四氢呋喃 | 109-99-9
中文名称
四氢呋喃
中文别名
氧化四亚甲基;1,4-环氧丁烷;无水四氢呋喃;四氢化氧杂茂;氧戊环;氧杂环戊烷
英文名称
tetrahydrofuran
英文别名
Tetrahydrofurane;THF;oxolane
CAS
109-99-9
化学式
C4H8O
mdl
——
分子量
72.1069
InChiKey
WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-108°C
-
沸点:66 °C
-
密度:0.887 g/mL at 20 °C
-
蒸气密度:2.5 (vs air)
-
闪点:>230 °F
-
溶解度:可溶于水
-
最大波长(λmax):λ: 245 nm Amax: ≤0.26λ: 275 nm Amax: ≤0.046λ: 315 μm Amax: ≤0.0044
-
介电常数:11.6(-70℃)
-
暴露限值:TLV-TWA 200 ppm (590 mg/m3) (ACGIH, MSHA, and OSHA); STEL 250 ppm (ACGIH); IDLH 20,000 ppm (NIOSH).
-
LogP:0.45 at 25℃
-
物理描述:Tetrahydrofuran appears as a clear colorless liquid with an ethereal odor. Less dense than water. Flash point 6°F. Vapors are heavier than air.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless, mobile liquid
-
气味:Ether-like odor
-
味道:PUNGENT TASTE
-
蒸汽密度:2.5 (NTP, 1992) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:Vapor pressure = 0.06 atm at 0 °C, 0.11 atm at 10 °C, 0.173 atm at 20 °C, 0.26 atm at 30 °C
-
亨利常数:Henry's Law constant = 7.05X10-5 atm-cu m/mole at 25 °C
-
大气OH速率常数:1.61e-11 cm3/molecule*sec
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
无色透明液体,带有类似醚的气味。能与水混溶,并且与水形成的共沸混合物能够溶解醋酸纤维素和咖啡因等生物碱,其溶解性能优于单独使用四氢呋喃的效果。一般的有机溶剂如乙醇、乙醚、脂肪烃、芳香烃及氯化烃等在四氢呋喃中都能很好地溶解。该物质在空气中容易与氧化合生成爆炸性的过氧化物,在常温下易着火,对金属无腐蚀性,但可侵蚀许多塑料和橡胶。由于沸点和闪点较低,贮存时需注意空气中的氧能与其作用生成有爆炸性的过氧化物。在光照或无水条件下,过氧化物更易于形成。因此,通常会加入0.05%~1%的对苯二酚、间苯二酚、对甲苯酚或亚铁盐等还原性物质作为抗氧化剂,以抑制过氧化物的生成。操作人员应穿戴防护用具。
-
化学性质:该物质在空气中由于自氧化作用会产生爆炸性的过氧化物。使用硝酸进行氧化时会生成丁二酸,在氧化铝催化下于300~400℃与氨反应可得到吡咯烷,而于400℃与硫化氢反应则能产生四氢噻吩。在氯化锌存在的情况下,受酸或酰氯的作用容易开环生成1,4-丁二醇和1,4-二卤化物;在光的影响下常温下会进行氯化生成2,3-二氯四氢呋喃,其第二位的氯原子非常活泼,可以被烷氧基、乙酸基或Grignard试剂中的烷基直接取代。使用酸式磷酸盐为催化剂时,在270℃可使四氢呋喃脱水生成丁二烯;在加热条件下与氯化氢气体反应会重排成4-氯丁醇,而三氯化铝存在下则能定量生成丁醇。
-
稳定性:稳定
-
禁配物:酸类、碱、强氧化剂和氧
-
避免接触的条件:光照和空气
-
聚合危害:聚合
-
-
自燃温度:321 °C (610 °F)
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke & irritating fumes.
-
粘度:0.53 cP at 20 °C
-
腐蚀性:Tetrahydrofuran will attack some forms of plastics, rubber, and coatings.
-
燃烧热:-14,990 BTU/lb = -8330 cal/g = -348.8X10+5 J/kg
-
汽化热:180 BTU/lb= 98.1 cal/g= 4.1X10+5 J/kg
-
表面张力:26.4 dynes/cm at 25 °C
-
电离电位:9.45 eV
-
聚合:Hazardous polymerization may occur.
