OCH2CH2Cl}]2, 2, has been isolated from MoCl5/dioxolane. The mixed oxo-chloro species WOCl4, 1c, reacts with 1,3-dioxolane, selectively giving the coordination adduct WOCl4(κ1-C3H6O2), 3. Dimethoxymethane, CH2(OMe)2, undergoes activation including C–H bond cleavage when reacted with氯化钼5,1a和WCl 6,1b,激活1,3-二氧戊环在氯化溶剂室温:化合物[MoOCl 3 Ô C(H)OCH 2 CH 2氯}] 2,2,已经从分离氯化钼5/二氧戊环。混合的氯代氧WOCl 4,1c,与1,3-二氧戊环选择性地给协调加合物WOCL 4(κ 1 -C 3 ħ 6 Ò 2),3。二甲氧基甲烷,CH 2(OME)2,经过活化,包括CH键裂解当与反应1A,得到钼络合物[MoOCl 3 Ô C(H)OME}] 2,4,和Mo 2 Cl 5(OMe)5,5。的反应1B用CH 2(OR)2(R =甲基,乙基)继续经由ö -abstraction与形成氧代衍生物的WOCL 4 [O(R)CH 2 CL](R = Me中,图6a R =; Et,6b)与等摩尔量的氯化钙。的反应中1A,b与CMe 2(OMe)2 导致 氧化异丁烯,MeC(O)CH C(Me)2。一系列通式ROCH的简
-
Determination of the hydrogen-bond basicity of weak and multifunctional bases: the case of lindane(γ-hexachlorocyclohexane)作者:Carole Ouvrard、Maryvonne Luçon、Jérôme Graton、Michel Berthelot、Christian LaurenceDOI:10.1002/poc.688日期:2004.1determining the hydrogen-bond (HB) basicity of lindane (γ-hexachlorocyclohexane): (i) experimental Fourier transform IR measurement of a sum of individual 1:1 equilibrium constants for the formation of 1:1 4-fluorophenol-lindane hydrogen-bonded complexes in CCl4; (ii) calculation of the overall HB basicity from octanol–water partition coefficients; (iii) correlation of the HB