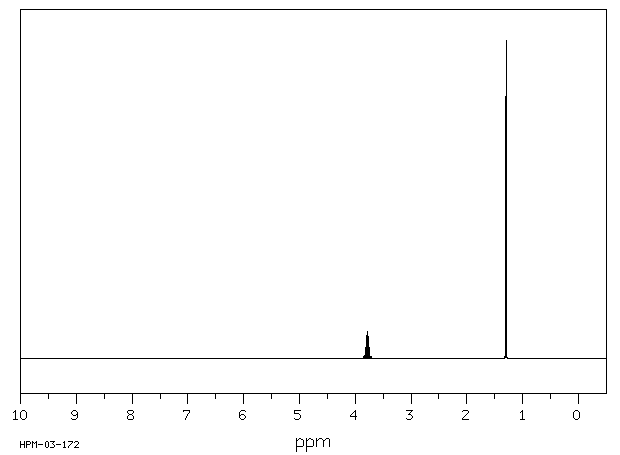
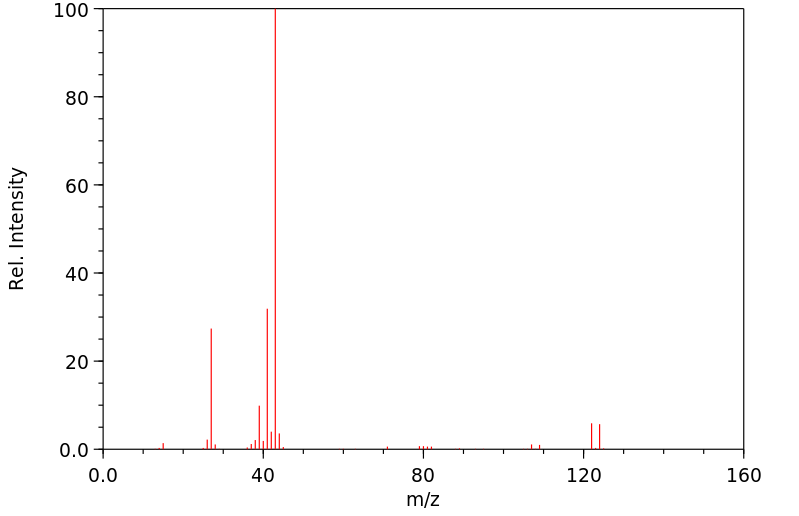
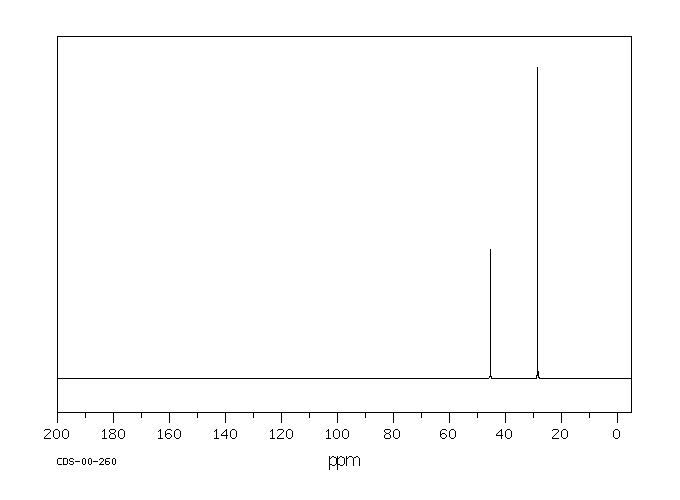
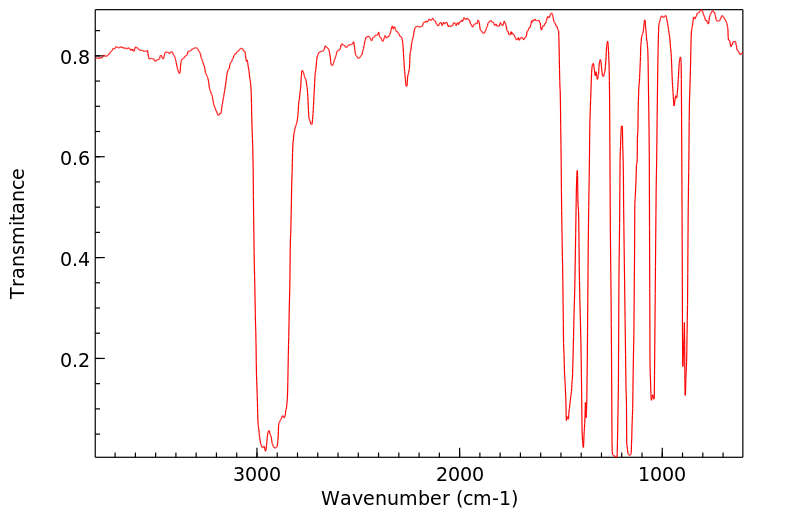
毒理性
有机溴化物化合物,尤其是烷基溴化物,是强烈的烷基化剂。因此,它们可以随机地修改蛋白质和脂质的表面,导致酶、转运蛋白或膜功能的破坏。最可能的蛋白质靶标之一是TRPA1离子通道,它在眼睛、鼻子、嘴巴和肺部的感官神经(三叉神经)中表达。烷基溴化物对DNA的烷基化也可能导致突变。2-溴丙烷通过产生ROS(活性氧种)触发线粒体依赖的凋亡途径。2-溴丙烷还被证明可以诱导DNA损伤,损害功能性抗氧化细胞防御,并在培养的莱迪希细胞中增强脂质过氧化。
Organobromide compounds, especially alkylbromides are strong alkylating agents. Consequently they can randomly modify the surfaces of proteins and lipids, leading to the disruption of enzyme, transporter or membrane functions. One of the most probable protein targets is the TRPA1 ion channel that is expressed in sensory nerves (trigeminal nerve) of the eyes, nose, mouth and lungs. Alkylation of DNA by alkylbromides may also lead to mutations. 2-bromopropane triggers the mitochondrion-dependent apoptotic pathway via ROS (reactive oxygen species) generation. 2-bromopropane has also been shown to induce DNA damage, impair functional antioxidant cellular defenses, and enhance the lipid peroxidation in cultured Leydig cells.
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)