-
气味阈值:Odor Threshold Low: 0.09 [mmHg]; Odor Threshold High: 61.0 [mmHg]; Detection odor threshold from AIHA (mean = 31 ppm)
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.4050 at 20 °C/D
-
解离常数:pKa = -2.08
-
相对蒸发率:8 (Butyl acetate = 1)
-
保留指数:617 ;630 ;626 ;609 ;610 ;620 ;622 ;626 ;629 ;619 ;636 ;612.5 ;620 ;613.7 ;614.3 ;615 ;615 ;638 ;608 ;612 ;627 ;615 ;638 ;618
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.5
-
重原子数:5
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:9.2
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
代谢
体外研究...表明THF首先被微粒体酶羟基化,然后在细胞质的存在下进一步裂解为直链脂肪酸。
In vitro studies ... indicated that THF was first hydroxylated by the microsomal enzymes and further cleaved to the straight chain fatty acid in the presence of cytosol.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
人类毒性:关于四氢呋喃(THF)对人类毒性的数据相当有限。人类可能的口服致死剂量为50-500毫克/千克。在测试THF的药理特性以及技术人员进行动物实验时,报告了严重的枕部头痛。预期在暴露于2.5%浓度的THF后会发生毒性(TCLo)。动物毒性:动物研究表明,THF仅通过急性暴露为“中等毒性”,口服途径报告的最低LD50为1900-2900毫克/千克。吸入的中位致死浓度随暴露时间的延长而变化,但在1小时或更短的暴露时间内,所有物种的浓度均大于20,000 ppm。动物研究的报告记录,皮肤和粘膜(包括眼睛、鼻子和上呼吸道)的刺激是低浓度暴露(约100-200 ppm)的主要效应。高急性剂量(约25,000 ppm)产生麻醉,诱导和恢复期延迟,伴有血压下降和强烈的呼吸刺激。麻醉与死亡之间的安全余地很小。记录的其他影响是长期暴露于THF水平(>1000 ppm)后对肝脏、肾脏和肺的损害。毒性的表现随暴露途径的不同而有所变化,吸入THF观察到上呼吸道的刺激,口服摄入后出现胃肠道的炎症。关于致癌性的唯一报告是对小鼠皮肤肿瘤的测试,其中每周两次将THF应用于皮肤,进行25次暴露,观察期为17.5个月。未观察到致癌效应。使用 Ames 测试测试 THF 的致突变性时为阴性;然而,它似乎增强了某些色氨酸-吡咯物质的致突变性。没有提供关于代谢、吸收和分布的信息。关于排泄的唯一报告是在母乳中发现了THF。
HUMAN TOXICITY: Data pertaining to the toxicity of tetrahydrofuran (THF) in humans is quite limited. The probable oral lethal dose in humans is 50-500 mg/kg. Severe occipital headaches were reported in the testing for pharmacological properties of THF & among technicians performing animal experiments. Toxicity (TCLo) is expected following exposure to a 2.5% concn of THF. ANIMAL TOXICITY: Animal studies indicate that THF is only "MODERATELY TOXIC" from acute exposure with the lowest reported LD50's of 1900-2900 mg/kg by oral route. Median lethal concns by inhalation varied with the duration of exposure but were >20,000 ppm with all species for exposures of 1 hr or less. Reports of animal studies document irritation of the skin & mucous membranes, including the eyes, nose, & upper respiratory tract, as the predominant effect from lower exposures (about 100-200 ppm). High acute doses (about 25,000 ppm) produced anesthesia with delayed induction & recovery periods, accompanied by a fall in blood pressure & strong respiratory