basicity of chloroalkanes with the我们使用四种方法确定林丹(γ-六氯环己烷)的氢键(HB)碱度:(i)实验性傅立叶变换IR测量单个1:1平衡常数之和,以形成1:1 4 CCl 4中的-氟苯酚-林丹氢键复合物; (ii)根据辛醇-水分配系数计算总体HB碱度;(iii)氯烷烃的HB碱性与氯原子周围的静电势之间的相关性;(iv)氯代烷烃的HB碱度与其计算出的与氟化氢的络合物的焓的相关性。始终发现,林丹仍然是弱的HB碱,因为多功能性不能完全补偿氯原子彼此之间施加的吸电子感应效应。实际上,只有五个氯原子充当HB受体,一个轴向氯由于感应效应而失活。立体电子效应导致三中心氢键的形成。版权所有©2003 John Wiley&Sons,Ltd.
-
Glucagon antagonists/inverse agonists申请人:Noro Nordisk A/S公开号:US06503949B1公开(公告)日:2003-01-07Disclosed is a novel class of compounds of formula (I) wherein V, A, Y, Z, R1, E, X and D are as defined in the specification. These compounds act to antagonize the action of the glucagon hormone on the glucagon receptor. Owing to their antagonizing effect of the glucagon receptor, the compounds are suitable for treating or preventing glucagon-mediated conditions and diseases such as hyperglycemia, Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes and obesity.揭示了一类新的化合物,其化学式为(I),其中V、A、Y、Z、R1、E、X和D的定义如规范中所述。这些化合物作用于拮抗胰高血糖素激素对胰高血糖素受体的作用。由于这些化合物对胰高血糖素受体的拮抗作用,它们适用于治疗或预防由胰高血糖素介导的疾病和病症,如高血糖、1型糖尿病、2型糖尿病和肥胖症。
表征谱图
-
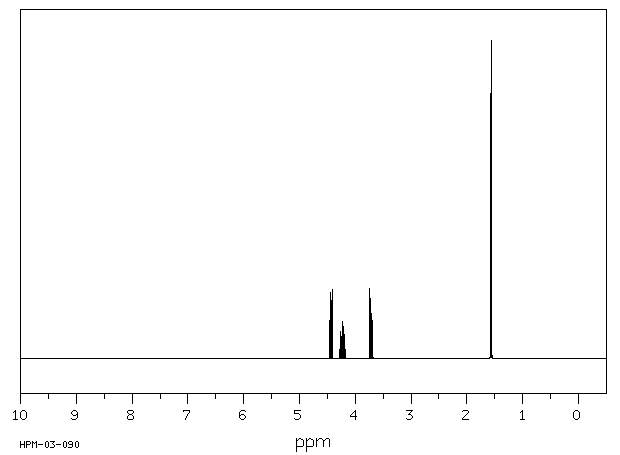
氢谱1HNMR
-
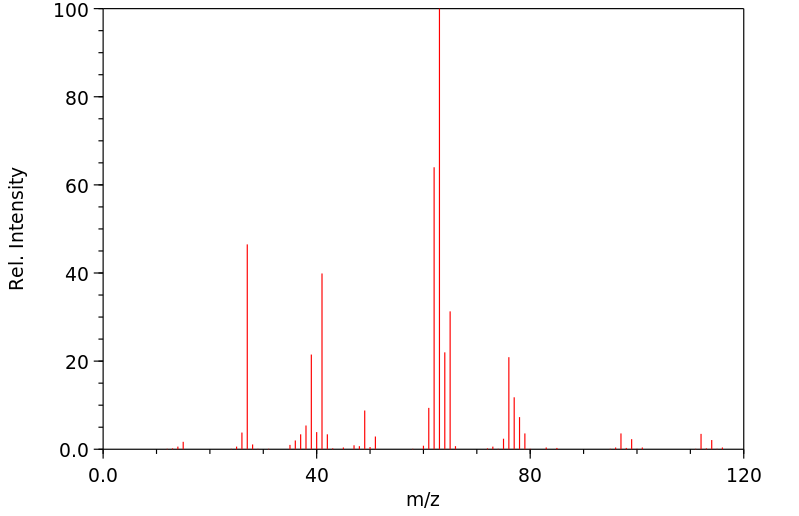
质谱MS
-
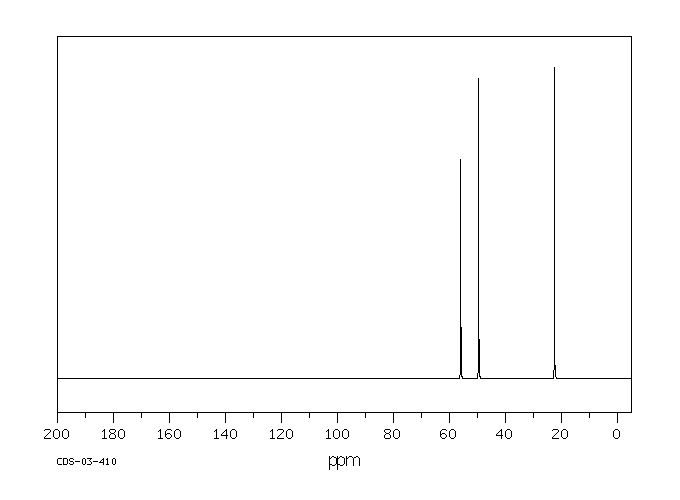
碳谱13CNMR
-
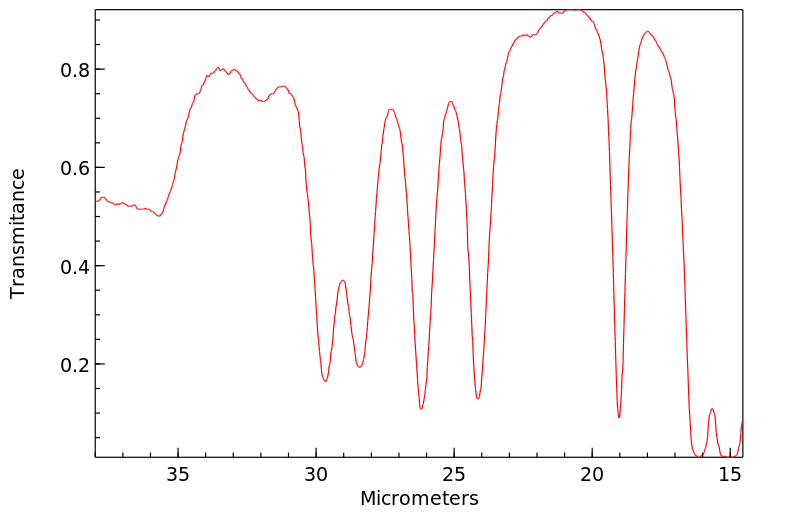
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息