stimulation. The margin of safety between anesthesia & death is small. Other effects recorded are those of damage to liver, kidneys, & lung after prolonged exposures to levels of THF >1000 ppm. Toxic manifestations varied somewhat with the route of exposure with irritation of upper respiratory tract observed with inhaled THF & inflammation of the GI tract following oral ingestion. The only report on carcinogenicity is that of a test for skin tumors in which THF was applied to the skin of mice twice/wk for 25 exposures with an observation period of 17.5 months. No carcinogenic effect was observed. THF was negative when tested for mutagenicity using the Ames test; however, it would appear to enhance the mutagenicity of certain tryptophan-pyrolysate substances. No information is presented on metabolism, absorption, & distribution. The only report on excretion is the finding of THF in mother's milk.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
A3; 已确认的动物致癌物,对人类的相关性未知。
A3; Confirmed animal carcinogen with unknown relevance to humans.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
国际癌症研究机构致癌物:四氢呋喃
IARC Carcinogenic Agent:Tetrahydrofuran
来源:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
毒理性
国际癌症研究机构(IARC)致癌物分类:2B组:可能对人类致癌
IARC Carcinogenic Classes:Group 2B: Possibly carcinogenic to humans
来源:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
毒理性
国际癌症研究机构专著:第119卷:(2019年)一些在啮齿动物中引起尿路肿瘤的化学物质
IARC Monographs:Volume 119: (2019) Some Chemicals That Cause Tumours of the Urinary Tract in Rodents
来源:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
吸收、分配和排泄
在大鼠的三个不同吸入实验中测定了各种器官中的四氢呋喃(THF)水平以及排泄率:1)30分钟暴露于45毫克/升(15,000 ppm);2)每天30分钟,连续7天暴露于45毫克/升(15,000 ppm);3)每天1小时,每周5天,连续12周暴露于9毫克/升(3000 ppm)。结果:1)暴露结束后立即观察到以下THF浓度顺序:血液>大脑>肾脏>心脏>肝脏>脾脏>肺。肺中的浓度最低:200毫克/千克,其他器官:480-600毫克/千克(呼出空气中的最大排泄)。1小时后,70-80%已被排出器官;其余部分在12-13小时内缓慢消失。2)在最后一次暴露后直接,最低值是130-300微克/千克,与单次暴露相同。初始阶段的排泄在1或3小时后THF浓度较高时较弱。6小时后,排泄率与单次暴露研究相似。3)在最后一次暴露后直接,THF浓度最高的是胸腺(160微克/千克)和脾脏(110微克/千克),其他器官为60-100微克/千克。胸腺在6小时后也具有器官中最高的浓度;肺和其他器官的浓度相似(表明呼出排泄减少);THF的完全排泄在大约12小时内,与1)和2)相同。结论:组织水平取决于呼出空气中的THF浓度。最大的排泄发生在呼出空气中。/从德语翻译/
THF levels in various organs as well as excretion rates were determined in three different inhalation experiments in rats: 1) 30 min exposure to 45 mg/L (15,000 ppm); 2) 30 min/day, 7 day exposure to 45 mg/L (15,000 ppm); 3) 1 hr/day, 5 days/week, 12 weeks exposure to 9 mg/L (3000 ppm). Results: 1) Immediately after the completion of the exposure the following order of THF concentrations were seen: blood > brain > kidneys > heart > liver > spleen > lung. The lowest concentration was in the lung: 200 mg/kg, in the other organs: 480-600 mg/kg (maximum excretion in exhaled air). After 1 hr 70-80% had been excreted from the organs; the remainder slowly disappeared over 12-13 hr. 2) Directly after the final exposure, the lowest value was 130-300 ug/kg as in the single exposure. Excretion in the initial phase was weaker with higher THF concentrations after 1 or 3 hr. After 6 hr the excretion rate was similar to the single exposure study. 3) Directly after the last exposure the highest THF concentration was in the thymus (160 ug/kg) and spleen (110 ug/kg), 60-100 ug/kg in the other organs. The thymus also had the highest concentration of the organs after 6 hr; the concentrations in the lungs and other organs were similar (an indication of reduced exhaled excretion); complete excretion of THF was in about 12 hr as in 1) and 2). Conclusion: tissue levels are dependent on THF-concentrations in exhaled air. Greatest excretion occurs in exhaled air. /Translated from German/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
将300 mg/kg四氢呋喃(THF)作为10%的水溶液单次口服给予大鼠(未给出品系和性别)。在给药后10-300分钟处死动物,并测定肝脏、肾脏、大脑、脾脏、肌肉、脂肪组织和血液中的THF浓度(凝胶柱,质谱)。血液中THF的最高值在给药后1小时(约为200 mg/kg)。血液中的生物半衰期为5小时。脂肪组织和肾脏中的THF浓度比血液中高1.3-1.4倍;肝脏、大脑、脾脏和肌肉中的水平与血液相似。在两只兔子口服700 mg/kg后,也发现了相似的浓度水平(半衰期为4-6小时;THF(脂肪组织)/THF(血液)比例为1.4,其余器官的比例为0.5-0.9)。在第二项大鼠实验中,再次使用了300 mg/kg的剂量。测量了血液中的THF浓度24小时。它在给药后1.5-2小时迅速上升到最大值150 mg/kg;此后,它逐渐下降,在24小时内降至零。血液中的生物半衰期:7.5小时。/从德语翻译/
A single oral application of 300 mg/kg THF as a 10% aqueous solution was given to rats (strain and sex not given). The animals were killed 10-300 min following application and the THF concentration in liver, kidneys, brain, spleen, muscle, adipose tissue, and blood determined (gel column, mass spectroscopy). The highest THF value in the blood was at 1 hr post-application (about 200 mg/kg). The biological half-life in blood was 5 hr. THF concentrations in adipose tissue and kidneys were 1.3-1.4 times higher than in blood; levels in liver, brain, spleen, and muscle were similar to blood. Comparable levels were found in two rabbits after oral application of 700 mg/kg (half-life 4-6 hr; THF(adipose tissue)/THF(blood) ratio 1.4, ratio for remaining organs 0.5-0.9). In a second experiment with rats, 300 mg/kg doses were again used. THF concentration in blood was measured over 24 hr. It climbed rapidly to a maximum of 150 mg/kg 1.5-2 hr post-application; thereafter it declined gradually to null over 24 hr. Biological half-life in blood: 7.5 hr. /Translated from German/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
四氢呋喃在12份收集于新泽西、宾夕法尼亚和路易斯安那4个城市的母乳样本中的1份中被报告有排出。
Excretion of tetrahydrofuran in mother's milk reported in 1 of 12 samples collected in 4 urban areas in New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Louisiana.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
接触四氢呋喃蒸汽的成年雄性大鼠,剂量为8.2微摩尔/升(200 ppm)、41微摩尔/升(1,000 ppm)或82微摩尔/升(2,000 ppm),每周5天,每天6小时,持续2至18周,显示出剂量依赖性的大脑和肾周脂肪溶剂负荷,两者之间线性相关。接触两周后,四氢呋喃的体内负荷似乎有所减少。这可能是由于氧化代谢增加,因为在第二周及以后,检测到肝脏和肾脏中7-乙氧基香豆素-O-脱乙基酶活性增强。最高剂量的接触还导致肝脏中醇脱氢酶和甲醛脱氢酶活性受到抑制。在小脑中没有检测到生化效应,而臀部肌肉标本显示出与剂量相关的琥珀酸脱氢酶活性增加。这表明对能量代谢有影响。肌肉乙酰胆碱酯酶活性也增加,表明可能对神经肌肉接头有影响。
Adult male rats exposed to tetrahydrofuran vapor at 8.2 (200 ppm), 41 (1,000 ppm) or 82 mumol/l (2,000 ppm) for 2 to 18 weeks, five days a week, 6 hrs daily, showed dose-dependent brain and perirenal fat solvent burden linearly correlated to each other. After two weeks of exposure, the body burden of tetrahydrofuran seems to decrease. This might have been caused by increased oxidative metabolism as enhanced 7-ethoxycoumarin-O-deethylase activity was detected in liver and kidneys in the second week and onwards. The exposure also caused inhibition of alcohol and formaldehyde dehydrogenase activities in liver at the highest dose. Biochemical effects in the cerebellum were not detected, while gluteal muscle specimens showed increased succinate dehydrogenase activity in a dose-related manner. This points to effects on the energy metabolism. Muscle acetylcholine esterase activity was also increased showing possible effects on the myoneural junctions.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:A
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 200 ppm (590 mg/m3), STEL: 250 ppm (735 mg/m3)
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:2,000 ppm [10% LEL]
-
安全说明:S16,S26,S29,S33,S36
-
危险品运输编号:UN 2924 3/PG 2
-
WGK Germany:1
-
海关编码:2932110000
-
危险类别:3
-
危险品标志:F
-
危险类别码:R19,R11,R36/37
-
RTECS号:MD0916000
-
包装等级:II
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS07,GHS08
-
危险性描述:H225,H302,H319,H335,H351
-
危险性防范说明:P210,P280,P301 + P312 + P330,P305 + P351 + P338,P370 + P378,P403 + P235
-
储存条件:储存注意事项: - 通常商品会添加稳定剂。 - 储存于阴凉、通风的库房,远离火种、热源。 - 库温不宜超过29℃。 - 包装要求密封,不可与空气接触。 - 应与氧化剂、酸类、碱类等分开存放,切忌混储。 - 采用防爆型照明和通风设施。 - 禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。 - 储区应备有泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。
制备方法与用途
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 4-甲氧基-1-丁醇 4-methoxybutanol 111-32-0 C5H12O2 104.149 四氢吡喃 Oxane 142-68-7 C5H10O 86.1338 1,4-二乙氧基丁烷 1,4-diethoxybutane 13344-00-8 C8H18O2 146.23 4-丁氧基丁醇 4-butoxy-1-butanol 4161-24-4 C8H18O2 146.23 正丁醇 butan-1-ol 71-36-3 C4H10O 74.1228 1,4-丁二醇 1,4-Butanediol 110-63-4 C4H10O2 90.1222 三甲氧基酯 trimethylene oxide 503-30-0 C3H6O 58.08 4-氯丁基甲基醚 4-(methoxy)-1-chlorobutane 17913-18-7 C5H11ClO 122.595 1-溴-4-甲氧基丁烷 4-Methoxy-1-bromobutane 4457-67-4 C5H11BrO 167.046 2-羟基四氢呋喃 2-hydroxytetrahydrofuran 5371-52-8 C4H8O2 88.1063 3-羟基四氢呋喃 3-Hydroxytetrahydrofuran 453-20-3 C4H8O2 88.1063 - 1
- 2
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 甲丁醚 Butyl methyl ether 628-28-4 C5H12O 88.1497 二丁醚 Butyl ether 142-96-1 C8H18O 130.23 四氢吡喃 Oxane 142-68-7 C5H10O 86.1338 1,4-二甲氧基丁烷 1,4-dimethoxybutane 13179-96-9 C6H14O2 118.176 4-乙氧基-1-丁醇 4-ethoxybutan-1-ol 111-73-9 C6H14O2 118.176 1,4-二乙氧基丁烷 1,4-diethoxybutane 13344-00-8 C8H18O2 146.23 4-丁氧基丁醇 4-butoxy-1-butanol 4161-24-4 C8H18O2 146.23 1,2-环氧丁烷 ethyloxirane 106-88-7 C4H8O 72.1069 正丁醇 butan-1-ol 71-36-3 C4H10O 74.1228 3-甲基四氢呋喃 3-methyltetrahydrofuran 13423-15-9 C5H10O 86.1338 3-甲氧基-1-丙醇 methoxypropanol 1589-49-7 C4H10O2 90.1222 1-丁氧基-4-甲氧基丁烷 1-Butoxy-4-methoxybutan 91391-43-4 C9H20O2 160.257 —— bis-(4-ethoxy-butyl)-ether 99106-87-3 C12H26O3 218.337 —— Bis-(4-methoxy-n-butyl)-ether 17913-19-8 C10H22O3 190.283 1,4-二丁氧基丁烷 1,4-dibutoxybutane 4161-40-4 C12H26O2 202.337 —— 1,6,11-Trioxacyclopentadecane 295-63-6 C12H24O3 216.321 甲基仲丁基醚 2-butyl methyl ether 6795-87-5 C5H12O 88.1497 2-甲基四氢呋喃 2-methyltetrahydrofuran 96-47-9 C5H10O 86.1338 1,4-丁二醇 1,4-Butanediol 110-63-4 C4H10O2 90.1222 三甲氧基酯 trimethylene oxide 503-30-0 C3H6O 58.08 异丁基甲基醚 isobutyl methyl ether 625-44-5 C5H12O 88.1497 4-氯丁基甲基醚 4-(methoxy)-1-chlorobutane 17913-18-7 C5H11ClO 122.595 2-羟基四氢呋喃 2-hydroxytetrahydrofuran 5371-52-8 C4H8O2 88.1063 - 1
- 2
- 3
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:[EN] METHOD FOR CATALYTIC OXYGENATION OF CYCLIC ETHERS WITH HOMO AND HETERO METALLIC MO/RU COMPLEXES AND MOLECULAR OXYGEN
[FR] PROCEDE D'OXYGENATION CATALYTIQUE D'ETHERS CYCLIQUES AVEC DES COMPLEXES HOMOMETALLIQUES ET HETEROMETALLIQUES MO/RU ET DE L'OXYGENE MOLECULAIRE摘要:已发明了一种用于环氧化环氧乙醚的工艺。该工艺的一般问题是使用昂贵且有毒的氧化剂、低TONs(周转数)、低选择性以及在高温下工作(能源成本)。通过采用适当的有机金属催化剂前体来解决这些问题。使用lnd(CO)3Mo-Ru(CO)2Cp、Cp(CO)3Mo-Ru(CO)2Cp和Cp(CO)2Ru-Ru(CO)2Cp或其他钌化合物,四氢呋喃(THF)的空气氧化反应在室温下进行,且选择性地产生Ϝ-丁酸内酯。使用催化剂可通过便宜的空气氧替代化学计量的有毒共氧化剂,在室温下工作,具有高选择性、高TONs,并且总体上制定了适用于环氧乙醚的绿色化学配方:公式(I)。该发明的工艺通过在催化过程中使用便宜的空气氧和具有无限催化剂寿命的纯水作为副产品,满足了绿色化学的需求。从相应的乙醚中可获得功能化内酯。公开号:WO2004033391A1 -
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:通过 InBr3/TMDS 环化二羧酸合成 3-取代四氢呋喃和 4-取代四氢吡喃衍生物摘要:据报道,使用 InBr3/TMDS 系统对二酸化合物进行有效还原,然后环化。该系统允许形成在 3 位或 4 位取代的五元和六元环醚。DOI:10.1002/ejoc.201200727
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:Oxidative decyanation of secondary nitriles to ketones摘要:DOI:10.1021/jo00170a043
文献信息
-
Facile Approach for C(sp3)–H Bond Thioetherification of Isochroman作者:Chun Cai、Jie Feng、Guoping Lu、Meifang LvDOI:10.1055/s-0034-1380125日期:——An unprecedented C–S formation protocol via the direct oxidative C(sp 3 )–H bond thioesterification of isochroman under metal-free conditions was developed. A series of isochroman derivatives could be afforded efficiently by the green, simple, and atom-economical method.
-
Synthetic Applications of Pd(II)-Catalyzed C−H Carboxylation and Mechanistic Insights: Expedient Routes to Anthranilic Acids, Oxazolinones, and Quinazolinones作者:Ramesh Giri、Jonathan K. Lam、Jin-Quan YuDOI:10.1021/ja9077705日期:2010.1.20carbon monoxide is discussed. Identification of two key intermediates, a mixed anhydride and benzoxazinone formed by reductive elimination from organometallic Ar(CO)Pd(II)-OTs species, provides mechanistic evidence for a dual-reaction pathway.
-
Substituted diether diols by ring-opening of carbocyclic and stannylene acetals作者:Rolando Martínez-Bernhardt、Peter P. Castro、Gayane Godjoian、Carlos G. GutiérrezDOI:10.1016/s0040-4020(98)00563-8日期:1998.7Reduction of malonaldehyde bis(ethylene and propylene acetals) with borane or monochloroborane produces diether diols 1 and 2 in high yield. Similar reduction of glyoxal bis(ethylene acetals) has only limited utility for the preparation of tetrasubstituted triethylene glycols 3. Organotin chemistry is complementary: stannylene acetals prepared from disubstituted vicinal diols can be alkylated with half
-
Solvent-Induced Structural Transformation and Luminescence Response in a Dumbbell-Shaped Crystalline Molecular Rotor作者:Le-Ping Miao、Qi Qi、Wen ZhangDOI:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c03504日期:2021.3.1Crystalline molecular rotors constitute a new class of stimuli-responsive molecular materials owing to inherent molecular dynamics. However, beyond the molecular level, the role of molecular packings on the bulk structures and related properties has yet to be fully understood. Herein, we report a crystalline molecular rotor showing solvent-induced structural transformation and luminescence response
-
Design, synthesis and evaluation of phthalide alkyl tertiary amine derivatives as promising acetylcholinesterase inhibitors with high potency and selectivity against Alzheimer's disease作者:Li Luo、Qing Song、Yan Li、Zhongcheng Cao、Xiaoming Qiang、Zhenghuai Tan、Yong DengDOI:10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115400日期:2020.4of phthalide alkyl tertiary amine derivatives were designed, synthesized and evaluated as potential multi-target agents against Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The results indicated that almost all the compounds displayed significant AChE inhibitory and selective activities. Besides, most of the derivatives exhibited increased self-induced Aβ1-42 aggregation inhibitory activity compared to the lead compound设计,合成和评估了一系列邻苯二甲酰基烷基叔胺衍生物,作为对抗阿尔茨海默氏病(AD)的潜在多靶标药物。结果表明,几乎所有化合物均显示出显着的AChE抑制和选择性活性。此外,大多数的衍生物显示出增加的自感甲β 1-42相比,铅化合物聚集抑制活性DL -NBP,有些化合物也发挥良好的抗氧化活性。具体而言,化合物I-8对AChE的抑制力最高(IC 50 = 2.66 nM),明显优于多奈哌齐(IC 50 = 26.4 nM)。此外,分子对接研究表明I-8可以与AChE的催化活性位点和外围阴离子位点结合。此外,化合物I-8在体外显示出优异的BBB渗透性。重要的是,逐步降低的被动回避测试表明,I-8可显着逆转东amine碱诱导的小鼠记忆缺陷。总的来说,这些结果表明I-8可能是用于进一步抗AD药物开发的有效且选择性的AChE抑制剂。
表征谱图
-
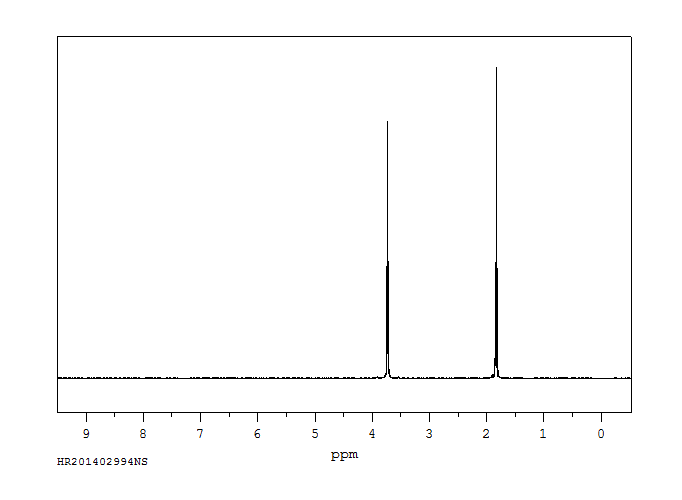
氢谱1HNMR
-
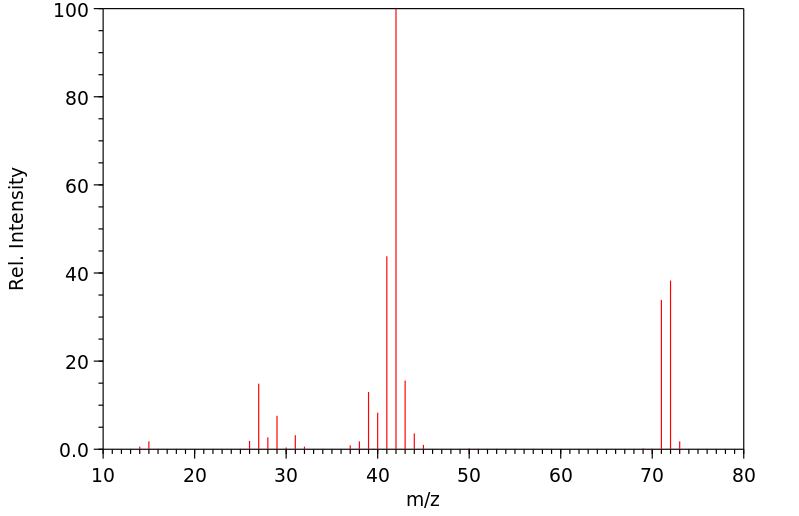
质谱MS
-
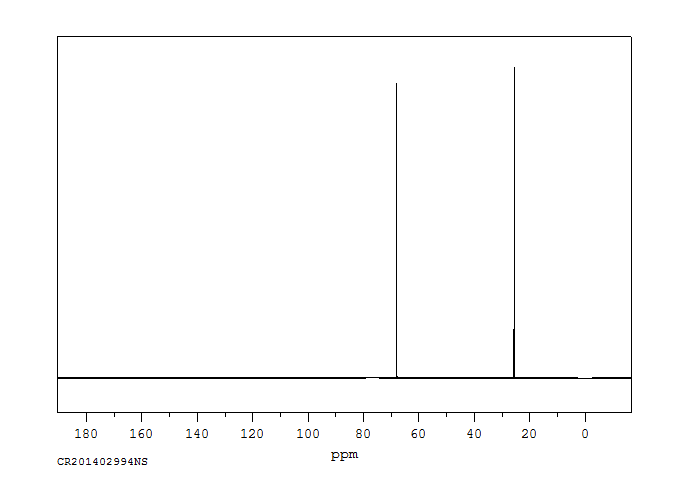
碳谱13CNMR
-
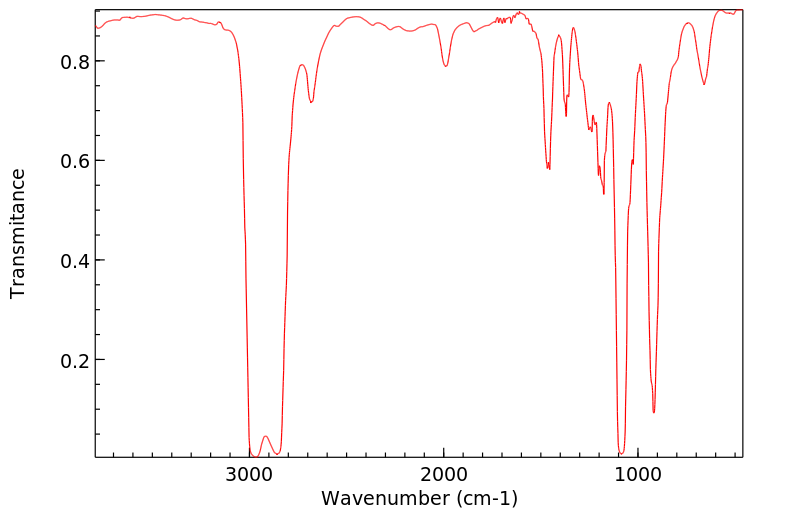
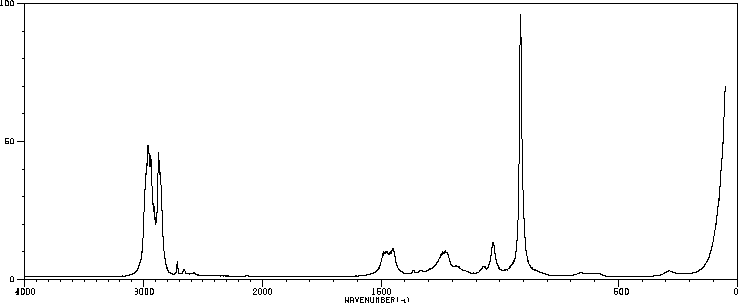
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
顺式-环氧丙烷-3,4-二胺二盐酸盐
顺式-2-(碘甲基)-3-羟基四氢呋喃
顺式-2-(碘甲基)-3-羟基四氢呋喃
青榄呋喃
茶香螺烷
苯胺,4-(2-哌嗪基)-
碳氯灵
硼烷四氢呋喃络合物
硫丹乙酯
甲基甲丙烯酰酸酯-叔丁基甲丙烯酰酸酯-月桂基甲丙烯酰酸酯共聚物
甲基丙烯酸四氢糠基酯
甲基[(噁戊环-2-基)甲基]胺盐酸
甲基2,5-脱水-3-脱氧戊酮酸酯
甲基(四氢呋喃-2-基甲基)砜
牛蝇畏
溴化锰(II)双(四氢呋喃)
溴化亚铁(II),双(四氢呋喃)
氧化芳樟醇
氘代四氢呋喃
异硫氰酸氢糠酯
异丙基-(四氢-呋喃-2-甲基)-胺
失水山梨醇
四氯双(四氢呋喃)合铌(IV)
四氢糠醇乙酸酯
四氢糠醇丙酸酯
四氢糠醇
四氢糠基硫醇
四氢呋喃氯化钛
四氢呋喃-D4
四氢呋喃-3-甲醛
四氢呋喃-2-甲醛
四氢呋喃-2-甲酰肼盐酸盐
四氢呋喃-2-乙酸
四氢呋喃
四氢-alpha-戊基-2-呋喃乙醇乙酸酯
四氢-alpha-[2-(四氢呋喃-2-基)乙基]-2-呋喃-1-丙醇
四氢-alpha,alpha,5-三甲基-5-乙烯基糠基乙酸酯
四氢-alpha,alpha,5-三甲基-5-(4-甲基-3-环己烯-1-基)呋喃-2-甲醇
四氢-N-[(四氢-2-呋喃基)甲基]-2-呋喃甲胺
四氢-N,2-二甲基-2-糠基胺
四氢-Alpha-戊基-2-呋喃甲醇乙酸酯
四氢-5-羟基呋喃-2-甲醇
四氢-5-甲基呋喃-2-甲醇
四氢-2-辛基呋喃
四氢-2-甲基-2-呋喃醇
四氢-2-呋喃基甲基3-氯丙酸酯
四氢-2-呋喃基氯乙酸甲酯
四氢-2-呋喃丙醇
四氢-2-呋喃-1-丙醇丙酸酯
呋喃,2-(二氯甲基)四氢-